For students stepping into personal finance, it is vital to grasp the roles of two main types of accounts: the Student Savings Account and the Student Checking Account. Each has its own job, making it simpler for students to handle their money during their school years. A student savings account is all about saving for later. When you put money into this account, the bank often adds a bit more over time. This extra bit, known as 'interest', is the bank's way of rewarding you for saving with them. On the other hand, a student checking account is primarily designed for daily transactions, offering quick, easy, and frequent access to funds. Most of these accounts come with a debit card, allowing for electronic payments and ATM withdrawals. They offer a degree of convenience that's essential for the bustling life of a student. Knowing the special features of each account can help students make smart money choices for their future. A student savings account is a type of bank account specifically tailored for students, often those in high school or college. This account provides a platform for individuals to deposit money, with the primary goal of accumulating savings over time. Unlike regular savings accounts, student savings accounts cater to the unique financial needs and limitations of students, often offering benefits like lower fees or no minimum balance requirements. The primary purpose of this account is to encourage young individuals to develop a habit of saving. It's also a stepping stone, introducing students to the world of banking and finance, ensuring they are better prepared for the financial responsibilities of adulthood. Typical features of a student savings account include: Interest Accrual: Like most savings accounts, student accounts accumulate interest, albeit at varying rates. Lower or No Minimum Balance: These accounts understand the financial constraints of students, often eliminating the need for a minimum balance. Limited Withdrawals: To maintain the purpose of savings, there might be a limit on the number of withdrawals or transactions one can make in a month. One of the most significant advantages of student savings accounts is their affordability. Most come with zero or very minimal maintenance fees. Additionally, the accumulated interest, although often modest, can be a great incentive for students to save. They also serve as an excellent introduction to the world of finance, giving students practical experience in managing a bank account. The interest rates, while guaranteed, are typically lower than other investment avenues. Also, there might be restrictions on the number of monthly withdrawals or transactions, making it less flexible than other account types. A student checking account facilitates daily financial transactions. Unlike a savings account, a checking account is designed primarily for frequent deposits and withdrawals, making it suitable for handling everyday expenses. The primary role of the account is to provide students with an easy and efficient means to manage their daily finances. Whether it's paying for a meal, covering transportation costs, or purchasing study materials, a checking account ensures seamless transactions without the need to handle cash constantly. Typical features of a student checking account often include: Debit Card: Facilitates electronic transactions and cash withdrawals. Online and Mobile Banking: Allows for electronic fund transfers, bill payments, and account management. Overdraft Protection: Offers a safety net against accidental overspending. These accounts are typically user-friendly, ensuring students have easy access to their funds when they need them. The associated debit card, online, and mobile banking features offer the convenience of cashless transactions, which are increasingly becoming the norm. Furthermore, the potential overdraft protection can be a lifesaver, preventing hefty fees in case of accidental overspending. While incredibly useful, student checking accounts are not without limitations. Some might have transaction limits, fees for using ATMs outside the bank's network, or charges for not maintaining a certain monthly balance. Additionally, unlike savings accounts, checking accounts typically offer little to no interest on the deposited amount. While each account is uniquely designed to cater to different aspects of a student's financial journey, there are notable similarities between the two. Here are the shared features that bridge these accounts: Designed for Students: Both accounts are crafted with students in mind, typically those navigating high school or college years. Digital Accessibility: Both types of accounts allow students to manage their finances via online and mobile banking platforms. ATM Privileges: Holders of both accounts can usually access ATM services, facilitating easy withdrawals. Regular Account Updates: Whether it's a monthly or quarterly affair, account holders receive detailed statements for both types of accounts, which can be accessed electronically or sometimes in print. Safety Nets: Some banks extend overdraft protection to both accounts, ensuring students don't accidentally overspend and get caught up with hefty fees. Learning Opportunities: Recognizing the importance of financial literacy, many banks offer tools, resources, or workshops for both account types to help students better understand their finances. Maturity Transitions: As students grow, both accounts often evolve, transitioning to regular adult accounts, with some banks continuing the student benefits for a limited time post-graduation. While both cater to the same demographic, each has been tailored for distinct purposes and functions. Let's delve into the primary differences that set these two accounts apart: Primary Function: Savings account is designed for saving money over the long term, while a checking account is meant for daily transactions and regular expenses. Interest Rates: Savings account usually accrues interest, allowing savings to grow over time, while a checking account typically offers little to no interest on the deposited amount. Withdrawal Restrictions: Savings accounts have limits on the number of withdrawals per month to promote saving while checking accounts are designed for frequent transactions, thus usually have higher or no limits on withdrawals. Associated Tools: Savings account comes with passbooks or e-statements detailing interest earned and withdrawals, while a checking account is often accompanied by a debit card, online bill pay, and other transactional tools. Fees and Charges: Savings accounts may impose fees if the number of allowed transactions exceeds or if the balance falls below a specified minimum. When making a decision between both accounts, several factors should be taken into consideration. Consider your financial objectives and whether you prioritize saving money for the future. If you have long-term goals or want to build up an emergency fund, a student savings account may be more suitable. However, if your primary focus is on day-to-day expenses and immediate access to funds, a student checking account might be a better fit. Evaluate how often you need to access your money. Student checking accounts offer greater flexibility with unlimited withdrawals and deposits, making them convenient for frequent transactions. If you anticipate needing regular and immediate access to your funds, a checking account is likely the better choice. On the other hand, if you can limit your withdrawals and want to discourage impulsive spending, a savings account's withdrawal limits may be beneficial. Compare the interest rates offered by both account types. Student savings accounts generally provide higher interest rates than regular savings accounts, enabling your money to grow over time. However, some savings accounts may require a minimum balance or charge fees if your balance falls below a certain threshold. Checking accounts may have fees associated with services such as overdrafts or ATM usage. Consider these fees and rates to make an informed decision. Take into account the additional features provided by each account type. Student checking accounts often come with debit cards, online banking, mobile apps, and convenient tools for managing your finances. Some accounts may offer student discounts, cashback rewards, or waived fees as added benefits. Compare the features offered by different banks to find an account that aligns with your needs and preferences. Understanding the differences between a student savings account and a student checking account is crucial for students entering the realm of personal finance. A student savings account focuses on long-term saving goals, encourages disciplined saving habits, and offers the potential for higher interest rates. On the other hand, a student checking account is designed for daily transactions, providing convenient and frequent access to funds for day-to-day expenses. Both account types come with their own unique features, benefits, and limitations. When choosing between the two, factors such as saving goals, access to funds, interest rates and fees, and account features should be considered. By carefully evaluating these factors and selecting the account that aligns with your specific needs and financial objectives, you can effectively manage your money and make informed decisions for your financial future as a student.Student Savings Account vs Student Checking Account Overview
What Is a Student Savings Account?
Features
Benefits
Limitations
What Is a Student Checking Account?
Features
Benefits
Limitations
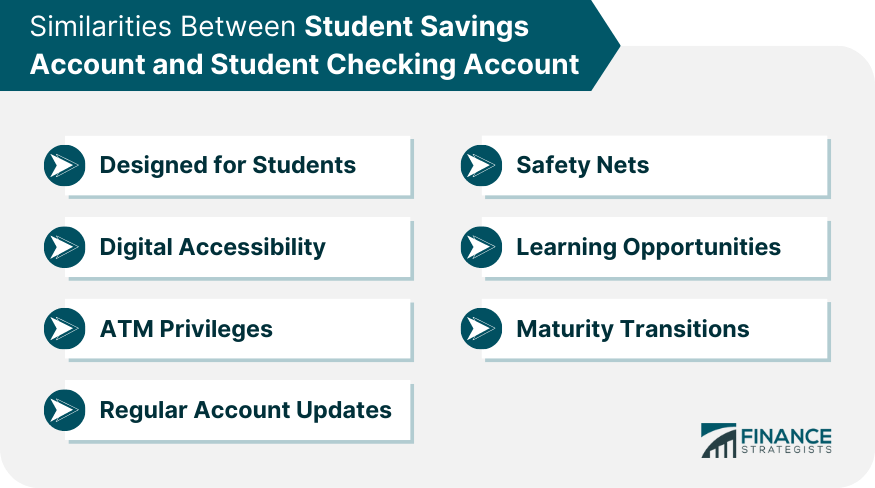
Similarities Between Student Savings Account and Student Checking Account
Key Differences Between Student Savings Account and Student Checking Account
While checking accounts could have fees related to overdrafts, out-of-network ATM use, or not maintaining a minimum balance.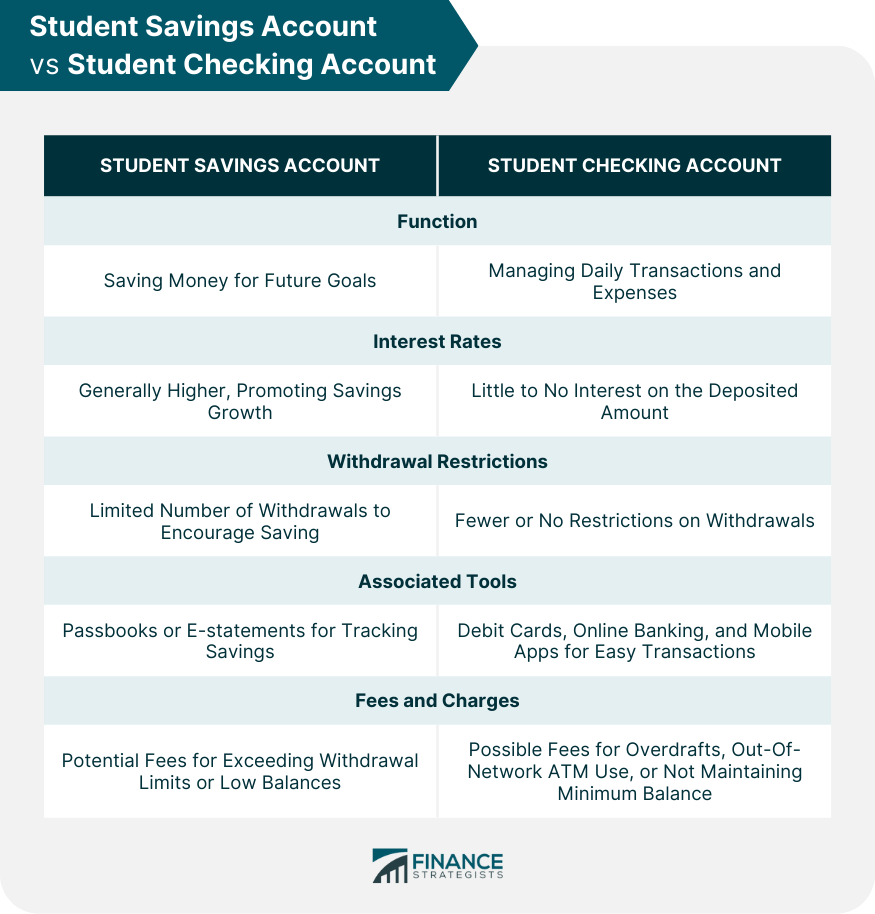
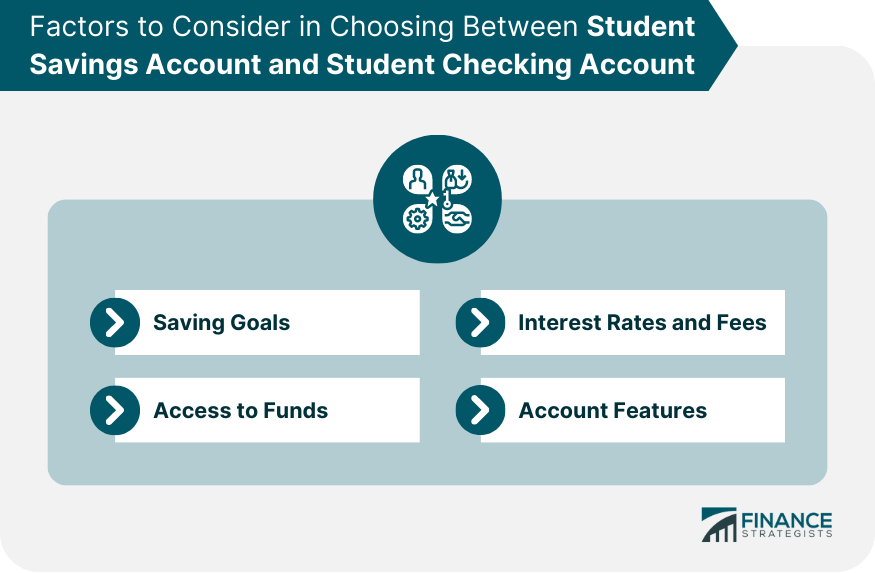
Choosing Between Student Savings Account and Student Checking Account
Saving Goals
Access to Funds
Interest Rates and Fees
Account Features
Bottom Line
Student Savings Account vs Student Checking Account FAQs
A student savings account is a bank account specifically designed for students, aimed at helping them save money for future goals.
A student checking account is a bank account that provides easy access to funds for daily transactions and expenses. It typically comes with features such as a debit card, online banking, and mobile banking apps, making it convenient for students to manage their finances.
The key differences between student savings accounts and student checking accounts lie in their primary functions and features. A student savings account focuses on long-term savings and often earns interest, while a student checking account is designed for daily transactions and provides immediate access to funds.
Both student savings accounts and student checking accounts are designed for students, offer digital accessibility through online and mobile banking, provide ATM privileges for withdrawals, offer regular account updates, and may provide learning opportunities for financial literacy.
Students should consider their saving goals, access to funds, interest rates and fees, account features, and overall financial situation.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











