A savings account is a type of deposit account provided by financial institutions like banks and credit unions. It is designed to hold funds that aren't intended for daily expenditure. It is one of the most traditional types of bank accounts, with distinctive features, including a safer and more organized way of storing money, earning interest, and sometimes, the provision of basic banking services like ATM access or online transfers. These accounts play a significant role in personal finance. Having a savings account encourages the habit of saving, providing a secure place to store money and grow wealth gradually. Not only does a savings account provide a safety net for unexpected expenses, but it also aids in planning for short-term or long-term financial goals. It offers an opportunity to save for specific objectives like vacation, education, or a new car while earning a modest interest income. Opening a savings account is typically a straightforward process. It involves providing some basic information, such as your name, address, and social security number, and making an initial deposit. Different banks have different requirements and procedures, but generally, you can open an account either in person at a bank branch, over the phone, or online. After the account is set up, you can start making deposits. A key feature of savings accounts is the interest-earning mechanism. Banks pay you interest on your deposit, which is typically compounded daily or monthly and paid out monthly or annually. The interest rate varies among banks and types of savings accounts. Generally, traditional brick-and-mortar banks offer lower interest rates, while online banks and credit unions tend to offer higher rates as they have lower overhead costs. The transaction capabilities of savings accounts are usually more limited than those of checking accounts. Deposits can be made through cash, checks, wire transfers, or electronic transfers. Withdrawals can be made through ATMs, bank tellers, or electronic transfers. However, there's a limit on certain types of withdrawals and transfers due to federal law, which allows up to six "convenient" transactions per month. When it comes to choosing a savings account, several factors need to be taken into consideration. These include the interest rate offered, any potential fees and charges, and the quality of customer service. An account with a high-interest rate is naturally preferable, but it's also important to weigh any potential costs associated with the account. Good customer service, including easy access to support and helpful online features, can also make a big difference in your banking experience. Comparing different banks can also be useful when looking for a savings account. Traditional banks, online banks, and credit unions all offer savings accounts, but they can have significantly different offerings. Online banks, for example, often offer higher interest rates than traditional banks, thanks to lower overhead costs. On the other hand, credit unions often offer lower fees than commercial banks. One of the primary benefits of a savings account is liquidity and accessibility. Unlike other types of investment accounts, a savings account provides quick access to your funds. Most banks provide ATM cards for savings accounts, allowing you to withdraw cash 24/7. With the advent of digital banking, online access to savings accounts has made managing funds even easier, enabling balance checks, fund transfers, and even mobile deposits anytime, anywhere. Savings accounts at FDIC-insured banks are protected for up to $250,000 per depositor, per bank. This means even if the bank fails, your money is safe. In addition, a savings account offers protection against theft or loss that can occur when holding large amounts of cash at home. Savings accounts also provide the potential to earn income through interest. While the rates may not be high, they offer a no-risk return on your money. Certain types of savings accounts, like high-yield savings accounts, can offer significantly higher interest rates than regular savings accounts, helping your money grow faster. Despite the benefits, savings accounts do have certain drawbacks. The most prominent one is the typically low-interest rates. When compared to other investment vehicles like stocks, bonds, or mutual funds, the return on a savings account is relatively low. Furthermore, the interest earned can sometimes fail to keep up with inflation, resulting in a loss of purchasing power over time. Another potential downside is the restrictions and limitations imposed on transactions. As mentioned earlier, federal regulations limit the number of certain types of transactions you can make from your savings account each month. Also, some banks require a minimum balance to open the account or avoid fees. Many banks charge fees for savings accounts, such as maintenance fees, minimum balance fees, and overdraft charges. While these are often waivable with certain conditions, they can eat into your savings if not managed properly. Once you've opened a savings account, it's important to manage it effectively. Regularly depositing into your savings, whether it's a portion of your paycheck or loose change at the end of the day, can help you grow your savings steadily over time. In addition, keep an eye on the interest rate. If it drops, you may want to consider switching to a bank that offers a better rate. In today's digital age, there are many tools and apps available to help you manage your savings account. Online banking features allow you to monitor your account, make transfers, and even deposit checks from your phone or computer. There are also various budgeting and savings apps available that can help you track your spending, set savings goals, and make the most of your savings account. A savings account is a valuable financial tool for individuals looking to save and grow their wealth gradually. It provides a secure place to store money while earning interest and offers convenience and accessibility through various banking channels. Opening a savings account is a straightforward process, and the interest-earning mechanism allows your money to grow over time. The benefits of a savings account include liquidity, safety, and the potential to earn income through interest. With quick access to funds and FDIC insurance, your money is protected even in the event of a bank failure. While the interest rates may not be as high as other investments, savings accounts provide a no-risk return on your money. However, savings accounts have limitations, including low-interest rates, transaction restrictions, and potential fees. It's important to consider these drawbacks when choosing an account and manage it effectively by making regular deposits and monitoring interest rates.What Is a Savings Account?
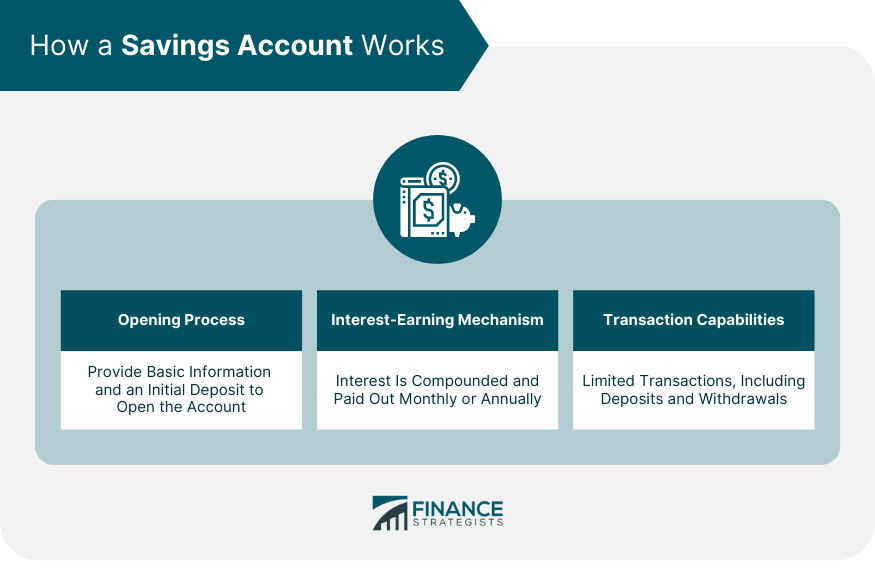
How a Savings Account Works
Opening an Account
Interest-Earning Mechanism
Transaction Capabilities
Choosing the Right Savings Account
Interest Rates
Customer Service
Bank Offerings
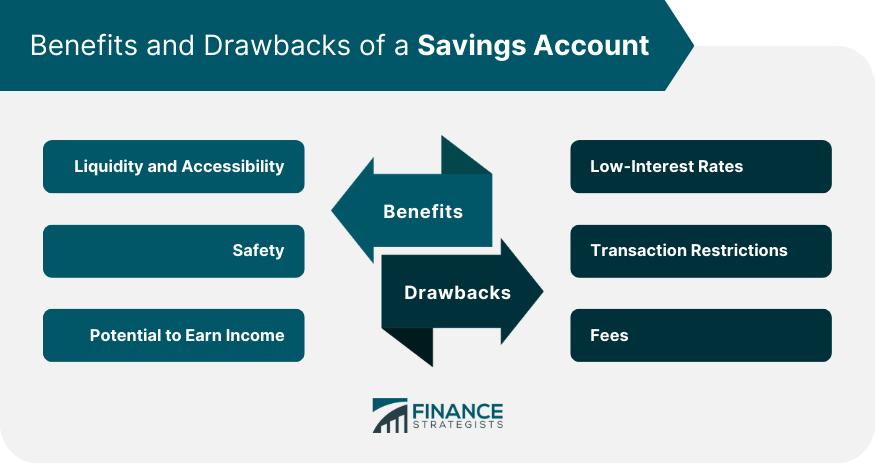
Benefits of a Savings Account
Liquidity and Accessibility
Safety
Earning Potential
Drawbacks of a Savings Account
Low-Interest Rates
Transaction Restrictions
Fees
Managing Savings Account
Conclusion
Savings Account FAQs
A savings account is a type of deposit account offered by banks where you can securely store your money and earn interest on your deposits.
To open a savings account, visit a bank branch, provide necessary identification documents, such as ID and proof of address, complete an application, and make an initial deposit.
A savings account encourages saving habits, provides a safe place for your money, offers interest income, and helps you plan for short-term and long-term financial goals.
Yes, savings accounts offer easy access to your funds. You can make deposits and withdrawals through various channels, including ATMs, bank tellers, and online banking platforms.
While a checking account is meant for everyday transactions, a savings account is designed to save money over time. Savings accounts usually offer higher interest rates and have limits on the number of withdrawals you can make per month.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











