Bank account bonuses, also known as bank incentives or promotional offers, are rewards provided by financial institutions to entice new customers to open accounts or encourage existing customers to engage in specific banking activities. These bonuses come in various forms, such as cash rewards, interest rate boosts, fee waivers, or gift cards. The primary purpose of bank account bonuses is twofold. Firstly, they serve as powerful marketing tools that help banks generate brand awareness and attract new customers. Secondly, bank account bonuses aim to build long-term customer relationships. Understanding how these bonuses work and evaluating them can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their banking relationships. The following are the specific details and mechanisms that underpin the workings of bank account bonuses: To qualify for a bonus, customers must meet certain eligibility criteria set forth by the bank. These criteria may include factors such as age, residency status, and citizenship. Additionally, banks may consider a customer's credit score as part of their eligibility assessment. Moreover, a customer's existing relationship with the bank can impact their eligibility for certain bonuses. For instance, a bank may offer exclusive bonuses to existing customers as an incentive for consolidating more accounts with the institution. This approach fosters customer loyalty and strengthens the relationship between the bank and its clients. Bank account bonuses can apply to various types of accounts, depending on the bank's marketing strategy and financial product offerings. The most common accounts that qualify for bonuses include: Checking Accounts: Banks often offer bonuses to encourage customers to open new checking accounts. The rationale behind this approach is that checking accounts serve as a central hub for customers' day-to-day financial transactions, making them more likely to engage with the bank's services. Savings Accounts: These accounts are designed for accumulating funds over time and typically earn interest. Banks may provide bonuses to incentivize customers to start saving with them or increase their savings balances. Money Market Accounts: MMA's combine elements of both checking and savings accounts, offering higher interest rates than regular savings accounts. Banks may offer bonuses to attract customers looking for competitive interest rates and more accessible funds. Certificates of Deposit (CDs): CDs are time deposits with fixed terms and interest rates. Banks may use bonuses to encourage customers to invest in CDs for specified durations, allowing the bank to secure longer-term deposits. The minimum deposit amount can vary significantly from one promotion to another and may range from a nominal sum to a more substantial investment. In addition to the initial deposit, some bank account bonuses stipulate that customers must maintain a minimum account balance for a specified period to be eligible for the reward. By setting minimum deposit and balance requirements, banks can attract customers who are genuinely interested in their services rather than those who are seeking to take advantage of the bonus and may not maintain a long-term relationship with the bank. Bank account bonuses can be enticing, but customers should approach them with careful consideration and evaluation. Here are key aspects to consider when evaluating bank account bonus offers: Banks may entice customers with cash bonuses, gift cards, interest rate boosts, or other rewards. Customers should consider the value of the bonus and compare it against any associated fees or requirements for the account. The type of reward offered may also influence the customer's preference. Some individuals may find cash bonuses more versatile, while others may appreciate interest rate boosts if they intend to maintain a higher account balance. Some accounts may have monthly maintenance fees, ATM fees, or overdraft fees that could erode the value of the bonus over time. Moreover, certain accounts may require customers to meet specific conditions to avoid fees, such as maintaining a minimum account balance or setting up direct deposits. Understanding these requirements is crucial to ensure that customers can avoid unnecessary charges and maximize the benefit of the bonus. Customers must fully comprehend the bonus requirements to ensure that they can meet them without undue hassle or difficulty. Common bonus requirements may include: Minimum Deposit: Some bank account bonuses may require customers to deposit a certain amount of money when opening the account. Minimum Balance: To be eligible for the bonus, customers may need to maintain a minimum account balance for a specific period. Transaction Activity: Some bonuses are contingent on a certain number of transactions, such as making a specific number of debit card purchases or setting up direct deposits. Account Duration: Customers may need to keep the account open for a minimum period to receive the full bonus amount. Customers need to be aware of these dates and plan accordingly to take advantage of the bonus before it expires. Banks use expiration dates to encourage prompt action from customers and prevent the indefinite extension of promotional offers. While bank account bonuses may seem like a straightforward and tax-free way to earn extra money, customers should be aware of the tax implications associated with these incentives. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) considers most bank account bonuses as taxable income, which means that customers are required to report them on their tax returns for the year in which they were received. When a customer receives a bank account bonus, it is considered a form of taxable income by the IRS. This means that the bonus amount must be included in the customer's annual income for tax purposes. The bank, as the issuer of the bonus, is responsible for reporting the amount to both the customer and the IRS. Depending on the type of bonus received, the bank will issue the appropriate tax form to the customer. For interest-bearing bonuses, such as those earned on a high-yield savings account, the bank will issue Form 1099-INT to report the interest income. For non-interest-based bonuses, such as cash bonuses or gift cards, the bank will issue Form 1099-MISC to report miscellaneous income. The bank account bonus, although initially enticing, may be subject to both federal and state income taxes, depending on the individual's tax bracket and the tax laws of their place of residence. The exact amount of tax owed on the bonus will depend on the customer's total income, deductions, and credits for the tax year. It is advisable to consult with a tax services professional or use tax preparation software to accurately calculate the tax owed on the bank account bonus and ensure compliance with all tax laws. In addition to federal taxes, customers may also be subject to state income taxes on the bank account bonus. The tax treatment of bonuses can vary from one state to another, with some states having no income tax at all while others impose significant tax rates. Customers should be aware of their state's tax laws and take them into account when calculating the overall tax liability on the bonus. Additionally, some states may have specific provisions regarding the taxation of bonuses, and customers should stay informed about any changes to tax regulations that could affect their tax situation. Customers who receive bank account bonuses may also consider utilizing tax-advantaged accounts, such as Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) or Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), if eligible. Depositing the bonus into these accounts can offer potential tax benefits, such as tax-deferred growth or tax-free withdrawals for qualified expenses. For customers seeking to make the most of bank account bonuses, employing effective strategies can enhance the benefits and rewards. Customers can strategically open new accounts during periods when banks offer special promotions or seasonal bonus offers. Financial institutions often introduce enhanced bonuses to attract customers during specific times of the year, such as the holiday season, the beginning of the year, or other significant events. By researching the promotional calendar of various banks and understanding when these attractive offers are available, customers can capitalize on the most rewarding opportunities. Customers can take advantage of various bonus opportunities by opening different types of accounts with the same bank or considering bonuses from different financial institutions. By diversifying their accounts and spreading their funds across multiple banks, customers can accumulate more rewards and optimize their earnings. Customers must be fully aware of the terms and conditions associated with bank account bonuses to prevent potential clawbacks. A clawback occurs when a bank reverses the bonus if certain requirements are not met or if customers close the account too soon after receiving the bonus. To avoid bonus clawbacks, customers should carefully read the fine print of the bonus offer and ensure they comply with all stipulated requirements. This may include maintaining a minimum account balance for the specified period, fulfilling transaction activity, or keeping the account open for a certain duration. Banks often offer loyalty rewards or premium account features to customers who have a history of maintaining a relationship with them. As customers build trust and demonstrate consistent banking habits, they become more attractive to the bank, leading to more favorable terms, better interest rates, and enhanced rewards. By nurturing a long-term relationship with a bank, customers can unlock ongoing benefits and create a strong financial partnership that continues to deliver value beyond the initial bonus. Bank account bonuses present opportunities for customers seeking to enhance their financial gains and establish relationships with financial institutions. By strategically timing the opening of accounts during special promotions and combining multiple bonuses, individuals can maximize their rewards and accumulate additional benefits. However, it is crucial for customers to be diligent in understanding the bonus requirements and avoiding potential clawbacks to safeguard their earnings. Furthermore, customers should be mindful of the tax implications of these bonuses and set aside funds to cover their tax liabilities. Nurturing a long-term relationship with a bank can unlock further perks and rewards, fostering a mutually beneficial partnership. By employing these strategic tactics and being well-informed, customers can make the most of bank account bonuses, contributing to their financial growth and success.What Is a Bank Account Bonus?
How Bank Account Bonuses Work
Eligibility and Account Requirements
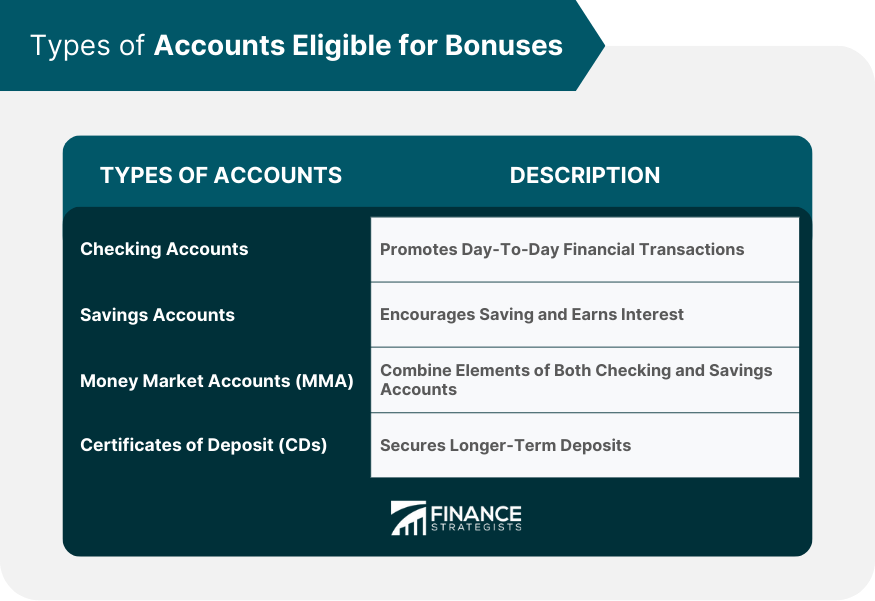
Types of Accounts Eligible for Bonuses
Minimum Deposit and Account Balances
Evaluating Bank Account Bonus Offers
Bonus Amount and Type
Account Fees and Terms
Bonus Requirements
Expiration Dates

Tax Implications of Bank Account Bonuses
Taxable Income and Reporting Requirements
Setting Aside Funds for Tax Liability
State Tax Considerations
Tax-Advantaged Accounts

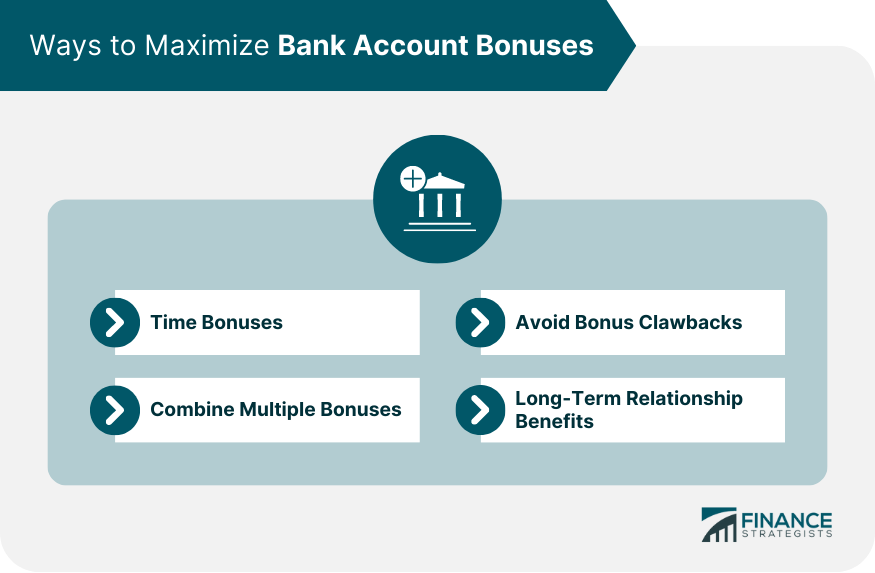
Maximizing Bank Account Bonuses
Timing Bonuses
Combine Multiple Bonuses
Avoid Bonus Clawbacks
Long-Term Relationship Benefits
Conclusion
How Do Bank Account Bonuses Work FAQs
Bank account bonuses are incentives offered by financial institutions to attract new customers or encourage specific banking activities. These rewards can come in the form of cash, interest rate boosts, fee waivers, or gift cards, motivating individuals to open accounts or engage in certain transactions.
Yes, most bank account bonuses are considered taxable income by the IRS. Customers are required to report the bonus amount on their tax returns for the year they receive it. Banks will issue appropriate tax forms, such as Form 1099-INT or Form 1099-MISC, to both the customer and the IRS.
To maximize the benefits of bank account bonuses, consider strategically timing the opening of new accounts during special promotions. You can also combine multiple bonuses by opening different types of accounts with the same or different financial institutions. Be sure to understand the bonus requirements to avoid potential clawbacks and set aside funds to cover tax liabilities.
Common bonus requirements include maintaining a minimum account balance, making a certain number of transactions, setting up direct deposits, or keeping the account open for a specified period.
Yes, you can have multiple bank account bonuses at the same time. By taking advantage of various offers from different banks, you can accumulate more rewards. However, ensure that you can meet the requirements for each bonus to avoid any potential issues or penalties.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











