The term "fiduciary" comes from the Latin word fiducia which means trust, faith or confidence. A person who owes a fiduciary duty has legal obligations to act in the best interests of another party or to manage another party's property as though it is their own. Trustees are individuals who hold, manage, and distribute money for someone else with the intent of using it for future purposes under the direction of the owner of the trust. Trustees have many duties that must be followed in order to maintain integrity within the investment community and protect all parties involved including beneficiaries, donors/grantors, investors, and creditors. A trustee holds legal title to assets on behalf of a beneficiary (beneficiary law). The trustee manages assets for the beneficiary and owes the beneficiary a fiduciary duty. The trustee must exercise care, diligence, skill, prudence, and caution when making decisions about the management of the trust assets. Fiduciary duties are not to be taken lightly because they provide a framework that helps trustees make sound investment decisions while being held accountable to those who entrusted them with their money. Have a financial question? Click here. Trustees are considered legal representatives of the beneficiary and are considered "agents" under law. Trustee duties are similar to those placed upon directors or managers of corporations where they are expected to act in the best interest of their clients. This framework for decision-making helps protect all parties involved while allowing for transparency and accountability at all times. Trustees are to have fiduciary duty for the following reasons: There are four general elements that fiduciaries must adhere to when performing their duties: This is the duty to use reasonable care, skill, and caution when making decisions about the management of trust assets. The trustee must act in good faith and with due diligence when making investment decisions on behalf of the beneficiary. This is the duty to act solely in the interest of the beneficiary. The trustee should not use their position to give them an unfair advantage over others (self-dealing). This is the duty to make decisions that are based on existing laws and regulations. Thus, the trustee should not engage in illegal activities when handling trust assets. This is the duty to act in good faith towards all parties involved including all investors, creditors, beneficiaries, donors/grantors, and other interested parties. The following are the fiduciary duties of trustees: The trustee must adhere to the terms of the trust. This means they must act in accordance with what was asked of them by the donor/grantor when establishing the trust. The terms of the trust refer to the guidelines that were set up by the donor/grantor. For example, if it is said in the trust to hold all assets for future generations or to pay out income every month, then the trustee must abide by this without engaging in illegal activities. The trustee is responsible for protecting the assets of the beneficiary. They must act prudently and manage these assets with care and caution when making investment decisions. The trustee cannot allow their own interests to interfere with the management of the assets (self-dealing). As fiduciary, trustees have ongoing duties that they must follow such as: maintaining accurate records; providing reports on an annual basis; filing taxes where necessary; complying with all state and federal laws; and, informing the donor/grantor or other interested parties of any material changes. The trustee must provide full disclosure to all interested parties about how assets are handled and maintained. The trustee must also carefully manage the trust's property while it is held in their care. The trustee has a duty to maintain accurate records of all transactions made on behalf of beneficiaries (entity accounting). They must ensure that they follow any statutes, rules, or provisions set forth by law that apply to record-keeping within trusts. The trustee must act diligently when making decisions about the trust. This means they should take all factors into consideration and make informed decisions that will be in the best interest of the beneficiary. In order to carry out their fiduciary duties, trustees are often responsible for investing trust assets. They must adhere to the standard of care when making these investments and ensure that any transactions made are in the best interest of the beneficiary. When trustees are appointed, they must act in the best interest of the beneficiary at all times. Fiduciary duties provide a framework for trustees to make sound investment decisions without having their own interests interfere. This helps protect all parties involved and builds trust within the investment community. Additionally, trustees must maintain accurate records of all transactions and communications made on behalf of the beneficiary. This allows for transparency and accountability while also ensuring that the trustee is in compliance with any applicable laws.Why Are Trustees Required to Have a Fiduciary Duty?
Elements of Fiduciary Duties
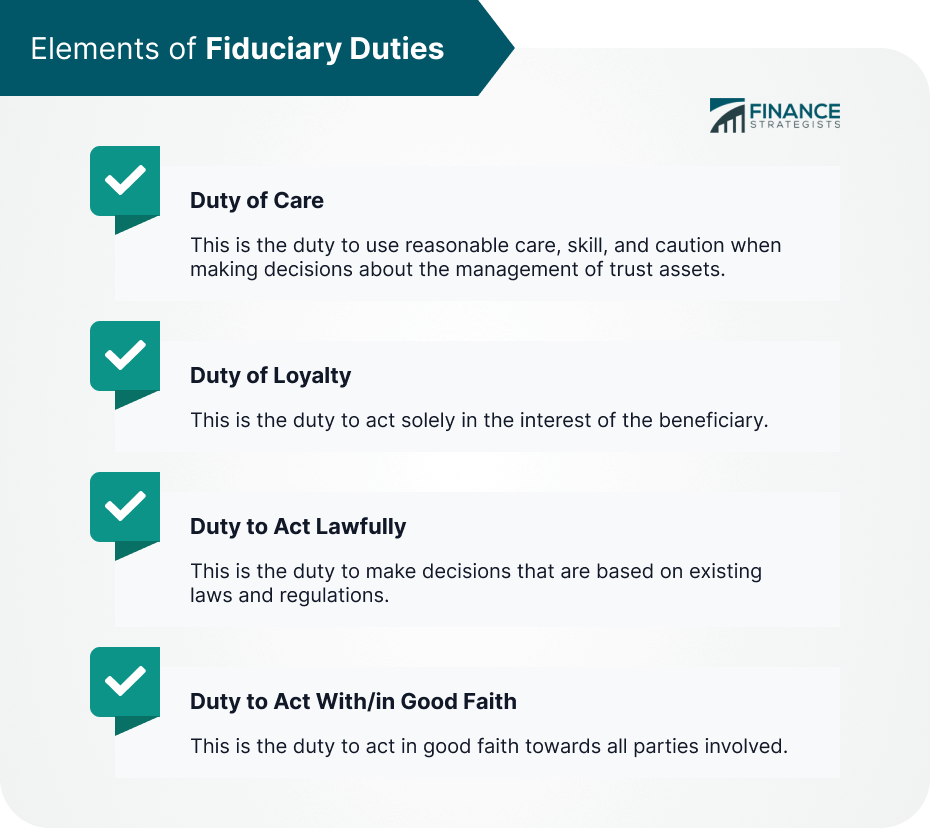
Duty of Care
Duty of Loyalty
Duty to Act Lawfully
Duty to Act With/in Good Faith
Fiduciary Duties of a Trustee
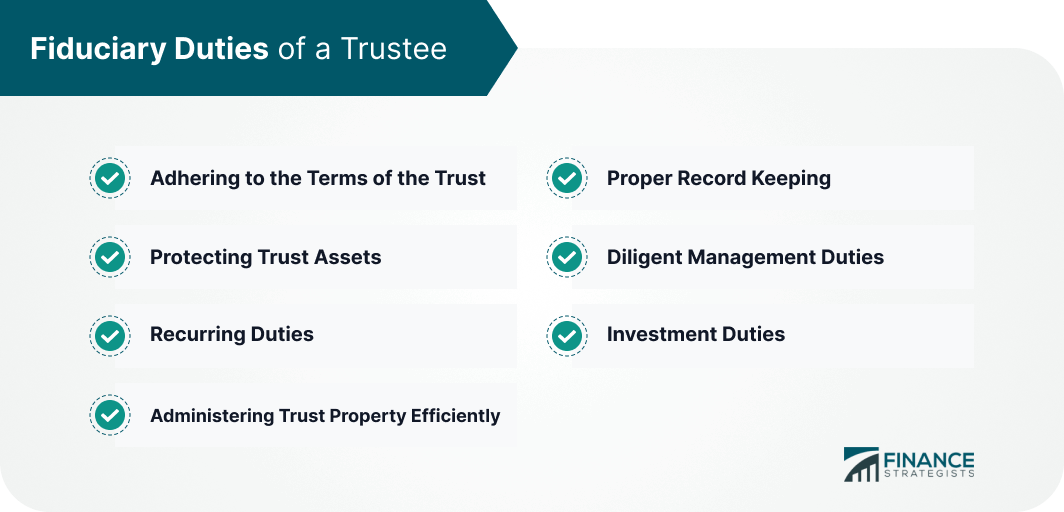
Adhering to the Terms of the Trust
Protecting Trust Assets
Recurring Duties
Administering Trust Property Efficiently
Proper Record Keeping
Diligent Management Duties
Investment Duties
The Bottom Line
Fiduciary Duties FAQs
Fiduciary duties refer to the responsibilities of those who have been entrusted with a fiduciary role. This could include trustees, directors or any other person acting in a position of trust on behalf of another party. Fiduciary duties require that these people act with the utmost care, loyalty and good faith in all matters relating to the trust.
Fiduciary duties impose a range of responsibilities on trustees and directors who have been entrusted with a fiduciary role. These obligations generally include being honest and fair in their dealings with others, avoiding conflicts of interest, acting in the best interests of the trust or company and exercising a duty of care in all matters relating to the trust. Fiduciary duties also include protecting the assets of a trust or company from potential harm or loss.
Fiduciary duties are enforced through civil and criminal sanctions, which can include fines or jail time. Fiduciaries are also liable for any harm that they cause to the trust, company or other parties due to their failure to fulfill their fiduciary obligations. Fiduciaries must always exercise reasonable care in all matters related to the trust and take steps to ensure that they are meeting their obligations.
Fiduciary duties may be enforced by courts through civil or criminal proceedings, depending on the nature and severity of the breach. Fiduciaries who breach their fiduciary obligations may be held liable for any harm caused to the trust, company or other parties as a result of their negligence or misconduct. Fiduciaries may also be fined or required to pay damages.
Fiduciary duties continue to apply during insolvency proceedings and Fiduciaries must still take steps to protect the interests of the trust, company or other parties. Fiduciaries should remain aware of their obligations and act with caution in all matters relating to the trust during insolvency proceedings.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















