An Individual Retirement Account Certificate of Deposit (IRA CD) is a unique kind of certificate of deposit (CD) that's held within an individual retirement account. This financial instrument merges the tax benefits inherent in an IRA with the predictability and stability offered by a CD. This blend allows investors to benefit from the best of both worlds, making IRA CDs an attractive component in retirement planning. The primary function of an IRA CD is to provide a safe and predictable investment vehicle for retirement savings. It caters to risk-averse individuals who prefer consistent returns over potential high gains tied to riskier investments. An IRA CD assures a return on investment, thereby acting as a crucial cornerstone in a diversified retirement portfolio. It's a way for investors to have peace of mind, knowing a part of their retirement nest egg is growing safely. An IRA CD operates by having money deposited for a fixed term, usually from a few months up to several years. During this term, the money accrues interest at a predetermined fixed rate. The interest generally compounds over time, leading to considerable growth especially for long-term investments. When the term ends, the investor can choose to renew the CD or withdraw the funds, including the interest earned. While IRA CDs and traditional CDs both involve depositing money for a fixed term, the significant difference lies in their tax treatment. Traditional CDs are generally held in a regular bank account, with the interest earned taxed in the year it was earned. On the other hand, an IRA CD is nested within an IRA, allowing for tax-deferred or tax-free growth, depending on the IRA type. This feature can lead to substantial savings in the long run. A Traditional IRA CD offers tax-deferred growth, meaning you won't pay taxes on the interest earned until you begin taking distributions in retirement. Your contributions may also be tax-deductible, depending on your income and participation in employer-sponsored retirement plans. This deduction could potentially lower your current taxable income, giving you immediate tax savings. On the other hand, a Roth IRA CD functions differently. Contributions to a Roth IRA CD are made with post-tax dollars, so you pay taxes upfront. However, once you reach retirement, all future withdrawals, including earnings, are typically tax-free, provided certain conditions are met. This advantage can be a boon if you expect to be in a higher tax bracket in the future or anticipate tax rates to rise. The process of opening an IRA CD starts with selecting a financial institution. Both banks and credit unions offer IRA CDs, but their terms, conditions, and interest rates may vary. As a prudent investor, it's crucial to shop around and compare the offerings of different institutions. By doing so, you can identify an institution that best aligns with your financial goals and requirements. Furthermore, keep in mind that some institutions might offer additional benefits like relationship rewards or higher rates for larger deposits. Before committing to an IRA CD, you need to thoroughly understand its terms and conditions. This understanding includes the term length, the interest rate, the minimum deposit requirement, and early withdrawal penalties. Reading the fine print and asking questions about any unclear terms can save you from potential pitfalls in the future. Remember, fully understanding what you're agreeing to is a key component of any successful investment. One of the significant advantages of IRA CDs is the tax benefits. Traditional IRA CDs offer tax-deferred growth, while Roth IRA CDs provide tax-free growth. These tax benefits can substantially enhance your overall return on investment. By utilizing these tax advantages, you're effectively leveraging the power of compounded growth, which can significantly add to your retirement nest egg. IRA CDs offer security and predictability, another major advantage. Unlike stocks and other volatile investments, IRA CDs provide a fixed interest rate, meaning you know exactly how much you'll earn by the end of the term. This can be especially reassuring during periods of market volatility, offering a safety net of sorts for your retirement savings. Although IRA CDs offer a measure of security, they typically deliver lower returns compared to riskier, more volatile investments like stocks or mutual funds. Consequently, you might miss out on potential earnings, particularly during strong market conditions. It's crucial to balance this trade-off between risk and return when considering an IRA CD. Another downside to IRA CDs is their limited liquidity. The nature of CDs involves keeping your money deposited for the agreed term. Should you need to withdraw your funds from the IRA CD prematurely, you'll likely face an early withdrawal penalty from your bank or credit union. This penalty can eat into your investment, and if you're under the age of 59½, the IRS may levy an additional penalty. This lack of liquidity means you should carefully consider your ability to commit funds for the term of the CD. Before investing in an IRA CD, you should assess the interest rate. The interest rate will play a significant role in determining the growth of your investment. While IRA CDs are considered safe, the return on investment may not keep pace with inflation, especially in a low-interest-rate environment. Therefore, it's essential to consider the current economic climate and future interest rate projections when making your decision. You want to ensure your savings grow and don't lose purchasing power over time. Understanding the implications of early withdrawal is another crucial aspect to consider. Like traditional CDs, IRA CDs impose penalties for withdrawing your money before the term ends. In some instances, these penalties might eat into the initial deposit, negating the growth achieved. Plus, if you're under 59½, the IRS may also impose a penalty. Therefore, if you anticipate needing the invested funds before the term ends, you might want to explore other investment options with less stringent withdrawal rules. When comparing IRA CDs with 401(k) plans, several factors come into play. 401(k)s often come with employer matching contributions, which can significantly augment your retirement savings. However, 401(k)s are typically invested in a mix of stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, which can be more volatile than an IRA CD. Hence, if the safety of your principal is a priority, an IRA CD might be more appealing. However, if you're willing to tolerate some risk for potentially higher returns and the advantage of employer matching, a 401(k) could be more beneficial. Compared to standard IRAs, both Traditional and Roth, IRA CDs offer less flexibility in terms of investment options. Standard IRAs allow investment in individual stocks, bonds, ETFs, and mutual funds, giving the potential for higher returns, albeit with higher risk. If you have a longer time horizon and a higher risk tolerance, investing in a diversified portfolio through a standard IRA might yield greater returns. However, if you're averse to risk and prefer assured returns, an IRA CD might be a better fit, offering predictable growth and peace of mind. IRA CDs offer a secure and predictable retirement savings option, combining the tax benefits of IRAs with the stability of CDs. Whether you opt for a Traditional or Roth IRA CD, both provide unique tax advantages, enhancing your overall return on investment. However, potential lower returns and limited liquidity might not suit every investor's profile. The choice between an IRA CD, 401(k), or standard IRA depends on your risk tolerance, financial goals, and retirement planning strategy. As a diligent investor, understanding the working mechanism, tax implications, and potential pitfalls of IRA CDs is key. Therefore, engage with your chosen financial institution, be it a bank or credit union, to fully comprehend the terms and conditions before committing. If you're ready to explore the potential of IRA CDs, consider reaching out to your bank to discuss how these investment vehicles could enhance your retirement strategy.What Is an IRA CD?
How IRA CDs Work
Mechanism of IRA CDs
Differentiating IRA CDs From Traditional CDs
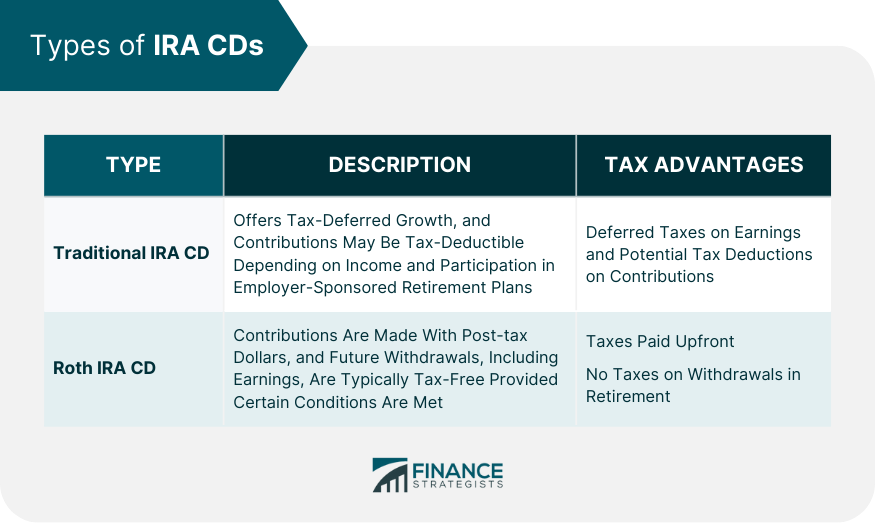
Types of IRA CDs
Traditional IRA CD
Roth IRA CD
How to Open an IRA CD
Choose a Bank or Credit Union
Understand the Terms and Conditions
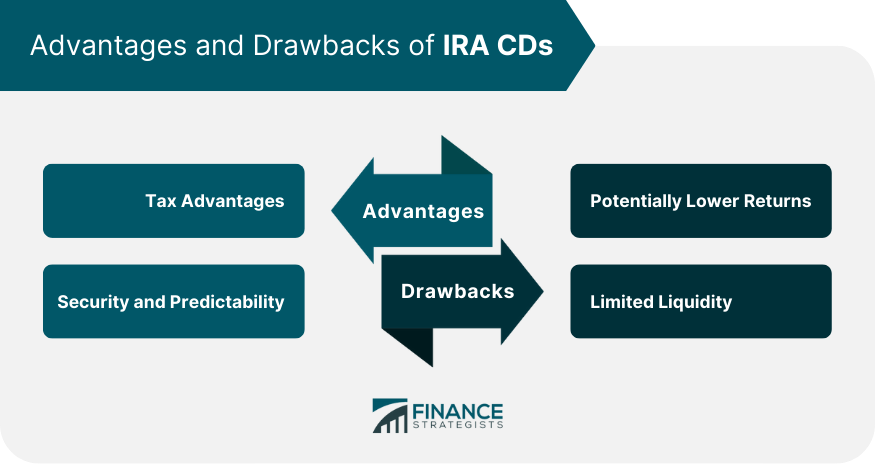
Advantages of IRA CDs
Tax Advantages
Security and Predictability
Drawbacks of IRA CDs
Potentially Lower Returns
Limited Liquidity
Considerations Before Investing in IRA CDs
Interest Rate Evaluation
Early Withdrawal Penalties
IRA CDs vs Other Retirement Investment Options
Comparison With 401(k)s
Comparison With Standard IRAs
Bottom Line
IRA CDs FAQs
An IRA CD is a type of certificate of deposit held within an individual retirement account, offering tax benefits and stable returns.
An IRA CD operates by depositing money for a fixed term during which the money earns interest at a predetermined rate.
Traditional IRA CDs offer tax-deferred growth while Roth IRA CDs offer tax-free growth, enhancing the overall return on investment.
IRA CDs typically provide lower returns compared to riskier investments and have limited liquidity due to early withdrawal penalties.
Unlike riskier investments like stocks or 401(k)s, an IRA CD offers fixed returns and principal safety, though it may yield lower returns.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











