An offshore bank account refers to a bank account opened and maintained in a country different from the residence of the account holder. It is termed "offshore" due to the nature of the account being located outside the native country of the individual or corporation. The mechanics of an offshore bank account are similar to that of a regular bank account: they can include checking and savings facilities, online banking, and other related services. However, the differentiating factor is the legal and regulatory environment under which the foreign bank operates, often offering certain advantages not available in the account holder's home country. Setting up an offshore bank account involves selecting a reputable bank in a stable foreign jurisdiction, complying with their documentation requirements, and understanding the associated tax and legal implications. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to open an offshore bank account: Decide why you want to open an offshore account. This could be for reasons like asset protection, tax savings, business operations, or investment purposes. Research various jurisdictions that offer offshore banking. Look for political and economic stability. Understand the country's regulations concerning offshore banking, including any reporting requirements. Consider any tax treaties between your home country and the offshore jurisdiction. Once you've chosen a jurisdiction, research banks in that country. Prioritize banks with good reputations and strong financial health. Check the services they offer and the fees associated with those services. Read reviews and perhaps even connect with existing clients to get first-hand feedback. Different banks have different requirements. Typically, they will need: Proof of identity (passport, national ID) Proof of address (utility bill, bank statement) Bank reference or letter of recommendation from your current bank Details about the source of your funds Completed application forms Online Applications: Begin by visiting the official website of the bank you've selected. Navigate to the offshore or international account opening section. Fill out the online application form, ensuring that all the information is accurate. Some banks have a comprehensive online interface where you can upload required documents directly. Securely submit your application. Many banks will provide a reference number or acknowledgment receipt. Keep this for future reference. Personal Visit: Some jurisdictions or banks prioritize face-to-face interactions to establish a client relationship. Schedule an appointment. Ensure you have all your necessary documents. It might be beneficial to carry originals along with multiple copies. During the meeting, a bank representative will guide you through the application process, answer any questions you might have, and provide insight into the bank's services and fee structures. Upon completion of the application, you'll typically receive an acknowledgment or a temporary account number. Once you've applied, the bank's internal team will begin verifying the information provided: Your documents will be checked for authenticity. The bank might contact the reference provided (typically your current or previous bank) to verify your financial standing and credibility. They might also conduct background checks to ensure compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations and counter-terrorism financing measures. After successful verification, the bank will officially approve your account. You will receive your account details either through secure email or postal mail. Some banks provide a welcome kit, which includes checks, an ATM card, internet banking credentials, and a welcome guide. Activate any online banking or mobile banking services by following the bank's guidelines, which often involve setting secure passwords and enrolling in two-factor authentication for added security. Depending on the bank and the type of account, you may be required to make an initial deposit. This can be done through wire transfers, checks, or, in some cases, through online payment gateways. Ensure you keep a receipt or acknowledgment of this deposit for your records. Set up your preferred means of communication with the bank, be it through email, phone, or mail. Ensure you have contacts for customer service should you have any questions or need assistance. Periodically, the bank might send updates on their services, changes in fees, or regulatory updates. Ensure you stay updated with these communications. To adhere to international standards against money laundering and other illicit activities, offshore banks require several identification documents from potential account holders. This can include a valid passport, proof of address (like a utility bill or bank statement), and sometimes, a notarized copy of these documents. Many financial institutions have bolstered their verification processes as part of their commitment to international regulatory standards. One commonly mandated requirement is proof of residence. This can take the form of utility bills, lease agreements, or official government correspondence that verifies the applicant's residential address. Alongside this, in a global effort to curtail illicit financial activities such as money laundering, terrorism financing, and other economic offenses, banks have amplified their due diligence procedures. Now, they often demand a comprehensive understanding of the origin of the depositor's funds. This means that when one seeks to deposit a substantial sum into an offshore account, they may need to provide documentation like salary slips, inheritance papers, sale deeds, or business revenues. Some offshore banks might request a reference letter from your current bank, vouching for your financial reliability. This document typically confirms the duration of your banking relationship and states that you've been a client in good standing. As global financial regulations evolve, the banking and tax laws of your chosen jurisdiction might also change. These jurisdictional changes can have significant implications for individuals and businesses engaged in offshore banking or operating in international markets. It is crucial to stay proactive in understanding these changes to ensure compliance and avoid potential pitfalls. Consulting with legal or financial professionals well-versed in offshore banking can provide valuable guidance and support in navigating jurisdictional changes effectively. Clear and detailed records play a crucial role in demonstrating the legitimacy of funds and transactions associated with offshore accounts. Such records provide a transparent trail of financial activities, including the source of funds, the nature of transactions, and the parties involved. In case of any inquiries or investigations by authorities, these records serve as evidence to substantiate the lawful origin and use of funds. Having comprehensive records allows you to provide a clear and verifiable account of your financial activities, ensuring that your offshore banking activities are conducted in compliance with applicable laws and regulations. This transparency helps build credibility, instilling confidence in the legitimacy of your financial affairs. It's wise to periodically review your offshore account's performance, fees, and associated services. Given the changing nature of global finance, newer and better banking products or investment opportunities might arise. Regular reviews enable you to assess the performance of your offshore accounts, evaluate associated fees and services, and make informed decisions to keep your offshore banking strategy aligned with your evolving financial objectives. Additionally, it is crucial to keep your personal details updated with the bank, such as changes in address or contact information, to ensure uninterrupted services and efficient communication. Opening an offshore bank account involves determining your needs, choosing the right jurisdiction and bank, understanding the requirements, applying for the account, undergoing verification, and finally, receiving account approval and activation. Compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, such as providing necessary identification documents, proof of residence or source of funds, and banking references, is essential. Best practices for offshore account maintenance include staying informed about jurisdictional changes, maintaining clear and transparent records, conducting regular financial reviews, and keeping personal details updated. By following these best practices and maintaining a proactive approach to offshore banking, individuals and businesses can enhance their financial opportunities while safeguarding their assets and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Regular reviews and updates help optimize offshore banking strategies and maximize financial opportunities.What Is an Offshore Bank Account?
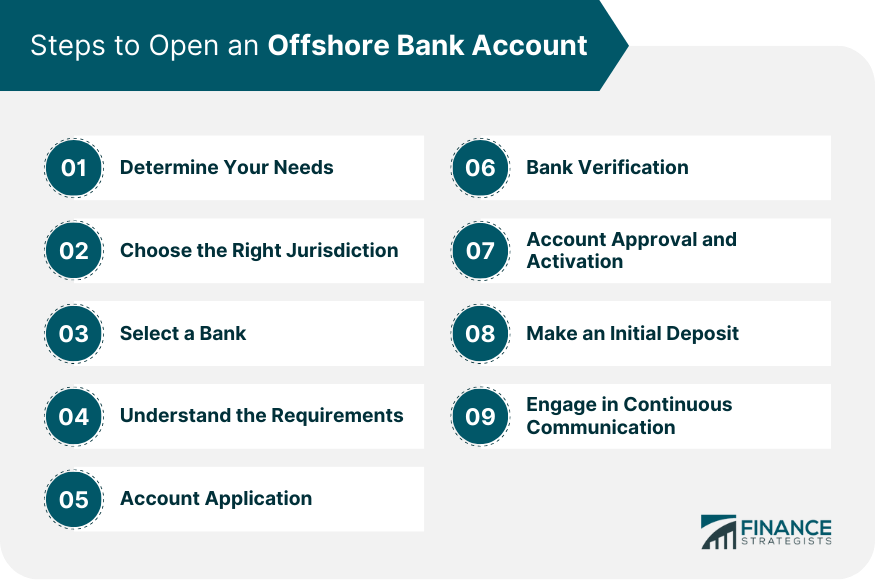
Steps to Open an Offshore Bank Account
Step 1: Determine Your Needs
Step 2: Choose the Right Jurisdiction
Step 3: Select a Bank
Step 4: Understand the Requirements
Step 5: Apply for the Account
Step 6: Undergoing Verification
Step 7: Account Approval and Activation
Step 8: Making the Initial Deposit
Step 9: Continuous Communication
Legal and Compliance Requirements
Necessary Identification Documents
Proof of Residence or Source of Funds
Banking References or Financial History
Best Practices for Offshore Account Maintenance
Jurisdictional Changes
Clear and Transparent Record Keeping
Regular Financial Reviews and Updates

Conclusion
How to Open an Offshore Bank Account FAQs
An offshore bank account is a bank account opened and maintained in a country different from the residence of the account holder, offering advantages such as financial privacy, asset protection, and potential tax benefits.
Determine your needs, choose a jurisdiction and bank, understand the requirements, apply for the account, undergo verification, receive approval and activation, make an initial deposit, and set up your preferred means of communication with the bank.
Commonly required documents include a valid passport, proof of address, bank references, financial statements, proof of the source of funds, and possibly additional documentation based on the bank's due diligence requirements and local regulations. It's important to consult with the chosen bank for specific document requirements.
The best practices for opening an offshore bank account include thorough research on suitable jurisdictions, selecting reputable banks, understanding tax implications, complying with documentation requirements, maintaining clear and transparent records, and conducting regular financial reviews.
Opening an offshore bank account is legal, but it's important to comply with tax and reporting requirements in your home country. Consult with legal and tax professionals to ensure compliance with all applicable laws and regulations.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











