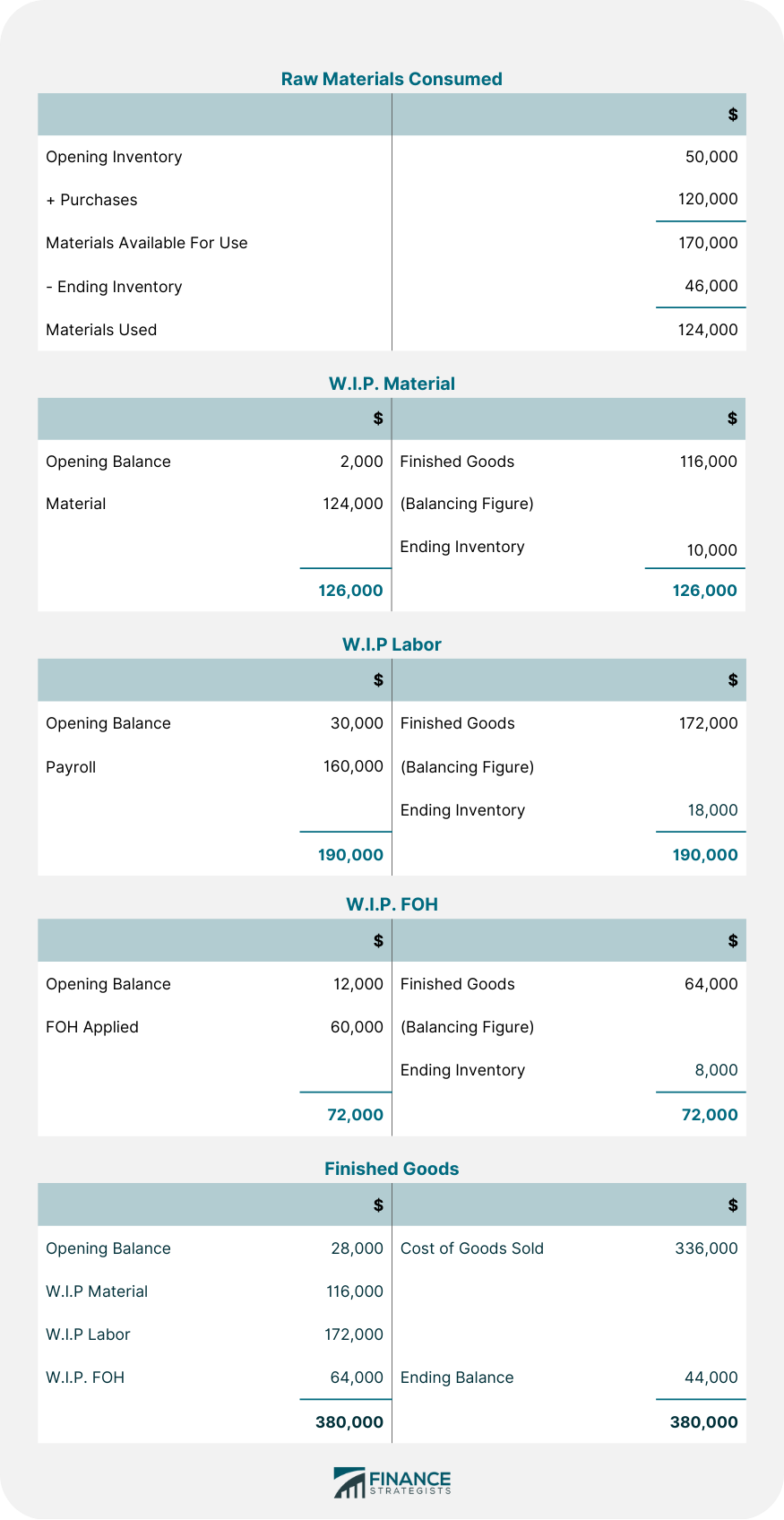
Excellent Ltd. had the following inventories on 1 April 2019:
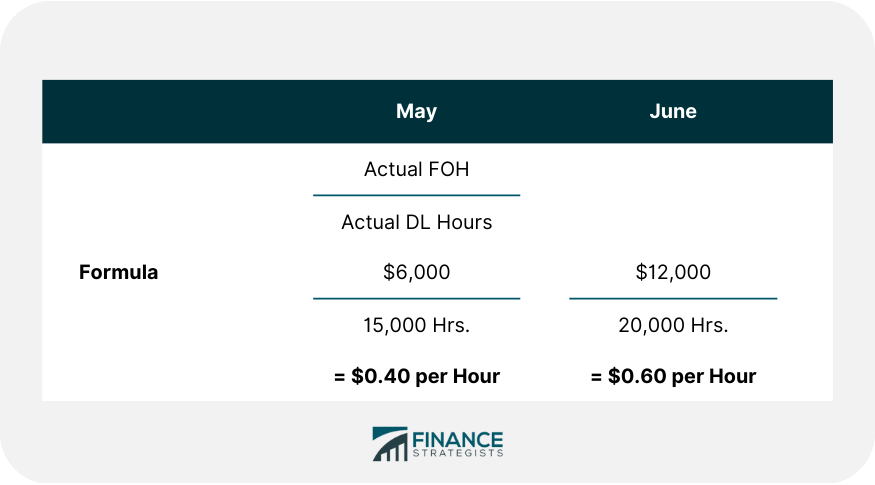
During the month, the cost of materials purchased was $120,000. Also, the direct labor cost was $160,000 and factory overhead applicable to production was $60,000. On 30 April, the inventories were as follows: The Moon Manufacturing Co. has a partial job order costing system instead of predetermining a factory overhead rate. The company computes a separate factory overhead rate at the end of each month. This rate is used to charge the factory overhead to the jobs worked on during the month. The number of direct labor hours used on the jobs is the basis of such allocation. The table below shows the actual factory overhead costs and the direct labor hours for May and June. Required: The company should use predetermined FOH rates for correct calculations and control. John Manufacturing Company has a job order costing system. It compiled the following data for 2019.Problem 1: Job Order Costing Cycle


Required: Prepare journal entries on April 30 to show the flow of cost through the proper summary accounts, and also give the subsidiary records.Solution

Calculations Explained
Problem 2: Charging Actual FOH to Jobs

During this two-month period, one customer sent in an identical order each month, calling for the production of 1,000 units. This required 400 direct labor hours at $1 per hour and materials amounting to $750.
Solution
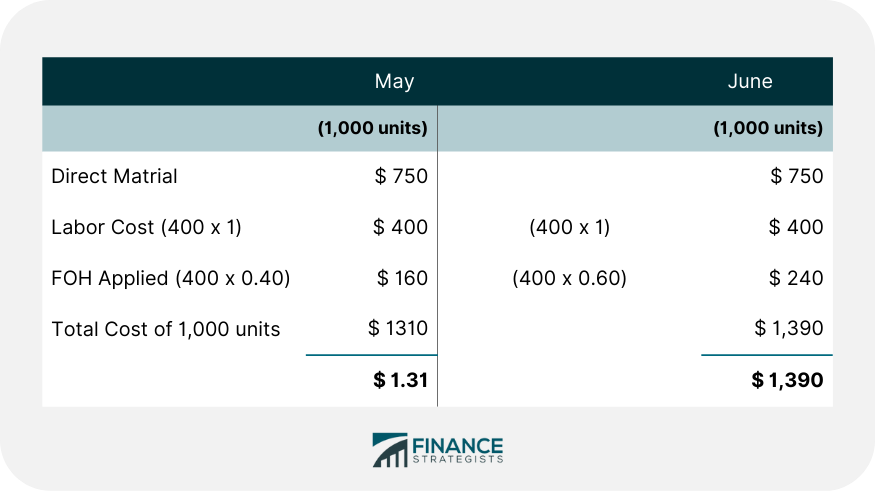
It is clear from the above calculation that charging actual FOH costs to jobs gives inaccurate and misleading results. Calculations Explained
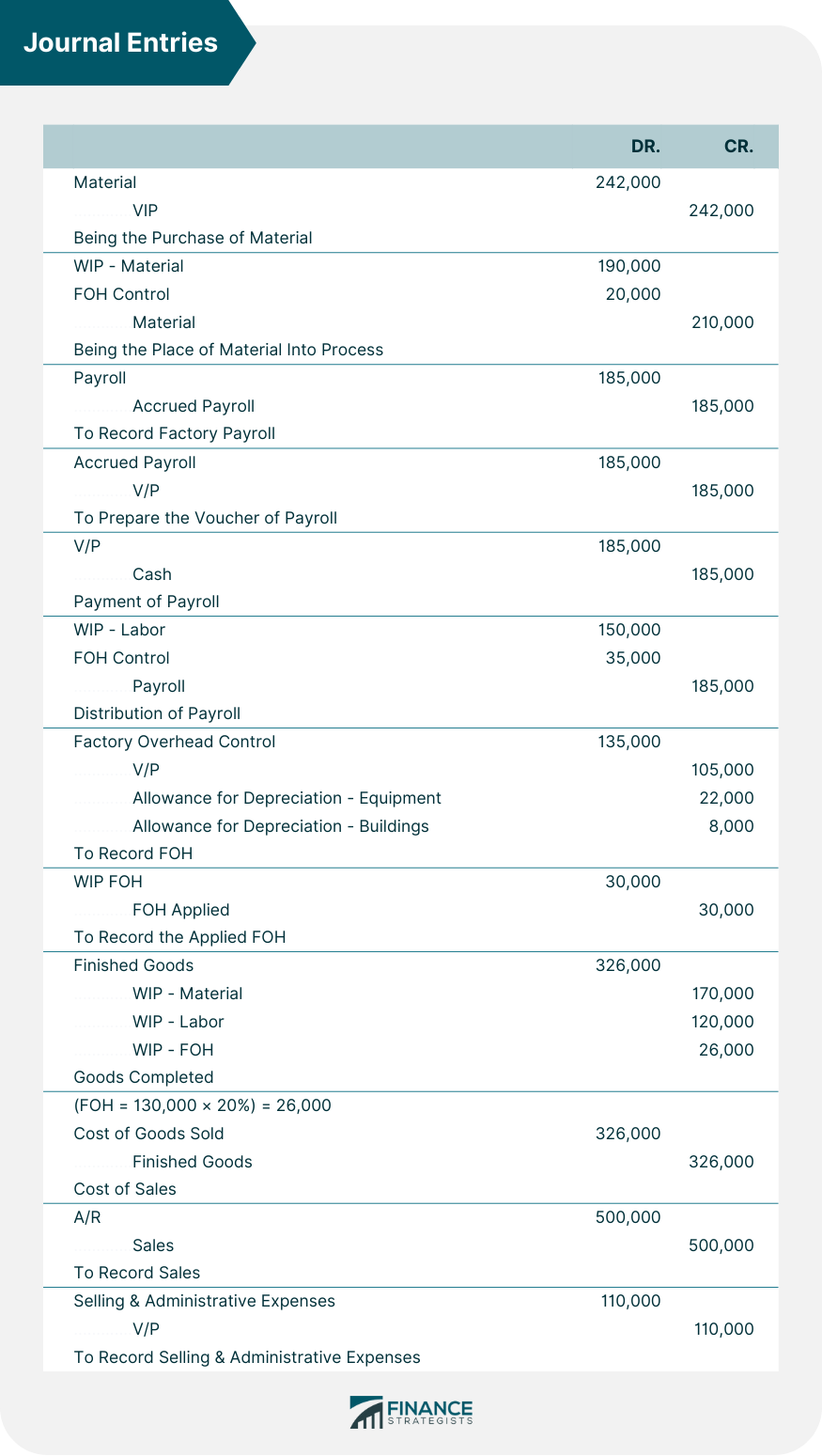
Problem 3: Journal Entries For Cost Cycle
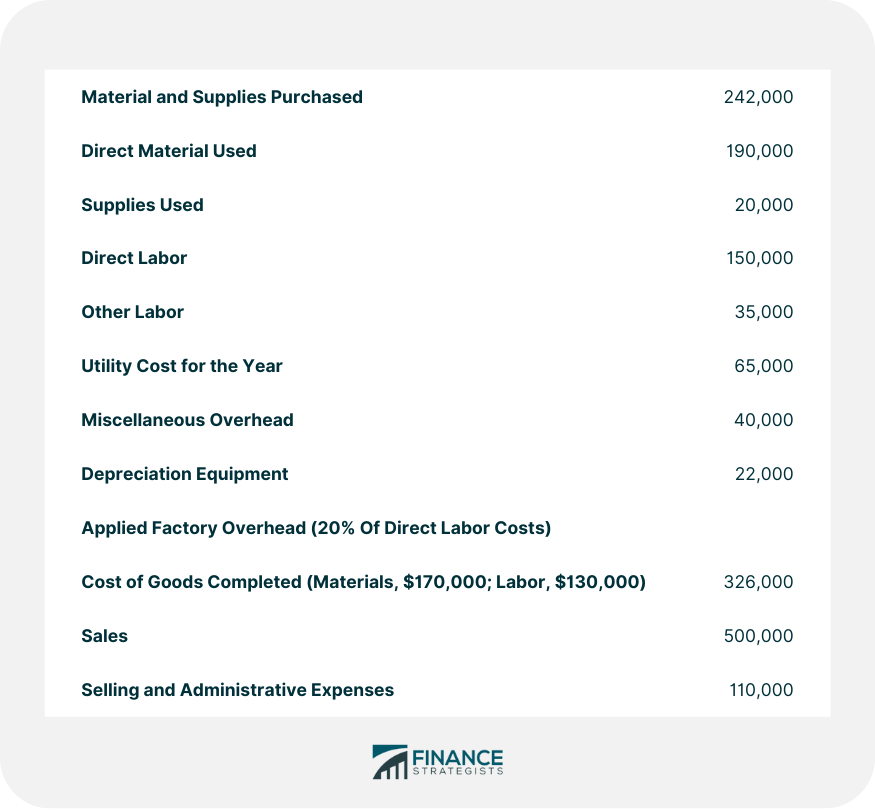
Required:
Solution
Net Income

Job Order Costing: Examples, Practical Problems, and Solutions FAQs
Job order costing is a special type of process costing system. Under this system, costs are assigned to jobs based on the number of direct labor hours required to manufacture each job. Costs are accumulated for each different job during the production process.
First, is the difficulty to estimate the cost of jobs when changes are made frequently in job specifications, the estimations can be done by appropriate formulae but if estimates vary frequently it will affect the accuracy of the calculation, etc.
The most common mistake when preparing a job order sheet is the use of the wrong job order number.
Because once the calculation is done, we will be able to determine how much we spend on each product we produce. This analysis allows us to see if we are making a profit or loss for every product we sell which helps us determine what price point should be set for our products
The problem with job order costing is that it can get very costly because it assigns product costs using a more complex allocation system, usually requiring more detailed data for each job.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











