Seed capital, also known as seed funding or seed money, is the initial funding that a startup or entrepreneur raises to develop an idea for a new business or product. Typically, it is used to cover the costs of creating a proposal and getting a business off the ground. Seed capital differs from other forms of funding, such as venture capital or angel investing, in that it is typically provided at an earlier stage of business development and involves smaller amounts of funding. Alphabet, Google's parent company, provided seed funding in 2016 to the Center for Resource Solutions to support their initiative to implement renewable energy certification programs in Asia. Google currently holds the title of the world's largest non-utility purchaser of renewable energy, and this partnership is part of their efforts to power their global data centers and, eventually, their entire operations with renewable energy sources. Seed capital is often used by company founders to finance critical early-stage activities such as hiring key team members, conducting market testing, and developing prototypes of future offerings. This funding round typically provides the company with a year or more to complete these essential tasks. The amount of seed capital raised can vary widely, from a few thousand dollars to several million. Tech startups in Silicon Valley typically begin with seed capital ranging from $1 to $4 million, with the number of investors ranging from one to a dozen or more. In exchange for the seed capital, founders may give up to 20% ownership of the company to the investors. For new businesses, running out of cash can be a significant issue. Therefore, founders typically aim to raise as much money as possible during the seed round. However, the risk of running short on funds must be balanced with the risk of losing control of the company by giving up too much equity in the startup phase. After the seed funding has been utilized or is about to be depleted, assuming the offering and business model are promising, founders often hold a second round of financing, commonly referred to as the Series A round. This round typically raises a larger amount of money, often from venture capitalists, in exchange for another share of ownership, often around 20%. The primary source of business startup capital often originates from personal savings of the founder or founders. Bank loans, the most common funding option, are usually unavailable to companies lacking a track record of consistent sales and profits. To cover startup costs, founders can leverage personal assets such as their homes, using second mortgages and home equity loans, but at the risk of losing these assets if the company does not succeed. Family and friends are other common sources of seed capital. However, seeking capital from personal connections can lead a founder to accept money from individuals who may not fully understand the risks involved in funding a startup. If the company fails, seed investors could lose their entire investment, which may strain relations with family and friends. On the other hand, angel investors are high-net-worth individuals who may be willing to fund startups if they have no personal connections. These investors are typically more sophisticated and risk-aware than family and friends but may also demand greater ownership and control in the new venture. Crowdfunding has emerged as another viable source of seed capital. Entrepreneurs can turn to crowdfund platforms like Kickstarter, Indiegogo, and GoFundMe to raise funds for their startups. It can be equity-based, where investors receive an ownership stake in the venture; debt-based, where investors earn their money back with interest; or reward-based, which provides investors with products or services from the company. Further, it offers a relatively higher level of transparency into investing than what is available from a mutual fund’s prospectus, making it a well-established and attractive mechanism for raising money. Entrepreneurs seeking seed capital should take several steps to increase their chances of securing funding. Having a strong business plan is essential in securing seed capital. Entrepreneurs should create a comprehensive plan that outlines their product or service offering, target market, and growth strategy. The business plan should also detail financial projections and clearly understand the company's competitive landscape. Entrepreneurs should conduct thorough market research to understand the competitive landscape and identify potential challenges and opportunities. This research should include gathering data on customer preferences and behavior, market size and growth potential, and industry trends. Entrepreneurs should be prepared to pitch their business idea to potential investors and communicate their value proposition effectively. This may involve creating a compelling presentation or video that highlights the unique aspects of the product or service offering and the potential market size. Entrepreneurs should also be prepared to answer questions about the business and demonstrate their passion and commitment to the venture. Entrepreneurs should network with potential investors to build relationships and gain insights into their investment criteria. Attending networking events and conferences can provide valuable opportunities to meet with investors and learn more about the startup funding process. Seed capital plays a critical role in the business lifecycle, providing entrepreneurs with the initial funding to turn their ideas into viable businesses. Typically, it funds product development, market research, and the recruitment of key personnel. As the business grows, additional funding may be required to support expansion and growth initiatives. Thus, seed capital can be used to fuel growth and innovation in a variety of ways. For example, it can be used to fund product development, launch marketing campaigns, and recruit key personnel. Seed capital can also be used to build infrastructure, such as IT systems or manufacturing facilities, to support growth and expansion. By acquiring complementary businesses or technologies, startups can expand their product offerings and customer base and accelerate their growth. As businesses seek to secure additional funding beyond the seed stage, they may face a number of challenges. They may need to demonstrate a track record of success and a clear path to profitability to attract venture capitalists and other institutional investors. It is important for businesses to strike a balance between funding growth initiatives and managing cash flow and to remain focused on their core mission and values as they navigate the challenges of the business lifecycle. While seed capital and venture capital may share some similarities, they are distinct forms of financing that serve different stages in a startup's life cycle. Seed capital is typically the initial funding raised to develop a business idea and take it to the point where it can be presented effectively to venture capital firms. This initial funding is generally much smaller than the amount provided by venture capitalists and is used to cover the costs of market testing, hiring key team members, and developing prototypes. Angel investors or crowdfunding platforms often provide it. Venture capital, on the other hand, is a larger investment made by venture capital firms to help startups scale their business. This type of financing typically covers product development, market research, and prototype production, among other things. Most startups at this stage have offices, staff, and consultants, even though they may not have a fully developed product. One of the primary differences between seed capital and venture capital is the stage of business development at which they are provided. Seed capital is provided in the early stages of a startup's development, while venture capital is generally provided to companies that have already launched their products or services and are looking to scale their business. Another key difference is the amount of funding provided. Seed capital is generally much smaller than venture capital, ranging from a few thousand dollars to several hundred thousand dollars. On the other hand, venture capital can range from several hundred thousand dollars to several million dollars. Despite these differences, seed capital and venture capital can be complementary forms of financing for startups. Seed capital can help entrepreneurs get their businesses off the ground. In contrast, venture capital can help them take their businesses to the next level by providing the resources necessary for growth and expansion. Seed capital is a critical source of initial funding for startups and entrepreneurs seeking to bring their ideas to life. It enables them to cover the costs of market testing, prototypes, and hiring key team members. Entrepreneurs seeking seed capital should take the time to develop a strong business plan, conduct thorough market research, craft an effective pitch, and network with potential investors. As businesses seek to scale and expand beyond the seed stage, they may require venture capital funding to support growth initiatives. Despite the differences between seed capital and venture capital, they can be complementary forms of financing for startups. As such, entrepreneurs should consider both options to secure funding for their businesses. A financial advisor can provide guidance and support throughout the funding process, helping you develop a comprehensive business plan, conduct market research, and connect with potential investors.What Is Seed Capital?
How Seed Capital Works
Sources of Seed Capital
How to Secure Seed Capital
Develop a Strong Business Plan
Conduct Thorough Market Research
Craft an Effective Pitch
Network with Potential Investors
Seed Capital and the Business Lifecycle
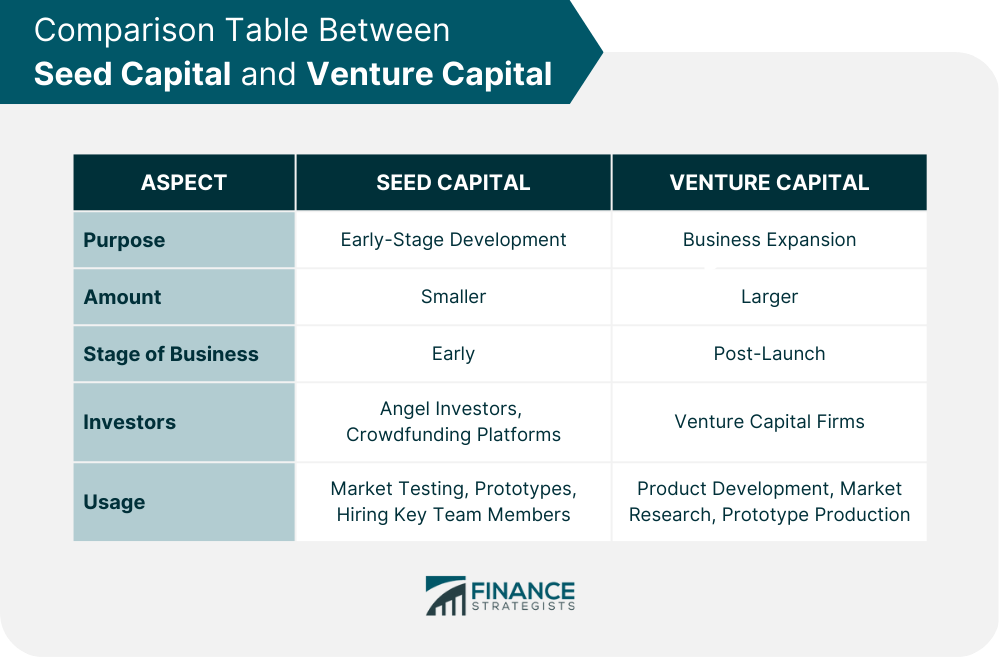
Seed Capital vs Venture Capital
Final Thoughts
Seed Capital FAQs
Seed capital is the initial funding that a startup or entrepreneur raises to develop an idea for a new business or product.
Seed capital can be provided by a variety of sources, including angel investors, venture capitalists, and crowdfunding platforms.
Seed capital investors evaluate potential investments based on a variety of factors, including the entrepreneur's background and experience, the strength of the business plan, and the potential market size for the product or service offering.
Entrepreneurs can secure seed capital by developing a strong business plan, conducting thorough market research, and effectively pitching their business idea to potential investors. It is also recommended to seek guidance from a financial advisor who specializes in seed capital investment.
Seed capital is typically provided at an earlier stage of business development and involves smaller amounts of funding than venture capital, which is typically provided to companies that have already launched their products or services and are looking to scale their business.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.















