Digital estate planning refers to the process of organizing and managing a person's digital assets and online accounts in the event of their incapacity or death. It involves identifying and documenting all of a person's digital assets, such as social media accounts, email accounts, online bank accounts, digital photos, and other digital files, as well as determining how they should be handled after the person's passing. This can involve designating beneficiaries or executors, setting up digital trusts or wills, and providing access to login credentials and other important information to designated individuals. Digital estate planning is becoming increasingly important in the digital age, as more of our lives and assets are stored and managed online.
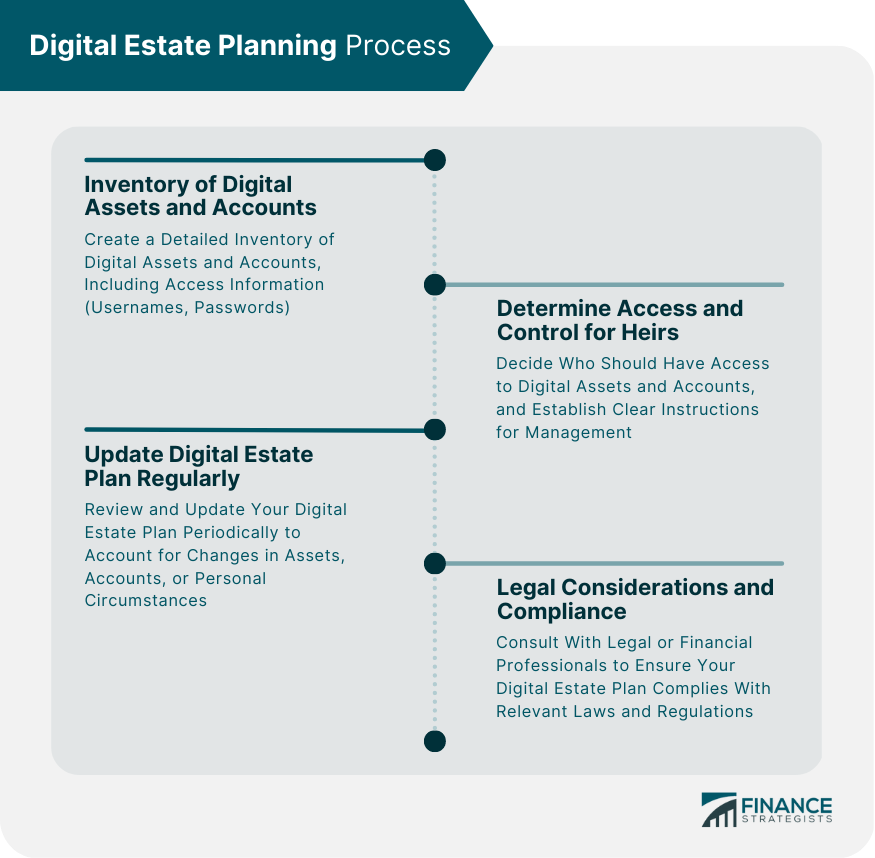
Financial accounts form a significant part of a digital estate. These accounts may include: 1. Online Banking: Online savings and checking accounts, as well as any other online financial services. 2. Investment Accounts: Brokerage accounts, retirement accounts (e.g., IRAs, 401(k)s), and other investment platforms. 3. Cryptocurrency Wallets: Digital wallets holding cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, or other altcoins. Digital assets are valuable virtual items that can have a significant impact on an individual's financial portfolio. These assets may consist of: 1. Digital Collectibles: Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) representing ownership of unique digital art, music, or other creative works. 2. Domain Names and Website Ownership: Websites, blogs, or online stores owned and managed by the individual. 3. Intellectual Property: Digital books, photographs, designs, software, or other creative works owned by the individual. An individual's online presence can also be a part of their digital estate. This includes: 1. Social Media Accounts: Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn, and other social media profiles. 2. Email Accounts: Personal and professional email accounts. 3. Online Memberships and Subscriptions: Streaming services, e-commerce platforms, and other subscription-based services. A comprehensive digital estate planning process includes the following steps: Inventory of Digital Assets and Accounts: Create a detailed inventory of all digital assets and accounts, including usernames, passwords, and other necessary access information. Keep this inventory secure and up to date. Determining Access and Control for Heirs: Decide who should have access to your digital assets and accounts in the event of your death or incapacity. Establish clear instructions for managing and distributing these assets. Regularly Updating Digital Estate Plan: Review and update your digital estate plan regularly to account for any changes in your digital assets, accounts, or personal circumstances. Legal Considerations and Compliance: Consult with a legal or financial professional to ensure that your digital estate plan complies with relevant laws and regulations. Several tools and resources can assist you in creating and maintaining a digital estate plan: Password Managers and Secure Storage: Use password managers or secure storage options to keep your access information safe and organized. Digital Estate Planning Software: Digital estate planning software can help you create, manage, and update your plan with ease. Professional Services: Attorneys, financial planners, and other professionals can provide guidance and assistance in developing a comprehensive digital estate plan. Digital estate planning come with a variety of challenges and risks, such as: Cybersecurity Threats: Hacking, identity theft, and other cybersecurity threats that can compromise your digital estate. Privacy Concerns: Sharing sensitive information about your digital assets and accounts can lead to privacy concerns. Evolving Legal and Regulatory Landscape: The legal and regulatory landscape around digital estate planning is continuously changing, making it essential to stay informed and adapt as needed. In contrast, case studies illustrating the consequences of inadequate or nonexistent digital estate planning highlight the potential risks and losses that can occur when digital assets are not properly managed. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the world of digital estate planning. Some key trends to watch for include: Integration With Traditional Estate Planning: Traditional estate planning tools and methods will increasingly integrate with digital estate planning, streamlining the overall process. Technological Advancements in Digital Estate Management: Emerging technologies, such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and biometric authentication, will play a growing role in digital estate management. Growing Awareness and Adoption of Digital Estate Planning: As awareness of the importance of digital estate planning grows, more individuals will engage in the process, leading to greater adoption and improved best practices. Digital estate planning is an essential aspect of personal finance in the modern world. By understanding the components of a digital estate, following a comprehensive planning process, leveraging available tools and resources, and staying informed about challenges and risks, individuals can create and maintain a secure and effective digital estate plan. This will ensure that their digital assets and accounts are managed according to their wishes, providing peace of mind and financial security for themselves and their loved ones.What Is Digital Estate Planning?
Components of a Digital Estate
Financial Accounts
Digital Assets
Online Identities
Digital Estate Planning Process
Tools and Resources for Digital Estate Planning
Challenges and Risks in Digital Estate Planning
Consequences of Inadequate or No Digital Estate Planning
Future of Digital Estate Planning
The Bottom Line
Digital Estate Planning FAQs
Digital estate planning is the process of organizing, managing, and transferring your digital assets and accounts to your beneficiaries in the event of your death or incapacity. It is important because it ensures the proper handling of your digital assets, prevents unauthorized access, and protects your privacy and financial interests.
To start the digital estate planning process, begin by creating a detailed inventory of all your digital assets and accounts, including usernames, passwords, and other access information. Then, determine who should have access to your digital assets in case of your death or incapacity and establish clear instructions for managing and distributing these assets. Consult with a legal or financial professional to ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
Tools and resources that can assist with digital estate planning include password managers and secure storage solutions for organizing and protecting access information, digital estate planning software for creating and managing your plan, and professional services such as attorneys and financial planners for guidance and assistance.
When creating a digital estate plan, it is important to consider challenges and risks such as cybersecurity threats, privacy concerns, and the evolving legal and regulatory landscape surrounding digital assets. Staying informed and adapting your plan as needed will help mitigate these risks.
To ensure your digital estate plan remains up to date and effective, regularly review and update your inventory of digital assets and accounts, revise access and control instructions as needed, and stay informed about changes in relevant laws and regulations. Consulting with professionals and leveraging the latest tools and resources can also help you maintain an effective digital estate plan.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











