Trust litigation refers to the legal process that arises when disputes or issues occur surrounding a trust. These disputes can involve beneficiaries, trustees, or other interested parties. Trust litigation is essential for resolving disputes and ensuring that the intent of the trust creator (settlor) is fulfilled and the rights of beneficiaries are protected. Trust litigation is the legal process involving disputes, contests, or issues surrounding the administration or terms of a trust. This can involve various aspects of the trust, including management, distribution of assets, or the validity of the trust itself. Trust litigation is a specialized area of law, often requiring the assistance of experienced attorneys to navigate the complex legal issues that can arise. There are several reasons trust litigation may occur, including breach of fiduciary duty by the trustee, contesting the validity of the trust, removal or replacement of trustees, reformation or modification of the trust, and disputes over the distribution of assets. Trust litigation is essential for resolving these disputes and ensuring that the trust operates as intended by the settlor. Trust litigation plays a crucial role in resolving disputes that can arise in trust administration. It allows for the enforcement of the trust's terms, the protection of beneficiaries' rights, and the resolution of conflicts between trustees and beneficiaries. Additionally, trust litigation can result in the removal of a trustee who has breached their fiduciary duties or the modification of a trust to better align with the settlor's intent. Understanding the different types of trusts is essential for navigating trust litigation, as the type of trust involved can impact the legal issues and remedies available. Revocable trusts, also known as living trusts, are trusts that can be altered, amended, or revoked by the settlor during their lifetime. These trusts are commonly used for estate planning purposes to avoid probate and provide for the management of assets during the settlor's incapacity. Revocable trusts become irrevocable upon the death of the settlor. Irrevocable trusts are trusts that cannot be changed or terminated by the settlor after they have been created. These trusts provide a higher level of asset protection and tax benefits compared to revocable trusts. However, due to their inflexibility, disputes can arise over the administration or terms of an irrevocable trust, leading to trust litigation. Charitable trusts are created for the purpose of benefiting a charitable organization or promoting a charitable purpose. These trusts receive favorable tax treatment and can provide donors with income, estate, and gift tax benefits. Disputes in charitable trusts can involve issues with the trust's purpose, administration, or the charitable beneficiaries. Special needs trusts are designed to provide financial support for individuals with disabilities without jeopardizing their eligibility for government assistance programs. These trusts must be carefully crafted and administered to ensure they achieve their intended purpose. Trust litigation involving special needs trusts can involve disputes over the administration, management, or distribution of trust assets. In addition to the trusts mentioned above, there are various other trust structures used for specific purposes, such as asset protection trusts, spendthrift trusts, and generation-skipping trusts. Each trust structure has unique features and potential issues that can lead to trust litigation. Understanding the specific type of trust involved is crucial for effectively addressing and resolving trust disputes. There are several reasons why trust litigation may occur, including breaches of fiduciary duty, trust contests, trustee removal or replacement, trust reformation or modification, and disputes over asset distribution. Breach of fiduciary duty occurs when a trustee fails to act in the best interests of the trust beneficiaries. Some common breaches of fiduciary duty include the failure to properly manage trust assets, self-dealing or conflicts of interest, and failure to provide proper accountings or information to beneficiaries. A trustee has a legal duty to properly manage and invest the trust assets to preserve and grow the trust's value. If a trustee fails to do so, they may be held liable for breach of fiduciary duty, leading to trust litigation. Self-dealing occurs when a trustee engages in transactions that benefit themselves rather than the trust beneficiaries. Conflicts of interest arise when a trustee's personal interests conflict with their fiduciary duties. Both self-dealing and conflicts of interest can lead to trust litigation. Trustees are required to provide regular accountings and information to trust beneficiaries. If a trustee fails to fulfill this obligation, beneficiaries may initiate trust litigation to enforce their rights. Trust contests involve challenges to the validity of a trust, often based on claims such as lack of capacity, undue influence, fraud or duress, and ambiguity in trust documents. Lack of capacity refers to a situation where the settlor did not have the mental capacity to create a valid trust. Trust litigation can arise when beneficiaries or other interested parties contest the trust's validity based on the settlor's alleged lack of capacity. Undue influence occurs when a person exerts excessive pressure on the settlor to create a trust that benefits the influencer. Trust litigation may arise when beneficiaries claim that the trust is invalid due to undue influence. Fraud involves the intentional deception of the settlor to create a trust, while duress involves coercion or threats against the settlor. Both fraud and duress can lead to trust litigation if beneficiaries or other interested parties challenge the trust's validity. Ambiguity in trust documents can create confusion and disputes among beneficiaries and trustees. Trust litigation may arise to clarify the settlor's intentions and ensure the proper administration of the trust. Trust litigation may involve the removal or replacement of a trustee who has breached their fiduciary duties, mismanaged the trust, or is otherwise unsuitable to administer the trust. Beneficiaries may petition the court to remove and replace a trustee. Trust reformation or modification involves changing the terms of a trust to correct errors, clarify the settlor's intent, or address changed circumstances. Trust litigation can arise when beneficiaries or trustees seek court approval to reform or modify a trust. Disputes over the distribution of trust assets can lead to trust litigation when beneficiaries disagree on the interpretation of the trust terms or claim that the trustee is improperly distributing assets. The legal process of trust litigation involves several stages, including filing a petition or complaint, the discovery process, alternative dispute resolution, trial, and appeals. Trust litigation begins when an interested party files a petition or complaint with the court, outlining the issues in dispute and requesting relief, such as the removal of a trustee or the modification of a trust. The discovery process is a crucial phase in trust litigation where parties gather information and evidence to support their claims. This process includes document requests, interrogatories, and depositions. Document requests involve the exchange of relevant documents between parties, such as trust documents, financial records, and correspondence. These documents can provide important evidence for each party's case. Interrogatories are written questions that one party submits to another, requiring them to provide written answers under oath. These questions help clarify issues, gather information, and identify potential witnesses. Depositions involve the oral questioning of witnesses under oath, typically conducted by attorneys. Depositions provide an opportunity for parties to gather additional information, evaluate the credibility of witnesses, and gather evidence for trial. Alternative dispute resolution (ADR) methods, such as mediation and arbitration, can provide a more efficient and cost-effective means of resolving trust disputes compared to traditional litigation. Mediation is a voluntary, non-binding process where a neutral third-party mediator helps parties negotiate a settlement. Mediation can be a less adversarial and more collaborative approach to resolving trust disputes. Arbitration is a more formal ADR method where a neutral arbitrator hears each party's case and renders a binding decision. Arbitration can provide a faster and more private resolution to trust disputes than a court trial. If trust disputes cannot be resolved through ADR, the case may proceed to trial, where a judge or jury will hear evidence and determine the outcome. Trials can be lengthy and costly, but they provide an opportunity for parties to present their case and seek a judicial resolution. Following a trial, either party may appeal the court's decision if they believe legal errors were made. Appeals involve a higher court reviewing the trial court's decision for errors and, if necessary, modifying the judgment or ordering a new trial. Several key players are involved in trust litigation, including the trustee, beneficiaries, settlor or grantor, trust litigation attorneys, and expert witnesses. The trustee is responsible for managing the trust and acting in the best interests of the beneficiaries. In trust litigation, the trustee may be a defendant if they are accused of breaching their fiduciary duties or a plaintiff if they are seeking guidance from the court on trust administration. Beneficiaries are the individuals or entities who are entitled to receive benefits from the trust. They may initiate trust litigation to enforce their rights, challenge the validity of the trust, or seek the removal or replacement of a trustee. The settlor or grantor is the person who creates the trust. Although they may not be directly involved in trust litigation, their intentions and actions can be central to resolving disputes over trust validity or interpretation. Trust litigation attorneys are legal professionals who specialize in representing parties involved in trust disputes. They provide guidance, advice, and representation throughout the trust litigation process. Expert witnesses are professionals with specialized knowledge in areas relevant to trust litigation, such as trust administration, investments, or tax law. They provide testimony and opinions to help the court understand complex issues and make informed decisions. Preventing trust litigation involves proper trust drafting and execution, regular communication with beneficiaries, transparency in trust management, and the use of mediation and alternative dispute resolution options. A well-drafted trust document can help prevent ambiguities and disputes among beneficiaries and trustees. Engaging an experienced estate planning attorney to draft and execute the trust can minimize the risk of future litigation. Maintaining open lines of communication with beneficiaries can help prevent misunderstandings and disputes. By keeping beneficiaries informed about trust administration and addressing their concerns, trustees can foster a positive relationship and reduce the likelihood of litigation. Trustees should be transparent in their management of the trust, providing regular accountings and updates to beneficiaries. Transparency can help build trust among beneficiaries and reduce the chances of disputes arising from suspicions of mismanagement or breaches of fiduciary duty. Encouraging the use of mediation and alternative dispute resolution options can help resolve trust disputes more amicably and efficiently than traditional litigation. Incorporating ADR provisions in the trust document or seeking ADR when disputes arise can help prevent costly and time-consuming litigation. Understanding trust litigation is essential for settlors, trustees, and beneficiaries, as it plays a critical role in protecting beneficiaries' rights and trust assets. By learning about the common causes of trust litigation, the legal process, and the key players involved, parties can better navigate and resolve trust disputes. Implementing strategies for preventing trust litigation, such as proper trust drafting, open communication, and the use of alternative dispute resolution methods, can help maintain the integrity of the trust and avoid unnecessary conflict. Having a comprehensive understanding of trust litigation allows all parties involved in a trust to anticipate potential disputes, take proactive measures to avoid conflicts, and effectively address issues when they arise. This understanding can lead to more harmonious trust administration and better outcomes for beneficiaries. Trust litigation serves as an essential tool for ensuring that trustees fulfill their fiduciary duties, beneficiaries' rights are protected, and trust assets are managed and distributed according to the settlor's intentions. By holding trustees accountable and resolving disputes, trust litigation helps maintain the integrity of the trust and preserve its intended purpose. Preventing and resolving trust disputes involves a combination of proactive measures and effective dispute resolution techniques. Proper trust drafting, open communication, transparency in trust management, and the use of alternative dispute resolution methods can all contribute to preventing disputes and fostering a more collaborative approach to trust administration. When disputes do arise, understanding the legal process and engaging experienced trust litigation attorneys can help parties navigate the complexities of trust litigation and achieve a fair resolution. In conclusion, trust litigation is an integral aspect of trust administration, providing a means to resolve disputes, protect beneficiaries' rights, and ensure the proper management of trust assets. By understanding the causes, processes, and key players involved in trust litigation, parties can better navigate and address trust disputes. Implementing strategies to prevent trust litigation and seeking alternative dispute resolution methods can help maintain the integrity of the trust and avoid unnecessary conflict. Taking proactive steps to protect your assets and secure your loved ones' financial future is essential. The best way to achieve this is by seeking the guidance and expertise of an experienced estate planning lawyer. An estate planning lawyer can help you draft a comprehensive estate plan, including creating trusts that meet your unique needs and goals. They can also provide ongoing legal support to help you navigate changes in your life and the law, ensuring your estate plan remains up-to-date and effective.What Is Trust Litigation?
Types of Trusts
Revocable Trusts
Irrevocable Trusts
Charitable Trusts
Special Needs Trusts
Other Trust Structures
Common Causes of Trust Litigation
Breach of Fiduciary Duty
Failure to Properly Manage Trust Assets
Self-Dealing or Conflicts of Interest
Failure to Provide Proper Accountings or Information to Beneficiaries
Trust Contests
Lack of Capacity
Undue Influence
Fraud or Duress
Ambiguity in Trust Documents
Trustee Removal or Replacement
Trust Reformation or Modification
Disputes Over Distribution of Assets

Legal Process of Trust Litigation
Filing a Petition or Complaint
Discovery Process
Document Requests
Interrogatories
Depositions
Alternative Dispute Resolution
Mediation
Arbitration
Trial
Appeals
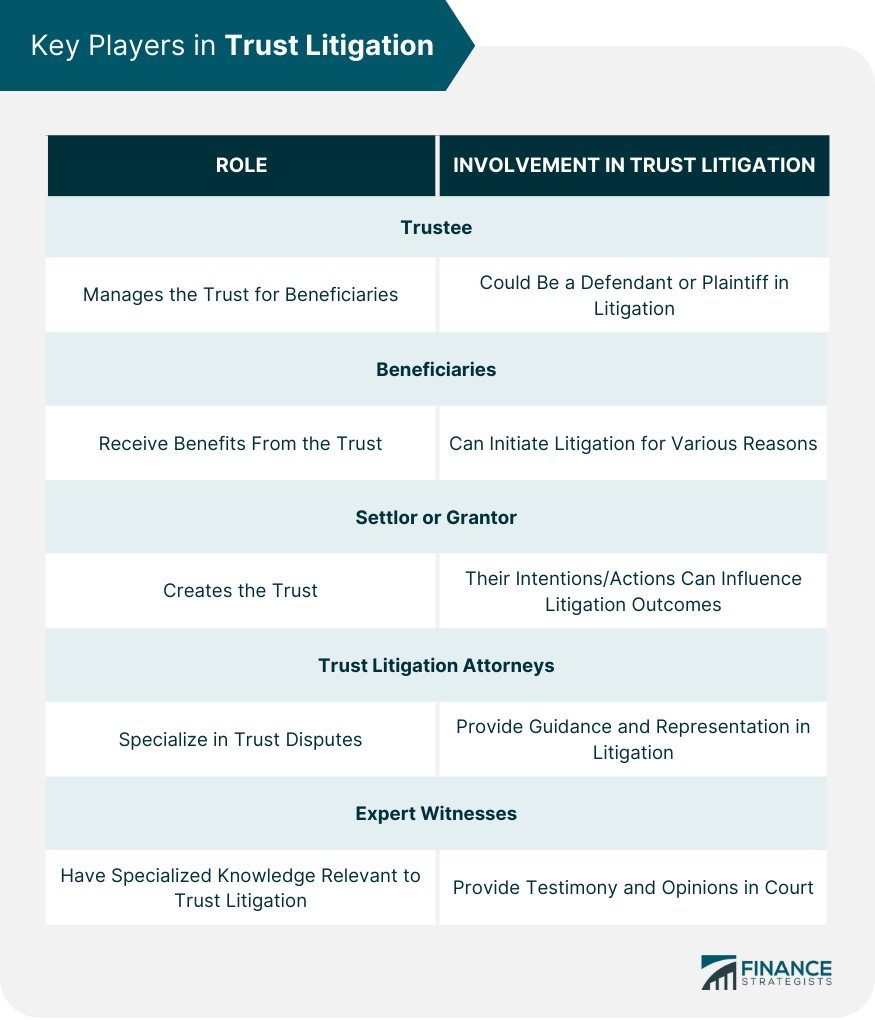
Key Players in Trust Litigation
Trustee
Beneficiaries
Settlor or Grantor
Trust Litigation Attorneys
Expert Witnesses
How to Prevent Trust Litigation
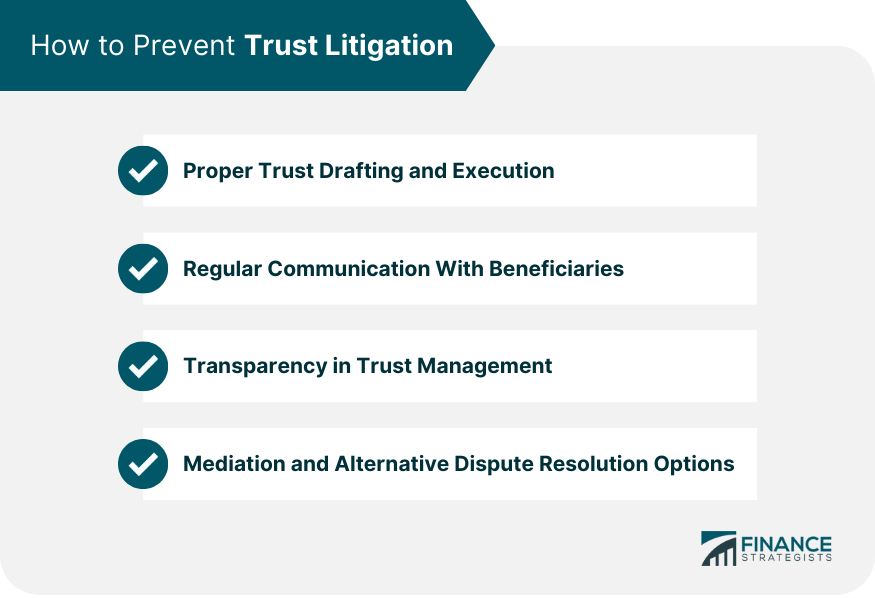
Proper Trust Drafting and Execution
Regular Communication With Beneficiaries
Transparency in Trust Management
Mediation and Alternative Dispute Resolution Options
Final Thoughts
Trust Litigation FAQs
Trust litigation is a legal process that arises when disputes or issues occur in the administration or interpretation of a trust. It is important because it helps protect beneficiaries' rights, ensures that trustees fulfill their fiduciary duties, and maintains the integrity of the trust according to the settlor's intentions.
Common causes of trust litigation include breach of fiduciary duty by the trustee, trust contests due to lack of capacity, undue influence, fraud, or duress, ambiguity in trust documents, trustee removal or replacement, trust reformation or modification, and disputes over the distribution of trust assets.
To prevent trust litigation, it's crucial to work with an experienced estate planning lawyer who can draft a well-structured trust document, ensuring clarity and avoiding ambiguities. Additionally, maintaining regular communication with beneficiaries, being transparent in trust management, and considering alternative dispute resolution methods can help minimize the risk of future litigation.
The legal process of trust litigation typically involves filing a petition or complaint, engaging in the discovery process (including document requests, interrogatories, and depositions), exploring alternative dispute resolution methods (such as mediation or arbitration), proceeding to trial if necessary, and potentially appealing the court's decision.
Key players in trust litigation include the trustee, who is responsible for managing the trust; beneficiaries, who have rights and interests in the trust; the settlor or grantor, who created the trust; trust litigation attorneys, who represent the parties in the dispute; and expert witnesses, who provide specialized knowledge to help the court understand complex issues related to the trust.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











