Account fees are charges imposed by financial institutions for the use and maintenance of various types of accounts, such as checking, savings, and credit card accounts. These fees are designed to cover the costs of providing banking services and generating revenue for financial institutions. Understanding and managing account fees are essential for maintaining financial health, reducing overall financial costs, and maximizing financial resources. By being aware of the various types of account fees and implementing strategies to minimize them, individuals can make more informed decisions about their finances and better allocate their resources. Account fees can come in many forms, including monthly maintenance fees, overdraft fees, ATM fees, late payment fees, account closing fees, and foreign transaction fees. Monthly maintenance fees are charges that financial institutions impose for the use and maintenance of a checking or savings account. These fees are designed to cover the costs of providing account services, such as account access, customer support, and transaction processing. Monthly maintenance fees can vary depending on the financial institution, account type, account balance, and other factors. Some institutions may waive or reduce monthly maintenance fees if certain conditions are met, such as maintaining a minimum account balance or setting up direct deposits. To avoid or reduce monthly maintenance fees, individuals can: Compare account options across different financial institutions to find accounts with low or no monthly maintenance fees. Maintain the minimum account balance required to waive the fee. Set up direct deposits or meet other requirements that may result in waived fees. Consider online or mobile-only banks, which often have lower overhead costs and may charge lower fees. Overdraft fees are charges imposed when an account holder withdraws more funds than are available in their account, resulting in a negative balance. These fees are meant to cover the costs of processing the overdraft and to discourage account holders from overextending their finances. Overdraft fees can occur when individuals make purchases, withdraw cash, or initiate transactions that exceed their available account balance. The fees can vary depending on the financial institution and the type of account. To avoid or reduce overdraft fees, individuals can: Regularly monitor their account balance and transaction history. Set up low balance alerts to receive notifications when their account balance falls below a certain threshold. Link a savings account or line of credit to their checking account to provide overdraft protection. Opt-out of overdraft protection, which may result in declined transactions but can prevent overdraft fees. ATM fees are charges imposed for using an ATM to withdraw cash, check account balances, or perform other transactions. These fees are meant to cover the costs of operating and maintaining ATM networks. ATM fees can vary depending on the ATM operator and the account holder's financial institution. Using an ATM outside of the account holder's bank network often results in higher fees. To avoid or reduce ATM fees, individuals can: Use ATMs within their financial institution's network. Choose a financial institution with a large, convenient ATM network or one that offers ATM fee reimbursements. Limit ATM usage by planning cash withdrawals and using other methods of payment, such as debit or credit cards. Take advantage of cashback options at retailers when making purchases to avoid ATM withdrawals. Late payment fees are charges imposed when account holders fail to make timely payments on credit cards, loans, or other financial obligations. These fees are meant to encourage timely payments and cover the costs of managing delinquent accounts. Late payment fees can be triggered when individuals fail to make payments by the due date or pay less than the minimum amount required. The fees can vary depending on the financial institution and the type of account. To avoid or reduce late payment fees, individuals can: Set up automatic payments to ensure timely payments are made. Use calendar reminders or mobile banking alerts to keep track of due dates. Contact their financial institution to request a due date change if the current due date is inconvenient. Pay more than the minimum amount due to reduce the risk of future late payments. Account closing fees are charges imposed when individuals close certain types of accounts, such as checking, savings, or investment accounts. These fees are designed to cover the costs of processing account closures. Account closing fees can vary depending on the financial institution and the type of account. Some institutions may waive closing fees if certain conditions are met, such as maintaining the account for a specific period. To avoid or reduce account closing fees, individuals can: Research account options and fee structures before opening an account to avoid potential closing fees. Maintain the account for the required period to qualify for a fee waiver. Contact their financial institution to discuss options for closing an account without incurring fees. Foreign transaction fees are charges imposed when account holders make transactions in foreign currencies or use their debit or credit cards abroad. These fees are meant to cover the costs of processing foreign transactions and currency conversion. Foreign transaction fees can vary depending on the financial institution and the type of account. Some institutions may charge higher fees for transactions in certain currencies or countries. To avoid or reduce foreign transaction fees, individuals can: Choose a credit card or account with low or no foreign transaction fees. Use local currency when traveling abroad to avoid currency conversion fees. Utilize mobile payment apps or digital wallets that offer low-cost international transactions. Managing account fees effectively can help individuals reduce their overall financial costs, freeing up resources for savings, investments, or other financial goals. By minimizing account fees, individuals can maximize their financial resources, ensuring that more of their money goes towards achieving their financial goals. Proper management of account fees can help maintain financial health and ensure progress towards financial goals by avoiding unnecessary costs and fees that can deplete resources and hinder financial growth. Regularly reviewing account fee structures can help individuals identify and avoid unnecessary fees, ensuring they are using the most cost-effective banking services. Comparing account fees across different financial institutions can help individuals identify the best banking options for their needs and potentially save money on fees. Fee-free or low-fee banking options can help individuals reduce their overall financial costs and maximize their financial resources by minimizing the impact of account fees on their finances. In some cases, individuals may be able to negotiate lower fees with their financial institutions by discussing their needs, financial situation, and comparing fees charged by competing banks. Regularly monitoring account activity and adjusting financial habits, such as using in-network ATMs or setting up automatic payments, can help individuals minimize fees and reduce their overall financial costs. Many individuals may be unaware of the various fees associated with their accounts, which can result in unnecessary financial costs and hinder their progress towards financial goals. Without proper research and understanding of account fees, individuals may inadvertently overpay for banking services, negatively impacting their financial health. Some individuals may struggle to access affordable banking options, potentially leading to higher fees and limited financial resources. Excessive account fees can have negative impacts on financial health, reducing available resources for savings, investments, and other financial goals. By conducting thorough research on banking options, individuals can make informed decisions about their accounts and potentially save money on fees. Prioritizing fee-free or low-fee accounts can help individuals reduce their overall financial costs and maximize their financial resources. Maintaining open communication with financial institutions can help individuals stay informed about their account fees and discuss potential fee reductions or waivers. Regularly reviewing and adjusting financial habits can help individuals minimize account fees and maintain financial health. Understanding and managing account fees are crucial for maintaining financial health, reducing overall financial costs, and maximizing financial resources. By being aware of the various types of account fees and implementing strategies to minimize them, individuals can make more informed decisions about their finances and better allocate their resources. Effective strategies for minimizing and managing account fees include regularly reviewing account fee structures, comparing account fees across financial institutions, utilizing fee-free or low-fee banking options, negotiating with financial institutions for lower fees, and monitoring account activity to adjust habits that may result in fees. To achieve long-term financial success, it is essential to remain committed to ongoing financial management and fee monitoring. By regularly reviewing account fees, adjusting financial habits as needed, and practicing responsible spending habits, individuals can maintain healthy account balances and work towards a more secure financial future.What Are Account Fees?
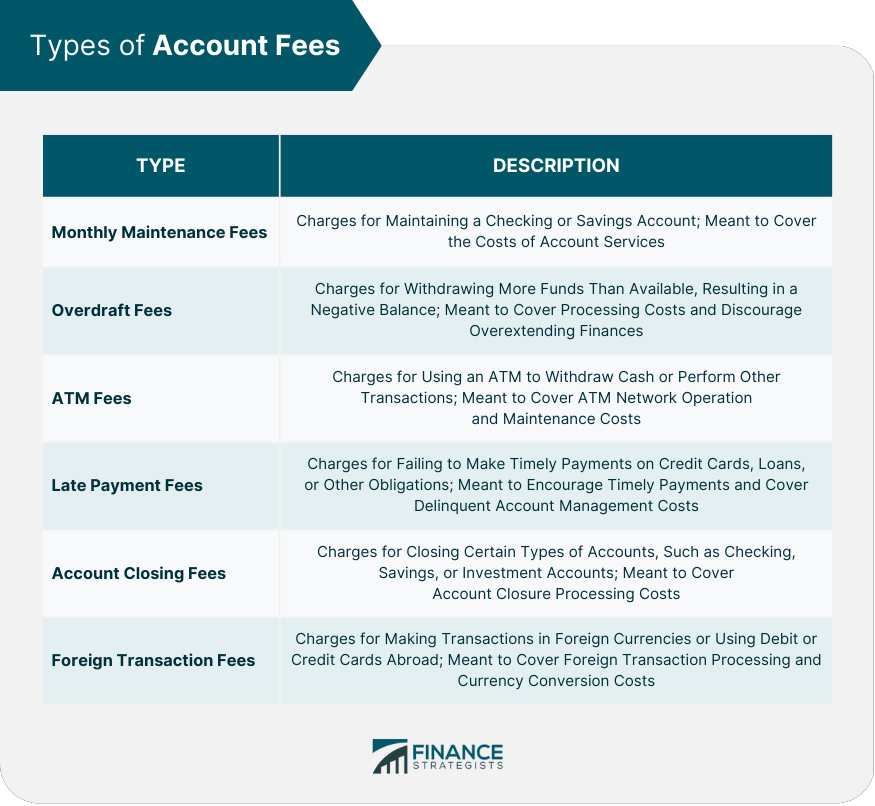
Types of Account Fees
Monthly Maintenance Fees
Definition and Purpose
Factors Affecting Monthly Maintenance Fees
Strategies to Avoid or Reduce Monthly Maintenance Fees
Overdraft Fees
Definition and Purpose
Factors Contributing to Overdraft Fees
Strategies to Avoid or Reduce Overdraft Fees
ATM Fees
Definition and Purpose
Factors Contributing to ATM Fees
Strategies to Avoid or Reduce ATM Fees
Late Payment Fees
Definition and Purpose
Factors Contributing to Late Payment Fees
Strategies to Avoid or Reduce Late Payment Fees
Account Closing Fees
Definition and Purpose
Factors Contributing to Account Closing Fees
Strategies to Avoid or Reduce Account Closing Fees
Foreign Transaction Fees
Definition and Purpose
Factors Contributing to Foreign Transaction Fees
Strategies to Avoid or Reduce Foreign Transaction Fees
Importance of Managing Account Fees
Reducing Overall Financial Costs
Maximizing Financial Resources
Maintaining Financial Health and Progress Towards Goals
Strategies for Managing Account Fees
Regularly Reviewing Account Fee Structures
Comparing Account Fees Across Financial Institutions
Utilizing Fee-Free or Low-Fee Banking Options
Negotiating With Financial Institutions for Lower Fees
Monitoring Account Activity and Adjusting Habits to Minimize Fees
Common Issues Related to Account Fees
Unawareness of Account Fees
Overpaying for Banking Services
Inability to Access Affordable Banking Options
Negative Impacts on Financial Health Due to Excessive Fees
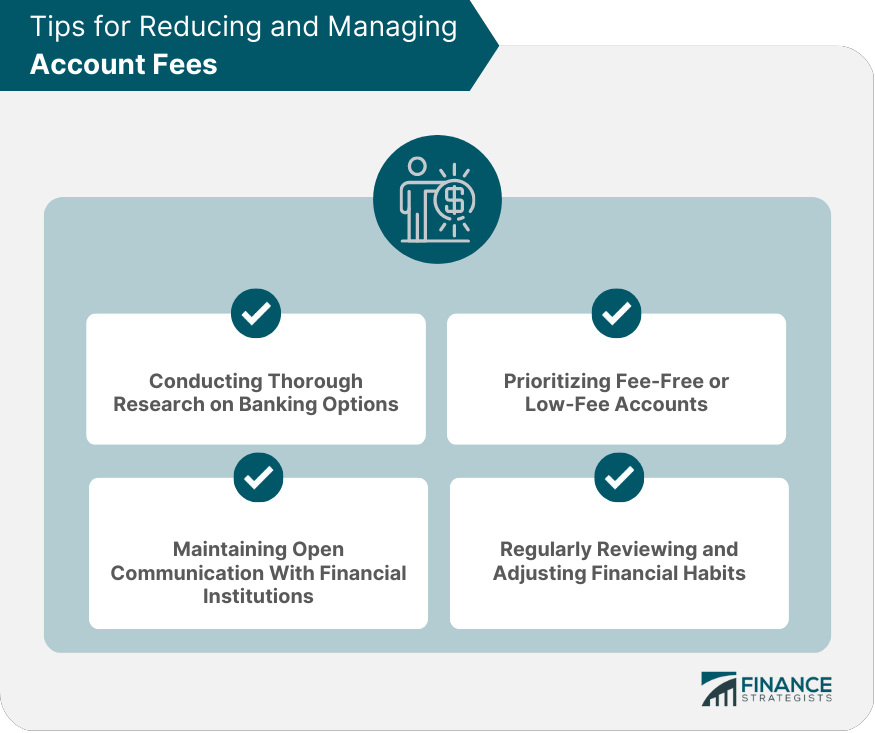
Tips for Reducing and Managing Account Fees
Conducting Thorough Research on Banking Options
Prioritizing Fee-Free or Low-Fee Accounts
Maintaining Open Communication With Financial Institutions
Regularly Reviewing and Adjusting Financial Habits
Conclusion
Account Fees FAQs
Account fees are charges assessed by financial institutions for various services related to maintaining and managing financial accounts.
Common account fees include monthly maintenance fees, overdraft fees, ATM fees, wire transfer fees, transaction fees, and penalty fees for account closures or early withdrawals.
Account fees can often be avoided by maintaining a minimum balance, choosing accounts with no or low fees, using in-network ATMs, opting out of overdraft protection, and carefully reviewing account agreements and disclosures.
When comparing account fees, one should consider the overall cost of the account, the fees charged for specific services, the penalties for noncompliance or account closure, and any benefits or rewards associated with the account.
Tips for managing account fees effectively include regularly reviewing account statements, tracking fees and charges, negotiating with financial institutions for reduced or waived fees, and seeking guidance from financial professionals if needed.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











