Definition of Fixed-Rate CDs and Variable-Rate CDs
Fixed-Rate and Variable-Rate Certificates of Deposit (CDs) stand out as two widely sought-after forms of time deposit provided by banks, each presenting distinct advantages to investors.
A Fixed-Rate CD offers a secure and predictable approach to savings, boasting a predetermined interest rate that remains constant throughout its specified term.
On the other hand, the Variable-Rate CD takes a more dynamic approach, with its interest rate subject to periodic adjustments based on an external benchmark, such as the prime rate or Treasury bill rate.
Overview of Their Key Differences
Fixed-Rate and Variable-Rate CDs are two prominent investment options offered by banks, differing significantly in how their interest rates operate.
Fixed-Rate CDs provide stability and peace of mind to investors since they offer a predetermined interest rate that remains constant throughout the entire term.
This means you know exactly how much interest you'll earn over the CD's duration, making it an attractive option for risk-averse individuals who seek guaranteed returns and want to protect their capital from market fluctuations.
On the other hand, Variable-Rate CDs come with a more dynamic approach, as their interest rates are linked to external benchmarks like the prime rate or Treasury bill rate. As these benchmarks fluctuate, so does the interest rate on the CD.
This creates the potential for higher returns during periods of rising interest rates, making it an appealing choice for those who believe rates will increase in the future.
Fixed-Rate CD
Features of a Fixed-Rate CD
Safety and Stability
The fixed interest rate offers a level of safety and stability because the return on investment is not dependent on market fluctuations. Regardless of how the financial markets perform, the interest rate will remain the same, providing a sense of security for investors.
Predictability in Returns
With a fixed interest rate, investors can easily calculate the total return they will receive at the end of the CD's term.
For instance, if you invest $10,000 in a 2-year Fixed-Rate CD with an annual interest rate of 3%, you can expect to earn $300 in interest each year, resulting in a total of $600 in interest over the entire term.
Ease of Financial Planning
The predictability in returns allows for easier financial planning. Investors know exactly how much interest they will earn and when they will receive it. This knowledge helps individuals or businesses to budget effectively and plan for future expenses or financial goals.
Liquidity Considerations
Fixed-Rate CDs typically have a fixed term, and withdrawing the funds before the CD matures may result in penalties or loss of some interest. Therefore, investors should carefully consider their liquidity needs before investing in a Fixed-Rate CD.

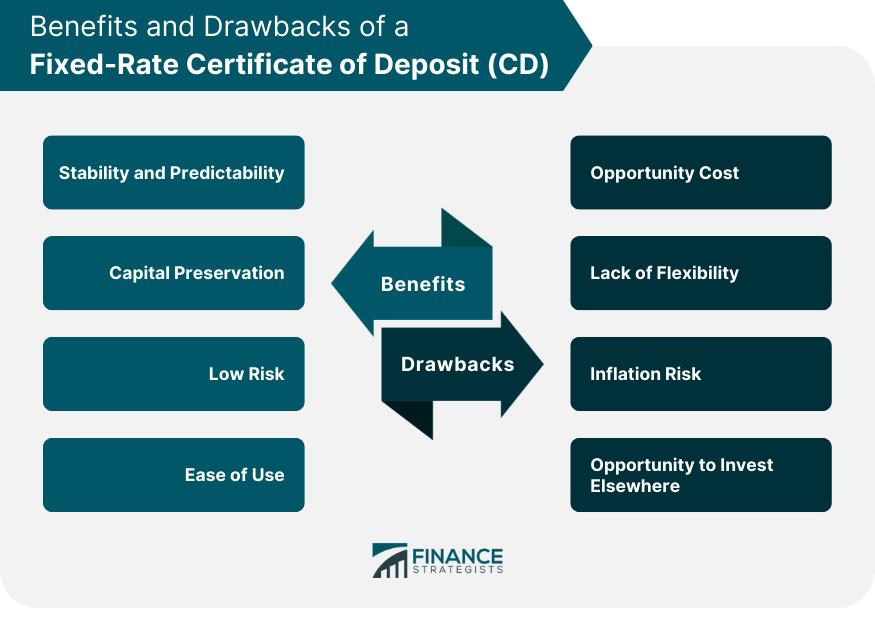
Benefits of a Fixed-Rate CD
Stability and Predictability
The interest rate remains constant throughout the entire term, so investors know exactly how much interest they will earn and can plan their finances accordingly.
This is particularly appealing to risk-averse individuals who want to avoid the volatility associated with other investments.
Capital Preservation
Fixed-Rate CDs are a conservative investment option that prioritizes capital preservation. Since the principal amount is not subject to market fluctuations, the risk of losing money is low, making it a relatively safe place to park savings.
Low Risk
Compared to riskier investments such as stocks or bonds, Fixed-Rate CDs carry a lower level of risk.
As long as the bank or credit union is insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) in the United States or a similar agency in other countries, the principal amount (up to the insured limit) is protected even if the institution faces financial difficulties.
Ease of Use
Fixed-Rate CDs are straightforward and easy to understand. There are no complex investment strategies to navigate, making them accessible to a wide range of investors, including those with limited investment knowledge.
Drawbacks of a Fixed-Rate CD
Opportunity Cost
One of the significant drawbacks of a Fixed-Rate CD is the possibility of missing out on higher returns if market interest rates rise during the term of the CD.
Since the interest rate is fixed at the time of investment, the investor may find themselves locked into a lower rate than what is currently available in the market.
Lack of Flexibility
Fixed-Rate CDs are designed for a specific term, often ranging from a few months to several years. During this time, withdrawing the funds before the CD matures can result in penalties or a loss of interest.
This lack of flexibility may be a concern for investors who need access to their money in case of unexpected expenses or emergencies.
Inflation Risk
Fixed-Rate CDs are not immune to inflation risk. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money over time, and if the CD's interest rate does not keep up with inflation, the real value of the returns may decrease. This is particularly relevant in periods of high inflation.
Opportunity to Invest Elsewhere
By committing funds to a Fixed-Rate CD, investors may miss opportunities to invest in other potentially higher-yielding assets that could offer better returns over the long term.
Variable-Rate CD
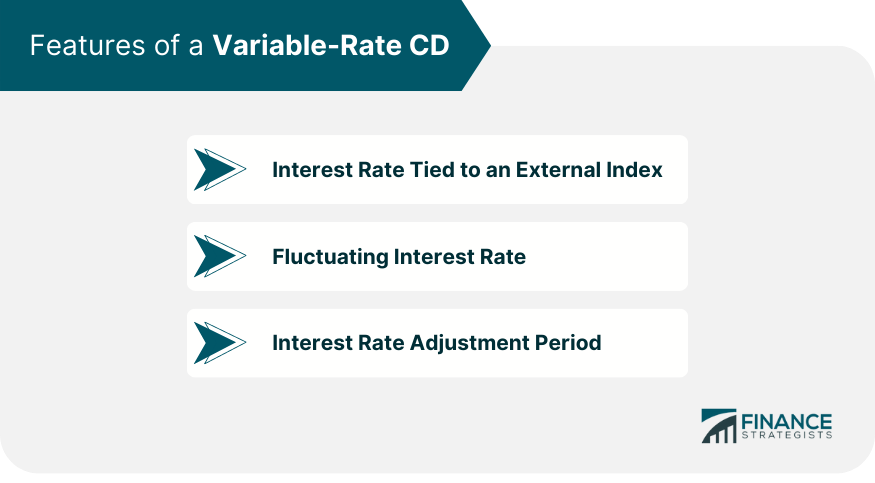
Features of a Variable-Rate CD
Interest Rate Tied to an External Index
The interest rate of a Variable-Rate CD is linked to a specific external benchmark, such as the Treasury bill rate, the prime rate, or the London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR).
The interest rate is not determined by the bank or credit union offering the CD but instead moves in accordance with the changes in the chosen benchmark.
Fluctuating Interest Rate
Since the interest rate is tied to an external index, it can vary throughout the term of the CD. As the benchmark rate changes, the interest rate on the Variable-Rate CD will adjust accordingly. This means that the returns on the investment can go up or down over time.
Interest Rate Adjustment Period
Variable-Rate CDs typically have a specific period at which the interest rate is adjusted. This period may vary depending on the CD's terms, ranging from monthly adjustments to annual adjustments.
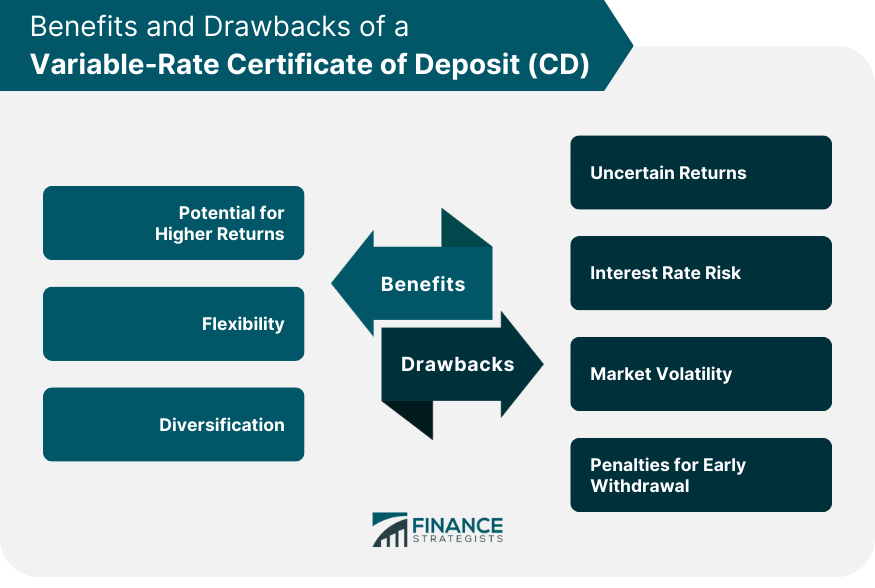
Benefits of a Variable-Rate CD
Potential for Higher Returns
One of the primary advantages of Variable-Rate CDs is the potential for increased returns if market interest rates rise.
As the interest rate is tied to an external benchmark, when the benchmark rate increases, the interest rate on the CD also rises, resulting in higher returns for investors.
This dynamic allows investors to take advantage of favorable interest rate environments and potentially earn more than they would with a Fixed-Rate CD.
Flexibility
Variable-Rate CDs often come with shorter terms compared to Fixed-Rate CDs, which may provide investors with more frequent opportunities to reassess their investment strategy.
If market conditions change, investors can take advantage of rising interest rates by rolling over or reinvesting in another Variable-Rate CD with a higher rate.
Diversification
Including Variable-Rate CDs in a diversified investment portfolio can be beneficial. These CDs offer a hedge against potential losses that could occur in other investments when interest rates rise.
By diversifying their holdings, investors can spread their risk and balance potential fluctuations in the value of their assets.
Drawbacks of a Variable-Rate CD
Uncertain Returns
The primary drawback of Variable-Rate CDs is that returns are not guaranteed. Since the interest rate is linked to an external benchmark, the returns can fluctuate over time.
If the benchmark rate falls, the interest rate on the CD will also decrease, leading to potentially lower returns compared to what could be obtained with a Fixed-Rate CD.
Interest Rate Risk
Variable-Rate CDs are exposed to interest rate risk, which refers to the potential for changes in interest rates to affect the value of the investment.
If interest rates fall during the CD's term, the investor may find themselves locked into a lower rate, missing out on potential higher returns that could be achieved with a Fixed-Rate CD.
Market Volatility
The uncertainty of variable returns can introduce additional market risk. If the benchmark rates fluctuate significantly, investors may experience a lack of predictability in their investment returns, which could lead to anxiety and concerns about financial planning.
Penalties for Early Withdrawal
Similar to Fixed-Rate CDs, Variable-Rate CDs may come with penalties for early withdrawal. If an investor needs to access their funds before the CD matures, they may face a penalty, potentially eroding some of their returns.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Fixed-Rate and Variable-Rate CDs
Investment Horizon: Short-Term vs Long-Term
Consider the time frame for your financial goals. If you have short-term goals, such as saving for an upcoming vacation or an emergency fund, Fixed-Rate CDs might be more suitable.
With a fixed interest rate and guaranteed return, you know exactly how much you'll earn at maturity.
On the other hand, if your goals are long-term, such as retirement planning or funding a child's education several years down the line, Variable-Rate CDs may be worth considering.
In a rising interest rate environment, Variable-Rate CDs have the potential to outperform Fixed-Rate CDs, offering the possibility of better returns over an extended period.
Market Interest Rate Forecast: Rising vs Declining Rates
Try to gauge the prevailing market interest rate environment and anticipate how it might change in the future. If you expect interest rates to rise, Variable-Rate CDs may be advantageous, as they can provide higher returns when the benchmark rates increase.
Conversely, if interest rates are expected to decline, Fixed-Rate CDs may offer better returns since they lock in a fixed interest rate at the time of purchase, shielding investors from potential rate cuts.
Financial Goals and Risk Tolerance
Capital Preservation vs Potential for Higher Returns
If your primary concern is capital preservation and you prioritize a secure, predictable return, Fixed-Rate CDs are the safer choice. They are ideal for risk-averse investors who seek a low-risk option.
Willingness to Accept Risk
If you are comfortable with some level of risk and are willing to take a chance for the possibility of higher returns, Variable-Rate CDs could be more appealing.
However, remember that the higher potential for returns comes with greater uncertainty due to fluctuating interest rates.
Diversification
Diversifying your investments can help mitigate risk and enhance overall portfolio performance. Instead of putting all your funds into either Fixed-Rate or Variable-Rate CDs, consider a balanced approach.
Allocate your funds across different investment vehicles, including stocks, bonds, and other assets, in addition to CDs. This way, you can capitalize on the advantages of each investment type while reducing exposure to their individual drawbacks.
Economic Conditions
Keep an eye on the overall economic conditions and interest rate trends. Economic indicators and central bank policies can influence interest rates.
Understanding the broader economic landscape can help you make more informed decisions regarding the timing and type of CD to invest in.

Conclusion
Fixed-Rate and Variable-Rate CDs are two distinct types of time deposits offered by banks, each with unique advantages for investors.
Fixed-Rate CDs offer a stable and predictable return with a fixed interest rate throughout the term, making them ideal for risk-averse individuals seeking guaranteed returns and capital preservation.
On the other hand, Variable-Rate CDs come with a dynamic approach, as their interest rates fluctuate based on external benchmarks like the prime rate or Treasury bill rate.
This provides the potential for higher returns during periods of rising interest rates, making them appealing to investors who believe rates will increase in the future.
When choosing between the two, investors should consider their investment horizon, market interest rate forecasts, financial goals, risk tolerance, and the broader economic conditions.
Short-term goals may benefit from the stability of Fixed-Rate CDs, while long-term goals in a rising rate environment may be better served by Variable-Rate CDs.
It's essential to understand the trade-offs between stability and potential for higher returns and to diversify investments to manage risk effectively.
Fixed-Rate vs Variable-Rate CD FAQs
The main difference is in their interest rate structure. Fixed-Rate CDs offer a constant interest rate throughout the term, while Variable-Rate CDs have an interest rate that fluctuates based on an external benchmark.
Fixed-Rate CDs offer more stability in returns since the interest rate remains unchanged. With Variable-Rate CDs, returns are subject to change based on market interest rate fluctuations.
In a rising interest rate environment, Variable-Rate CDs may yield better returns. As benchmark rates increase, the interest rate on Variable-Rate CDs also rises, potentially outperforming Fixed-Rate CDs.
Fixed-Rate CDs are better suited for conservative investors seeking capital preservation. With a fixed interest rate, they offer a secure and predictable approach to savings.
Variable-Rate CDs may be more appropriate for long-term financial goals in a rising interest rate environment. They offer the potential for higher returns over an extended period compared to Fixed-Rate CDs.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











