Accountants and controllers are both vital roles in the financial management of a business, each with distinct responsibilities and levels of authority. An Accountant is primarily responsible for managing and reporting a company's financial data. Their role includes tasks like financial forecasting, risk analysis, and tax planning. On the other hand, a Controller, often viewed as the head of a company's financial division, oversees all accounting operations. They are involved in the production of financial reports, maintaining the company's accounting system, and managing financial policies. The choice between an Accountant and a Controller significantly influences a business's financial decision-making and strategic growth, with the latter typically having a more strategic role. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses in choosing the right financial professionals to meet their specific needs. An accountant is a finance professional responsible for the management and reporting of an organization's financial data. Their duties typically encompass the preparation, analysis, and verification of financial documents to ensure the accuracy of information and compliance with established accounting standards and laws. They are also tasked with the preparation of tax returns and the development of strategies to minimize tax liabilities. At the heart of any successful business is an effective accounting system managed by a skilled accountant. Accountants are trained professionals who can handle a wide variety of financial tasks, from basic bookkeeping to complex tax strategies. Accountants perform a myriad of tasks, including financial forecasting, risk analysis, and budgeting. They create and review financial records, ensuring their accuracy and transparency. Accountants may also be involved in strategic tax planning, financial consulting, and cost management. To become an accountant, one typically needs at least a bachelor's degree in accounting or a related field. Many accountants pursue additional credentials, such as Certified Public Accountant (CPA), which is recognized globally and opens up more opportunities in the field. A controller, also known as a financial controller, serves a strategic role in the financial management of a company. They oversee all accounting operations, including the design and maintenance of accounting systems, preparation of financial reports, and coordination of the company's budget. A controller is essentially the head of the financial division of a company. This role typically requires a solid background in accounting, but it also necessitates an understanding of business strategy. Controllers oversee the production of periodic financial reports, maintain the company's accounting system, and ensure the company adheres to relevant legal and regulatory requirements. They also manage financial policies within a company, such as its budget and cash-flow management. Controllers typically hold a bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, or a similar field. However, most employers prefer candidates with a master's degree in business administration (MBA) or accounting. Additionally, professional designations like CPA or Certified Management Accountant (CMA) are highly valued. While accountants and controllers share many responsibilities, the roles have distinct differences. While accountants primarily handle data management and financial reporting, controllers are more involved in the strategic planning and financial management of a company. The controller's role is more executive in nature, ensuring the company's financial plans align with its business goals. Accountants are typically responsible for their individual workload and usually report to a manager or controller. On the other hand, controllers hold a higher level of authority, overseeing the entire accounting department. Although both roles require a solid education in accounting, controllers often possess more advanced degrees and certifications reflective of their broader scope of responsibilities. The need for an accountant or a controller depends heavily on the size and complexity of a business. For small businesses, an accountant might be sufficient to manage financial affairs, performing tasks such as bookkeeping, tax preparation, and basic financial reporting. As businesses grow and financial operations become more complex, a controller becomes necessary. They can manage an accounting team and make strategic financial decisions. In large corporations, the role of a controller becomes crucial. They play a significant part in strategic planning, budgeting, and managing the financial risks of the company. There's a clear career progression from accountant to controller, which often involves gaining additional education, certification, and experience. Usually, an individual starts as a junior or staff accountant, gains experience, and moves up to a senior accountant role. After several years of experience and with further education or certifications, they might step into a controller position. Key skills required for advancement include a strong understanding of accounting principles, excellent analytical skills, and leadership abilities. Additionally, experience in financial reporting, auditing, and strategic planning can help pave the way for a transition into a controller role. The decision between hiring an accountant or a controller has significant implications for a business. Controllers play a vital role in the financial decision-making process of a business. They provide the insights and analysis that drive strategic decisions, while an accountant typically focuses on maintaining accurate financial records. Controllers are instrumental in shaping business strategy. They understand the company's financial health in-depth, helping guide the company toward profitable growth. On the other hand, an accountant, while essential, is more focused on the tactical aspects of financial management. The roles of an accountant and controller are both essential but serve distinct functions within a business's financial management. While an accountant manages and reports financial data, ensuring accuracy and compliance, a controller adopts a more strategic role overseeing accounting operations and influencing business growth. The choice between an accountant and a controller depends largely on the size and complexity of a business. Smaller entities may suffice with an accountant, while larger, more complex organizations require the strategic insight of a controller. The progression from accountant to controller involves additional education, experience, and leadership skills. Ultimately, understanding the responsibilities, qualifications, and impact of both roles is critical to ensure a business's financial health and growth.Accountant vs Controller: An Overview
Accountant: Definition and Responsibilities
Definition
Key Responsibilities
Required Education and Certifications
Controller: Definition and Responsibilities
Definition
Key Responsibilities
Required Education and Certifications
Key Differences Between an Accountant and a Controller
Roles and Responsibilities
Level of Authority and Leadership
Educational Requirements and Certifications

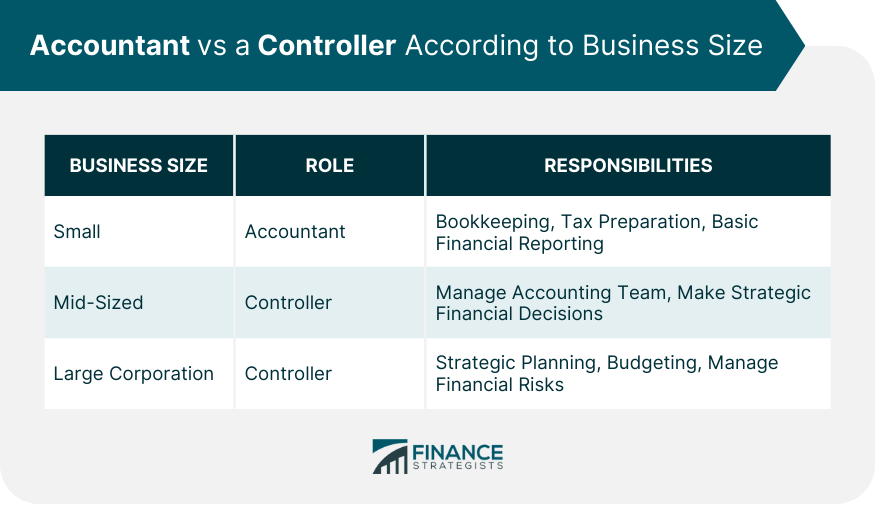
When Might a Business Need an Accountant vs a Controller?
Small Business Scenarios
Mid-Sized Business Scenarios
Large Corporation Scenarios
Career Pathways: From Accountant to Controller
Common Steps in Progression
Skills and Experiences Needed for Advancement
Implications of Choosing an Accountant vs a Controller for Businesses
Financial Decision-Making
Business Strategy and Growth
Bottom Line
Accountant vs Controller FAQs
An Accountant is responsible for managing and reporting a company's financial data, including tasks like financial forecasting, risk analysis, and tax planning.
A Controller oversees all accounting operations in a business, including the production of financial reports, maintaining the accounting system, and managing financial policies.
While both handle financial data, an Accountant focuses on data management and reporting, whereas a Controller is involved in strategic planning and financial management.
Both roles require a degree in accounting or a related field. However, Controllers often possess advanced degrees and certifications like CPA or CMA.
Small businesses may need an Accountant to manage financial affairs, while mid-sized to large businesses usually require a Controller for strategic financial decisions.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











