Estate freeze techniques are strategies used by individuals and business owners to transfer assets to the next generation while minimizing tax liabilities. These techniques allow the current owner to lock in the value of their assets at the current Fair Market Value (FMV) and avoid further increases in capital gains tax. Fair Market Value (FMV) is the price at which a property or asset would change hands between a willing buyer and a willing seller in an arm's length transaction. This concept is crucial in estate freeze techniques, as it is used to determine the value of assets being transferred. Capital gains tax is a tax levied on the profit made from selling an asset, such as real estate, stocks, or bonds. An estate freeze aims to minimize this tax burden on the future generation. LCGE is a tax provision that allows individuals to shelter a certain amount of capital gains from tax during their lifetime. This exemption can be used in conjunction with estate freeze techniques to further reduce tax liabilities. Attribution rules are tax provisions that prevent income splitting among family members. These rules can impact the effectiveness of certain estate freeze techniques, making it essential to consider them during the planning process. Section 85 rollover is a tax-deferral mechanism that allows individuals to transfer assets to a corporation in exchange for shares of equal value without triggering immediate capital gains tax. The tax implications of a Section 85 rollover are deferred until the shares are eventually sold or deemed disposed of, allowing for tax savings and better cash flow management. Section 85 rollovers offer tax deferral benefits but may require a more complex corporate structure and limit the use of LCGE. Family trusts are legal entities that can hold assets on behalf of beneficiaries. There are two main types: discretionary trusts and testamentary trusts. Family trusts allow income splitting among family members and can defer capital gains tax through the use of estate freeze techniques. Family trusts offer flexibility in asset management and tax planning, but they require ongoing administration and may be subject to attribution rules. A holding company is a corporation that owns shares in other companies. In an estate freeze, assets can be transferred to a holding company, and new shares issued to the next generation. Transferring assets to a holding company can defer capital gains tax and allow for income splitting among family members. Holding companies provide tax benefits and asset protection, but they may require more complex corporate structures and limit the use of LCGE. Life insurance products, such as universal life or whole life policies, can be used in estate freezes to provide tax-free death benefits to beneficiaries. Life insurance proceeds can be used to pay capital gains tax upon the death of the policyholder, effectively providing a tax-free estate freeze. Life insurance-based estate freezes offer tax benefits and simplicity, but they may require significant upfront premiums and ongoing payments. The size of the estate plays a significant role in determining the most appropriate estate freeze technique. Larger estates may require more complex strategies, such as holding companies or family trusts, to minimize tax liabilities effectively. The number of beneficiaries and their ages can impact the choice of estate freeze techniques. For example, a family trust may be more suitable for families with multiple beneficiaries, while life insurance-based strategies might work better for smaller families. Family dynamics and relationships should be considered when choosing an estate freeze technique, as some strategies may require ongoing collaboration and communication among family members. Different estate freeze techniques have varying tax implications. It is essential to understand the potential tax consequences of each strategy to maximize tax savings and minimize liabilities. Estate freeze techniques should align with the overall business succession plan. This ensures a smooth transition of ownership and management to the next generation, while also minimizing tax liabilities. Some estate freeze techniques may require significant upfront investments or ongoing payments, which can impact liquidity and cash flow. It is essential to consider the financial implications of each strategy to ensure it aligns with the current owner's financial goals and objectives. Financial planners, tax advisors, and estate lawyers play crucial roles in estate freeze planning. They provide expert guidance on tax laws, estate planning strategies, and legal requirements to ensure the chosen technique is implemented effectively. A collaborative approach involving all relevant professionals is essential to ensure a comprehensive estate freeze plan. This approach helps identify potential challenges and risks, as well as opportunities for tax savings and wealth preservation. Tax laws and regulations are subject to change, which can impact the effectiveness of estate freeze techniques. Regular reviews and updates to estate freeze plans are necessary to adapt to changing tax environments. Estate freezes can sometimes lead to disputes among family members. Proper communication, collaboration, and clear expectations can help minimize conflicts and ensure a successful estate freeze. Tax authorities may challenge the valuation of assets used in an estate freeze, leading to potential tax liabilities. Working with qualified professionals can help ensure accurate valuations and minimize the risk of disputes. Economic and market fluctuations can impact the value of assets used in estate freezes. Regular reviews and updates to estate freeze plans are necessary to adapt to changing market conditions. Estate freeze techniques are essential tools in estate and tax planning, offering benefits such as wealth preservation, tax minimization, and smooth succession. By understanding the different estate freeze techniques and considering factors such as estate size, family dynamics, and tax implications, individuals can choose the most appropriate technique for their specific situation. Working with qualified professionals and adopting a collaborative approach can help ensure successful estate freeze planning and long-term benefits for family and business succession. Regular reviews and updates to estate freeze plans are necessary to adapt to changing tax laws, regulations, and market conditions.Definition of Estate Freeze Techniques
Basic Concepts in Estate Freeze
Fair Market Value (FMV)
Capital Gains Tax
Lifetime Capital Gains Exemption (LCGE)
Attribution Rules
Types of Estate Freeze Techniques
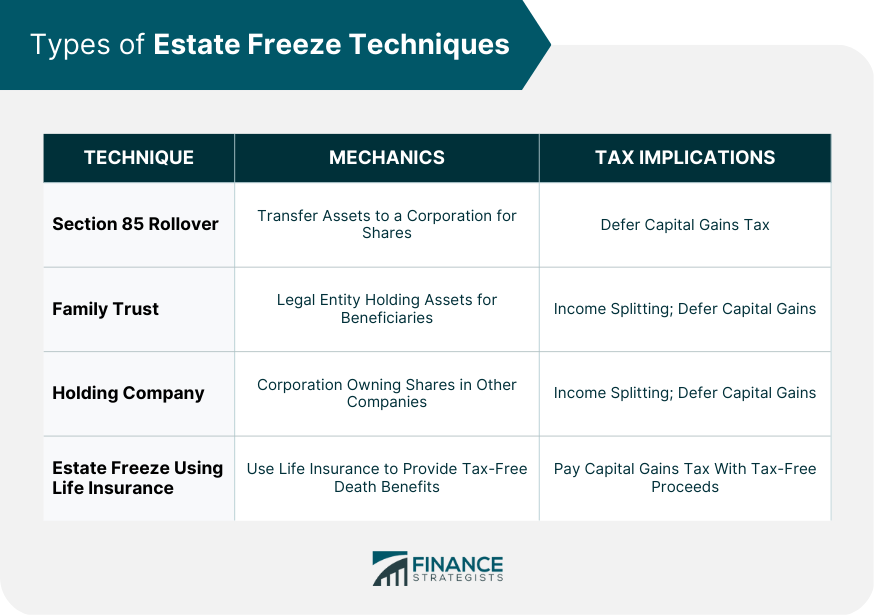
Section 85 Rollover
Family Trust
Holding Company
Estate Freeze Using Life Insurance
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Estate Freeze Technique
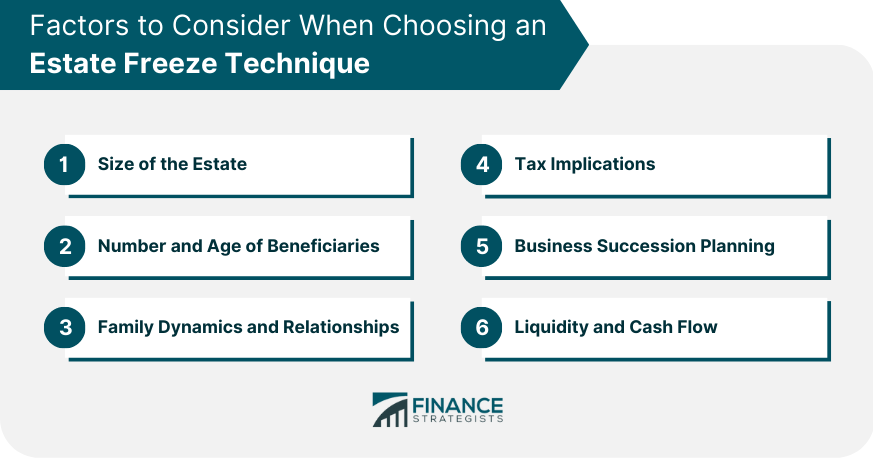
Size of the Estate
Number and Age of Beneficiaries
Family Dynamics and Relationships
Tax Implications
Business Succession Planning
Liquidity and Cash Flow
Professional Assistance in Estate Freeze Planning
Roles of Financial Planners, Tax Advisors, and Estate Lawyers
Importance of a Collaborative Approach
Potential Challenges and Risks of Estate Freezes
Changes in Tax Laws and Regulations
Disputes Among Family Members
Valuation Disputes With Tax Authorities
Economic and Market Fluctuations
Conclusion
Estate Freeze Techniques FAQs
Estate freeze techniques are strategies used to transfer assets to the next generation while minimizing tax liabilities. They allow the current owner to lock in the value of their assets at the current fair market value (FMV) and avoid further increases in capital gains tax. Estate freeze techniques are important in estate planning as they help preserve wealth, ensure smooth succession, and provide tax benefits.
The article discusses four main types of estate freeze techniques: Section 85 rollover, family trusts, holding companies, and estate freezes using life insurance. Each technique has its own mechanics, tax implications, and advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to understand and choose the most appropriate technique based on individual needs and circumstances.
Estate freeze techniques help reduce tax liabilities by locking in the value of assets at the current FMV, preventing further increases in capital gains tax. Additionally, certain techniques, such as family trusts and holding companies, can allow for income splitting among family members, further reducing overall tax burdens.
When choosing an estate freeze technique, it is essential to consider factors such as the size of the estate, number and age of beneficiaries, family dynamics and relationships, tax implications, business succession planning, and liquidity and cash flow. These factors can help determine the most suitable technique for a specific situation.
Financial planners, tax advisors, and estate lawyers play crucial roles in estate freeze planning. They provide expert guidance on tax laws, estate planning strategies, and legal requirements to ensure the chosen technique is implemented effectively. A collaborative approach involving all relevant professionals is essential to ensure a comprehensive estate freeze plan, identify potential challenges and risks, and maximize tax savings and wealth preservation.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











