Elder mediation is a process of conflict resolution that focuses on the unique issues and concerns of older adults and their families. It is a voluntary process that involves the intervention of a neutral third party (the mediator) to facilitate communication, negotiation, and problem-solving. The goal of elder mediation is to help older adults and their families find practical and mutually acceptable solutions to their disputes, emphasizing maintaining or improving their relationships. As the baby boomer generation reaches retirement age and beyond, the number of older adults is increasing rapidly. According to the United Nations, the global population of older adults (age 60 and over) is expected to double by 2050, reaching 2.1 billion people. This demographic shift has important implications for families, as older adults may require assistance and support from their adult children or other family members. However, family relationships can become strained as older adults face health problems, financial challenges, and other issues associated with aging. Family members may have different ideas about how to address these challenges, leading to disagreements, misunderstandings, and even conflict. Family dynamics can be complex, and conflicts may arise for a variety of reasons. For example, siblings may have different opinions about how to care for an aging parent, leading to arguments over issues such as living arrangements, medical treatment, and financial support. Adult children may also disagree about inheritance and other legal issues, which can lead to long-standing disputes that damage family relationships. Moreover, family dynamics may be further complicated by factors such as cultural differences, power imbalances, and past history of conflict. These factors can make it difficult for families to resolve their disputes on their own, leading to the need for an external mediator. Family conflict can have serious consequences for older adults, including increased stress, reduced quality of life, and negative health outcomes. Conflict can also have financial implications, such as legal fees and the costs associated with caring for an aging parent. In addition, unresolved conflict can lead to long-term damage to family relationships, which can be particularly harmful to older adults who may rely on their family members for support and care. Therefore, addressing conflict promptly and effectively is essential for promoting the well-being of older adults and their families. Before the mediation session, several steps are typically taken to prepare for the process. The first step is to select a mediator with the appropriate training and experience in elder mediation. The mediator should be neutral, impartial, and have no conflict of interest with any of the parties involved. The mediator should also thoroughly understand elder issues, family dynamics, and conflict resolution strategies. Once a mediator has been selected, the parties involved in the conflict must agree to participate in the mediation process. The mediator will then schedule a time and place for the mediation session. Before the mediation session, the mediator may ask the parties to provide information about the issues they wish to address and any documents or other materials that may be relevant to the dispute. The mediator may also provide the parties with information about the mediation process, including its purpose, benefits, and expectations. The mediation session typically consists of the following stages: At the beginning of the mediation session, the mediator will introduce the parties and explain the purpose of the mediation. The mediator will also explain the ground rules for the mediation, such as confidentiality and the need to treat each other with respect and civility. The mediator will then ask each party to describe their perspective on the issues at hand. The mediator may ask questions to clarify the issues and ensure that each party understands the other’s perspective. Once the issues have been identified, the parties will be asked to brainstorm potential solutions. The mediator will encourage creativity and help the parties to think outside the box. Once the parties have generated a list of potential solutions, they will be asked to evaluate each option and decide which ones are feasible and mutually acceptable. The mediator will facilitate the negotiation process and help the parties to reach an agreement that meets their needs and interests. After the mediation session, the mediator will prepare a written agreement that outlines the terms of the agreement. The parties will be asked to review and sign the agreement, indicating their commitment to abide by its terms. The mediator may also follow up with the parties after the mediation session to ensure that the agreement is being implemented and to address any issues that may arise. Elder mediation is generally less expensive than litigation or other forms of dispute resolution. This is because elder mediation is a voluntary process typically resolved in a single or a few sessions. In contrast, litigation can be a lengthy and expensive process that can take months or even years to resolve. Elder mediation is a confidential process, which means that the discussions that take place during the mediation session are private and cannot be disclosed to anyone outside of the mediation process. This can help protect the parties’ privacy and prevent sensitive information from being publicly disclosed. Elder mediation is focused on finding mutually acceptable solutions that can help to preserve or improve family relationships. Unlike litigation or other forms of dispute resolution, which can be adversarial and damage relationships, elder mediation promotes communication and understanding between the parties. Elder mediation can help empower older adults by giving them a voice in decision-making. Older adults may feel that their opinions and preferences are not being heard or respected by their family members. Elder mediation can provide a safe and supportive environment where older adults can express their concerns and preferences and be heard. Elder mediators must have the appropriate training and experience to handle the unique issues and concerns of older adults and their families. They must be knowledgeable about elder issues, family dynamics, and conflict resolution strategies. They must also be committed to upholding ethical standards of conduct and maintaining their professional integrity. Elder mediators must be neutral and impartial, meaning that they must not take sides or advocate for any particular outcome. They must be committed to helping the parties reach a mutually acceptable solution that meets their needs and interests. Elder mediators must obtain informed consent from the parties involved in the mediation process. This means that the parties must understand the purpose and nature of the mediation process and their rights and responsibilities. Elder mediators must also maintain confidentiality and ensure that the discussions that take place during the mediation process are private and confidential. Elder mediators must be sensitive to the cultural differences and diversity of the parties involved in the mediation process. They must respect the values and beliefs of each party and ensure that the mediation process is conducted in a respectful and inclusive manner. Elder mediation is an essential tool for resolving family conflict and promoting the well-being of older adults and their families. The elder mediation process can help address the complex issues and challenges that arise as older adults age and require assistance and support from their family members. By providing a safe and supportive environment for communication, negotiation, and problem-solving, elder mediation can help to preserve or improve family relationships, reduce stress, and promote the well-being of older adults. If you or a loved one is facing a family conflict related to aging, it may be time to seek the help of an estate planning lawyer. An estate planning lawyer can help you to navigate the legal and financial issues that may arise as you or your loved one age and can provide guidance and support as you plan for the future. Contact an estate planning lawyer today to learn more about how they can help you and your family.What Is Elder Mediation?
Need for Elder Mediation
Aging Population and Family Conflict
Complexities of Family Dynamics
Importance of Addressing Conflict
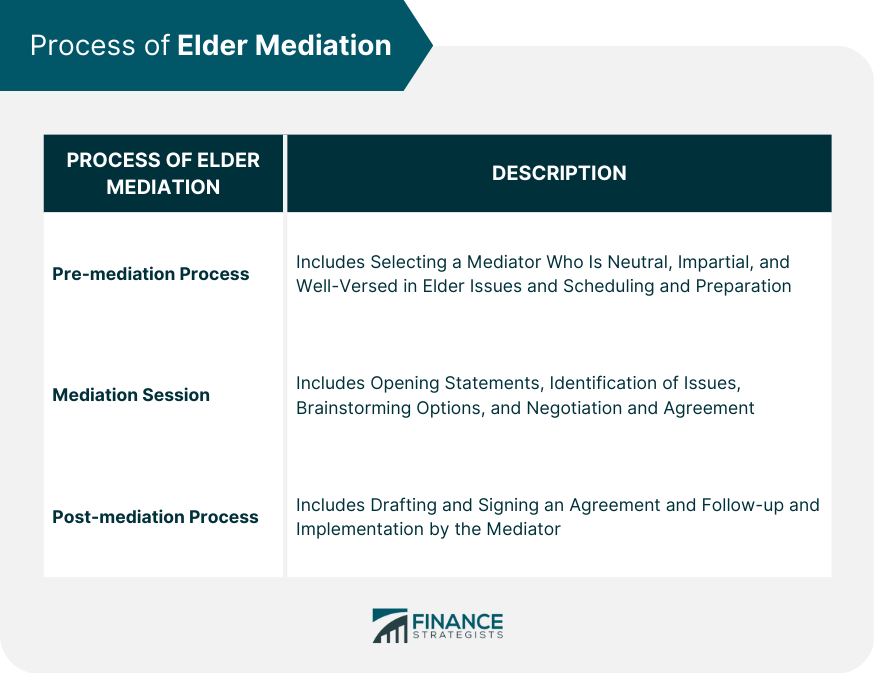
Process of Elder Mediation
Pre-mediation Process
Selecting a Mediator
Scheduling and Preparation
Mediation Session
Opening Statements
Identification of Issues
Brainstorming Options
Negotiation and Agreement
Post-mediation Process
Benefits of Elder Mediation
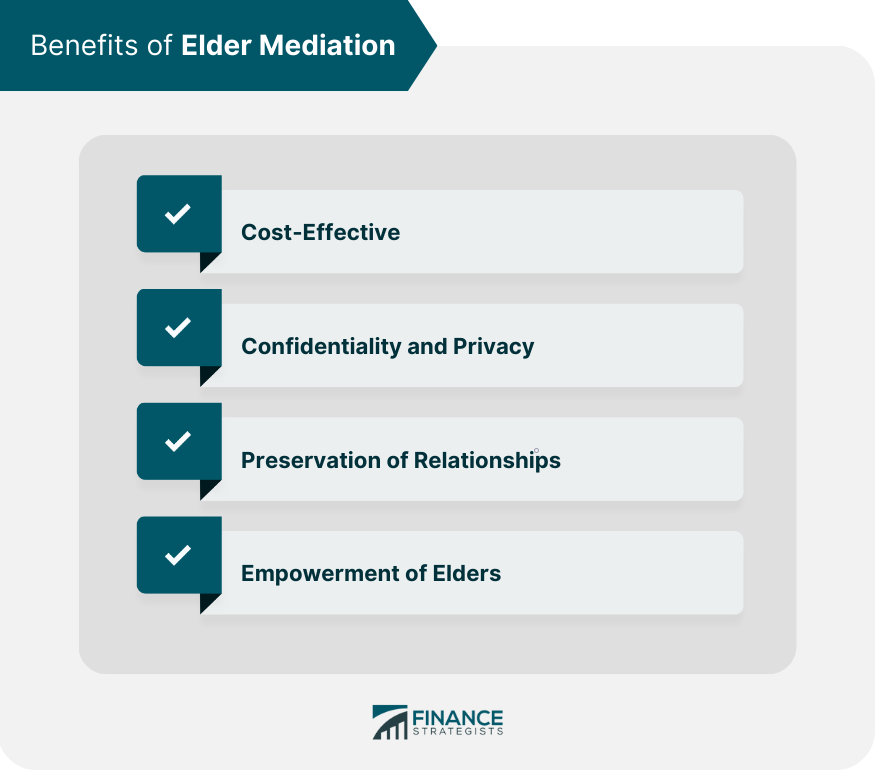
Cost-Effective
Confidentiality and Privacy
Preservation of Relationships
Empowerment of Elders
Ethical Considerations in Elder Mediation
Competence and Professionalism
Neutrality and Impartiality
Informed Consent and Confidentiality
Cultural Sensitivity and Diversity
Final Thoughts
Elder Mediation FAQs
Elder mediation is a voluntary process of conflict resolution that involves the intervention of a neutral third party (the mediator) to facilitate communication, negotiation, and problem-solving among older adults and their families.
Elder mediation is important because as older adults age and require assistance and support from their family members, family relationships can become strained, leading to conflict that can have serious consequences for the well-being of older adults and their families.
Elder mediation typically involves several stages, including the pre-mediation process (selecting a mediator and scheduling and preparing for the mediation session), the mediation session (opening statements, identification of issues, brainstorming options, and negotiation and agreement), and the post-mediation process (drafting an agreement and follow-up and implementation).
The benefits of elder mediation include cost-effectiveness, confidentiality and privacy, preservation of relationships, and empowerment of older adults.
Ethical considerations in elder mediation include competence and professionalism, neutrality and impartiality, informed consent and confidentiality, and cultural sensitivity and diversity. Elder mediators must be committed to upholding ethical standards of conduct and maintaining their professional integrity.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











