Offshore Asset Protection Trusts are legal entities established in a foreign jurisdiction, designed to protect an individual's or a corporation's assets from potential creditors, legal claims, or adverse financial circumstances. By transferring ownership of assets to an OAPT, the trust effectively separates the assets from the grantor, making it more difficult for creditors to access those assets. Offshore jurisdictions often have favorable trust and privacy laws, which provide enhanced protection and confidentiality. OAPTs are commonly utilized for wealth preservation, estate planning, and risk management purposes. However, it is important to ensure that the establishment and management of such trusts are in compliance with the applicable laws and regulations, including tax and reporting obligations. Discretionary trusts are one of the most common types of OAPTs. In this arrangement, the trustee has the discretion to manage and distribute the trust's assets to the beneficiaries, as per the guidelines provided by the grantor. This flexible structure allows for greater control over asset distribution, while also providing a robust layer of protection, as the beneficiaries do not have a fixed interest in the trust. Spendthrift trusts are specifically designed to protect the trust's assets from the beneficiaries' creditors. These trusts restrict beneficiaries from accessing the principal amount of the trust and only provide them with a predetermined income stream. This limitation ensures that the trust's assets remain protected from any legal claims against the beneficiaries. Hybrid trusts combine the features of both discretionary and spendthrift trusts. This unique structure provides the grantor with the flexibility to customize the trust's provisions according to their needs. Hybrid trusts offer a high level of asset protection and can adapt to various situations, making them an attractive choice for many individuals and corporations. Revocable trusts allow the grantor to maintain control over the trust's assets and make changes to the trust agreement throughout their lifetime. While revocable trusts offer some level of asset protection, they may not provide the same level of protection as irrevocable trusts, as the grantor's creditors can potentially access the trust's assets. Irrevocable trusts provide a higher level of asset protection than their revocable counterparts. Once established, the grantor cannot alter the trust's terms or reclaim the assets. This separation of control makes it more difficult for creditors to access the trust's assets, ensuring a higher level of protection. When setting up an OAPT, the choice of jurisdiction is crucial. Factors to consider include the jurisdiction's reputation, political stability, legal framework, and tax regulations. Popular offshore trust jurisdictions include the Cook Islands, Nevis, and Belize. Estate planning lawyers play a significant role in drafting the trust agreement, ensuring that it complies with local and international laws. Key elements of the trust agreement include the trust's purpose, identification of beneficiaries, appointment of trustees, and trust provisions. Transferring assets to the trust is an essential step in establishing an OAPT. Types of assets that can be transferred include real estate, bank accounts, investments, and personal property. The process and timeline for funding the trust depend on the type of assets and the jurisdiction's requirements. When establishing an OAPT, it's essential to understand the tax implications and reporting requirements. These trusts may offer potential tax benefits, but they must comply with the grantor's home country's tax laws. OAPTs must adhere to local and international regulations, including anti-money laundering rules and the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA). Failure to comply can lead to severe penalties and legal consequences. Transferring assets to an OAPT with the intent to defraud creditors can result in clawback provisions, allowing courts to reverse the transfers. Estate planning lawyers can help implement strategies to minimize these risks. OAPTs offer a high level of protection from creditors and litigation, making it difficult for claimants to access the trust's assets. Foreign jurisdictions often provide a higher level of privacy and confidentiality compared to domestic trusts, keeping the grantor's financial affairs discreet. Offshore trusts often allows for more flexible trust provisions, enabling the grantor to tailor the trust to their unique needs and circumstances. OAPTs enable grantors to diversify their investments in international markets, potentially reducing risk and increasing returns. OAPTs can face legal challenges and enforcement difficulties due to conflicts between the trust's jurisdiction and the grantor's home country. This may lead to complications in settling disputes and enforcing trust provisions. Setting up and maintaining an OAPT can be more expensive than domestic trusts, due to the costs associated with foreign legal services, trustee fees, and administration expenses. OAPTs may carry a negative connotation, as they are sometimes associated with tax evasion or illicit activities. This perception can potentially harm the grantor's reputation. Laws and regulations governing OAPTs can change, which may impact the trust's benefits and protections. It's essential to stay updated on any legal changes that could affect the trust's structure and effectiveness. When considering whether to establish an OAPT or a domestic trust, it's essential to weigh the similarities and differences between the two. Both trust types can provide asset protection, privacy, and estate planning benefits. However, OAPTs often offer enhanced asset protection, increased confidentiality, and investment diversification. Factors to consider when choosing between the two include the grantor's risk tolerance, financial goals, and tax situation. It's crucial to consult with an estate planning lawyer to determine which trust type best aligns with the grantor's needs and objectives. Offshore Asset Protection Trusts (OAPTs) can be an effective estate planning tool that offers unique advantages, such as enhanced asset protection, increased confidentiality, greater flexibility in trust provisions, and investment diversification. Estate planning lawyers play a crucial role in establishing OAPTs, from drafting the trust agreement to ensuring compliance with local and international laws. However, it's essential to consider the potential risks and challenges associated with OAPTs, including legal enforcement difficulties, costs, reputational risks, and changes in laws and regulations. By thoroughly evaluating the benefits and risks of OAPTs and seeking expert advice from estate planning lawyers, grantors can make informed decisions on whether this trust type is the right fit for their estate planning needs.Definition of Offshore Asset Protection Trusts (OAPTs)
Types of OAPTs
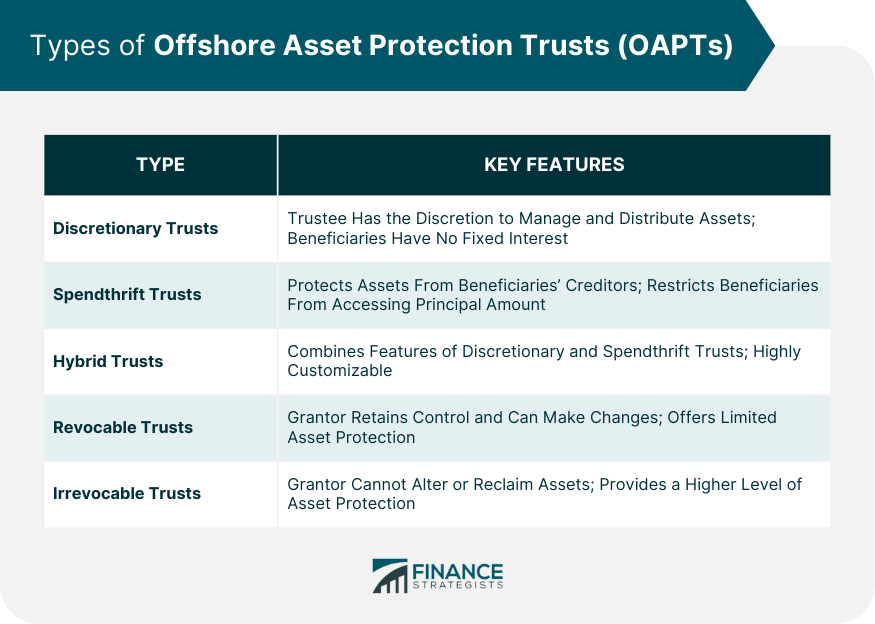
Discretionary Trusts
Spendthrift Trusts
Hybrid Trusts
Revocable Trusts
Irrevocable Trusts
Establishing an Offshore Asset Protection Trust
Choosing the Right Jurisdiction
Drafting the Trust Agreement
Funding the Trust
Legal Considerations for Offshore Asset Protection Trusts
Tax Implications
Compliance With Local and International Laws
Fraudulent Conveyance Concerns
Advantages of Offshore Asset Protection Trusts
Enhanced Asset Protection
Confidentiality and Privacy
Flexibility in Trust Provisions
Diversification of Investments
Potential Disadvantages and Risks of Offshore Asset Protection Trusts
Legal Challenges and Enforcement Difficulties
Costs and Fees Associated With Establishing and Maintaining the Trust
Reputational Risks
Changes in Laws and Regulations Affecting OAPTs
Comparing Offshore Asset Protection Trusts With Domestic Trusts
The Bottom Line
Offshore Asset Protection Trusts (OAPTs) FAQs
Offshore Asset Protection Trusts offer enhanced asset protection, increased confidentiality and privacy, greater flexibility in trust provisions, and the opportunity to diversify investments in international markets.
Estate planning lawyers play a vital role in drafting the trust agreement, ensuring compliance with local and international laws, advising on the choice of jurisdiction, and implementing strategies to minimize risks associated with fraudulent conveyance.
Offshore Asset Protection Trusts may offer potential tax benefits, depending on the grantor's home country's tax laws and the chosen jurisdiction. However, it's essential to understand and comply with all tax reporting requirements to avoid penalties and legal consequences.
Popular offshore trust jurisdictions include the Cook Islands, Nevis, and Belize, due to their favorable legal frameworks, political stability, and reputation for providing a high level of asset protection and privacy.
Some risks associated with Offshore Asset Protection Trusts include legal challenges and enforcement difficulties, costs and fees related to establishing and maintaining the trust, reputational risks, and potential changes in laws and regulations that could impact the trust's benefits and protections.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











