The U.S. banking system, recognized globally for its robustness, security, and wide array of services, plays a critical role not only in the domestic economy but also in the international financial landscape. This system garners substantial interest from abroad, allowing foreigners—even those not residing in the U.S.—to open a bank account. These accounts offer seamless transaction capabilities on U.S. soil, avenues for investment in U.S. markets, and access to top-tier banking services. Benefits for foreign account holders include easier transactions with U.S. businesses, accessibility to American financial products, and efficient management of U.S. income. It can also simplify the process of acquiring U.S. property or establishing a U.S.-based business, offering superior banking services compared to some home countries. In general, you must be at least 18 years old to open a bank account. Some banks, however, offer accounts to minors with a parent or guardian as a co-owner. It's important to check the specific age requirements at the bank of your choice since these policies can differ from one institution to another. Most U.S. banks will ask for some form of identification, such as a passport. Additionally, some banks may ask for a Social Security Number (SSN) or an Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN). If you don't have an SSN, which is common for non-residents, some banks may still allow you to open an account with an ITIN or other forms of identification. Occasionally, these banks may ask for a second form of ID, like a driver’s license or credit card from your home country. While many banks require a U.S. address, this isn't universal. Some banks will allow foreigners to use an international address, although this may limit your options for online banking or the types of accounts you can open. It's essential to review these details before selecting a bank to ensure that the bank's policies align with your circumstances. Local banks often offer personalized services and can be more flexible with their requirements, which may be beneficial for non-residents. National banks, on the other hand, typically have more resources and offer a wider range of services and account types. It's crucial to weigh the pros and cons of each to decide which type of bank best suits your needs. Online banks are becoming increasingly popular due to their convenience and often lower fees. However, many online banks have strict residency requirements, so it's essential to check their policies. If eligible, online banking can be a convenient option, especially for those living overseas who may not be able to regularly visit a physical branch. There are several types of bank accounts you can open, but the most common are checking and savings accounts. Checking accounts are designed for daily transactions, such as paying bills or making purchases, while savings accounts offer a place to store money and earn interest over time. Choosing the right type of account largely depends on your financial goals and the type of access you need to your funds. You'll typically need a valid passport and another form of ID, such as a driver's license. Some banks may also require a document proving your address. Ensuring you have the right documentation ready can expedite the account opening process. Banks typically require proof of address, which can be difficult for non-residents. However, some banks may accept a foreign address, or an affidavit of residence. The requirements can vary significantly from bank to bank, so it's beneficial to inquire directly with your chosen bank about what they will accept as proof of address. While not all banks require this, some may ask for a visa or other proof of legal immigration status. This requirement is often determined by the bank's policies and federal regulations, so it's crucial to inquire about this beforehand. An ITIN can serve in place of an SSN for tax purposes, and some banks may allow you to use this to open an account. It's worth noting that obtaining an ITIN can be a process in and of itself, so plan accordingly if you choose to go this route. Some banks require foreigners to apply for an account in person. This means you'll need to visit a branch with your documentation. While this may seem inconvenient, especially if you are not currently in the U.S., some people find value in the personalized assistance that can come with an in-person visit. Some banks offer online applications, which can be more convenient, especially if you don't live in the U.S. Make sure to check if the bank offers this option and what the requirements are. Online application processes can often be quicker and allow for easier document submission. Most bank accounts require an initial deposit to open the account. This amount can vary widely depending on the bank and account type. Understanding these requirements in advance can help you avoid unexpected surprises and prepare your funds accordingly. The lack of an SSN or ITIN can make opening a bank account more complicated, but not impossible. Some banks accept other forms of identification, and you can also apply for an ITIN if you're ineligible for an SSN. In addition, there are often resources available to help you understand and navigate this process. Providing a U.S. residential address can be tricky for non-residents. However, some banks may accept a foreign address or allow you to use a P.O. Box or the address of a friend or relative. Understanding this requirement can help you plan accordingly and explore possible solutions. You'll likely need to make an initial deposit to open your account. If you're opening an account from abroad, you'll need to consider exchange rates and international transfer fees. This may influence how much money you initially transfer to your new account, and when you choose to make this transfer. Some international banks offer accounts that allow you to hold funds in U.S. dollars. This can be a convenient option if such a bank operates in your home country. In addition, these banks often have global customer service and can assist with international financial needs. Some digital banks, or "neobanks," specialize in providing services to non-residents or people who frequently travel internationally. These banks often have less stringent requirements and can provide a practical alternative to traditional banking. Plus, their digital-first nature can make accessing and managing your money a seamless experience, regardless of where you are in the world. Prepaid debit cards can be a useful tool for making transactions in U.S. dollars. While they don't offer all the services of a traditional bank account, they do provide a way to pay bills or make purchases in the U.S. Plus, they are often available to individuals regardless of their residency status or credit history. Maintaining a positive banking history, such as avoiding overdrafts, can make it easier to open future accounts or apply for credit. In fact, a good banking history can often be a positive factor when applying for loans or other forms of credit in the U.S. Having a U.S. bank account could have tax implications, so it's important to consult with a tax professional who is familiar with both U.S. and international tax laws. Understanding potential tax obligations can help you avoid unexpected liabilities and comply with all relevant laws and regulations. Keep in mind that you'll be dealing with currency exchange whenever you transfer money to and from your U.S. account. Exchange rates fluctuate and can affect the value of your money, and banks may charge fees for currency conversion. It's wise to be aware of these rates and fees, and potentially explore ways to minimize their impact on your funds. Foreigners can indeed open bank accounts in the U.S., an opportunity that provides myriad benefits such as seamless transactions, access to U.S. investment avenues, and efficient management of U.S. income. While it does involve navigating some specific eligibility criteria such as age, documentation, and residency requirements, the process can be made smooth with the right information. Overcoming common challenges such as securing a U.S. address, obtaining an SSN or ITIN, and meeting initial deposit requirements is feasible with careful planning and proper resources. Additionally, there are alternatives to traditional U.S. bank accounts, such as international bank accounts, digital bank accounts, and prepaid debit cards. Lastly, keeping an eye on one's banking history, understanding potential tax implications, and being aware of currency exchange rates and fees can go a long way in managing the bank account effectively.Understanding the US Banking System
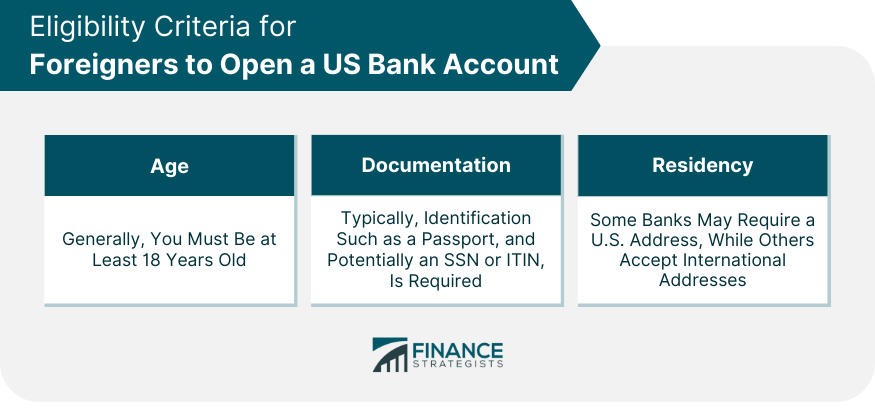
Eligibility Criteria for Foreigners to Open a US Bank Account
Required Age
Required Documentation
Residency Requirements
Step-By-Step Process for Opening a US Bank Account as a Foreigner
Select the Right Bank
Local Banks vs National Banks
Online Banks
Understand Account Types
Gather Necessary Documentation
Identification Documents
Proof of Address
Immigration Status
Tax Identification Number
Apply for the Account
In-Person
Online
Meet the Minimum Deposit Requirements

Common Challenges and Solutions for Foreigners Opening a US Bank Account
Obtaining a Social Security Number or ITIN
Securing a US Residential Address
Meeting Initial Deposit Requirements

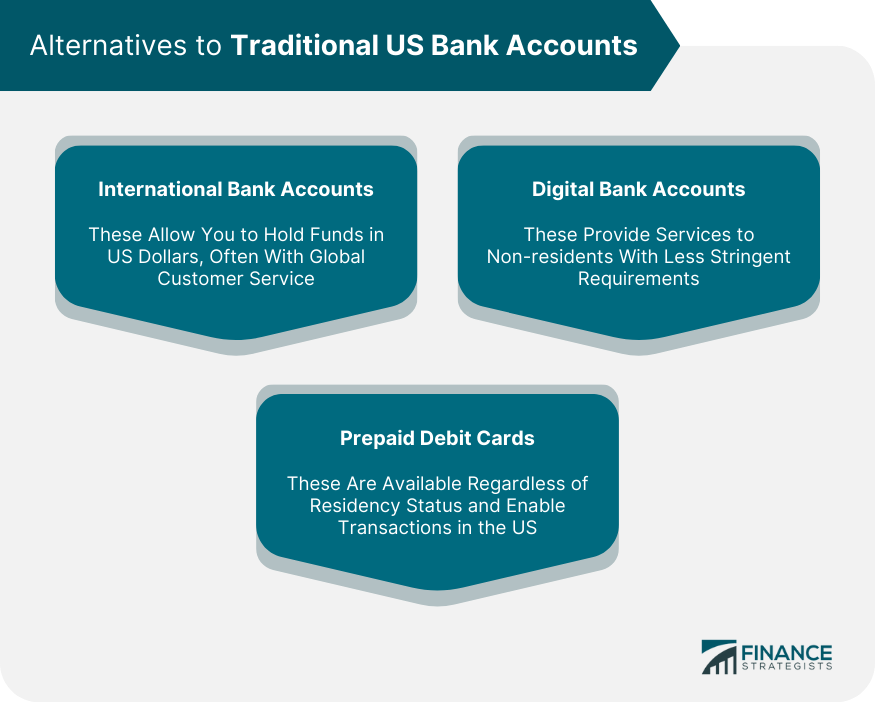
Alternatives to Traditional US Bank Accounts
International Bank Accounts
Digital Bank Accounts
Prepaid Debit Cards
Important Tips and Considerations
Importance of Maintaining Good Banking History
Tax Obligations
Currency Exchange Rates and Fees
Bottom Line
How Foreigners Can Open Bank Accounts in the US FAQs
Foreigners generally need to be at least 18, provide identification, potentially an SSN or ITIN, and sometimes a U.S. address to open a U.S. bank account.
The process includes choosing the right bank, understanding different account types, gathering necessary documents, applying (in-person or online), and meeting the minimum deposit.
Common challenges include the lack of an SSN or ITIN, providing a U.S. residential address, and meeting initial deposit requirements.
Alternatives include international bank accounts, digital bank accounts, and prepaid debit cards.
It's important to maintain a good banking history, understand potential tax obligations, and be aware of currency exchange rates and fees.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











