Advisory fees are the charges that financial advisors, planners, and other professionals charge their clients for the advice and services they provide. These fees can vary greatly depending on factors such as the type and complexity of services offered, the advisor's qualifications and experience, and the client's financial situation. It's crucial for clients to understand advisory fees and their impact on their investments and financial plans. In the financial industry, advisors use several common fee structures to charge clients for their services. Each fee structure has pros and cons, and the most appropriate one depends on the client's and advisor's specific needs and preferences. Asset-based fees, also known as assets under management (AUM) fees, are calculated as a percentage of the total value of a client's investment portfolio. This fee structure is most commonly associated with investment management services, where the advisor actively manages a client's investments to achieve specific goals. Retainer fees are fixed, recurring charges that clients pay to advisors for ongoing services. This type of fee structure is typically used for comprehensive financial planning, where the advisor provides continuous support and guidance on various aspects of the client's financial life. Hourly fees are charged based on the amount of time an advisor spends working on a client's specific needs. This fee structure is often used for clients who require limited or specialized advice, such as tax planning or investment analysis. Fixed fees, or flat fees, are charged as a one-time payment for a specific service or project. This fee structure is common for services like financial, retirement, or estate planning, where the advisor provides a tailored plan to address the client's goals. Performance-based fees are charged based on the investment returns generated by the advisor's management of a client's portfolio. This fee structure incentivizes advisors to achieve strong investment performance but may also introduce potential conflicts of interest. Creditors earn commissions when they buy or sell financial products on behalf of their clients. This fee structure is typically associated with broker-dealers and insurance agents, but it can lead to potential conflicts of interest if the advisor recommends products that generate higher commissions. A variety of factors can influence the fees that financial advisors charge their clients. Understanding these factors can help clients make informed decisions about the cost and value of advisory services. The complexity of a client's financial situation and the scope of their needs can significantly impact advisory fees. Clients with more complex financial situations or more extensive service requirements may be charged higher fees. The range and depth of services provided by an advisor play a crucial role in determining fees. More comprehensive and specialized services generally command higher fees due to the additional time, knowledge, and resources required. Advisors with more experience, advanced credentials, or specialized expertise may charge higher fees for their services. Clients should weigh the potential value of an advisor's experience and qualifications against the cost of their fees. Advisory fees can vary based on the advisor's geographic location, with higher fees often seen in areas with a higher cost of living or more competitive markets. The size and type of the advisory firm can also influence fees, with larger firms and those offering a broader range of services potentially charging higher fees. Advisory fees can vary depending on the specific service being provided. Clients need to understand the typical fee structures associated with each service to make informed decisions about the cost and value of the advice they receive. Investment management fees are typically charged as a percentage of assets under management (AUM). The advisor receives a portion of the client's portfolio value as compensation for managing their investments. This fee structure aligns the advisor's incentives with the client's investment performance. Financial planning fees can be structured in various ways, including flat fees, hourly rates, or retainer fees. The choice of fee structure depends on the scope and complexity of the financial planning services provided and the preferences of the client and advisor. Retirement planning fees can also vary, with flat fees, hourly rates, or retainer fees being common options. The appropriate fee structure depends on the level of detail and ongoing support required by the client to achieve their retirement goals. Tax planning and preparation fees are often charged as either hourly rates or fixed fees, depending on the complexity of the client's tax situation and the advisor's expertise in tax matters. Estate planning fees are typically charged as fixed fees or hourly rates, as these services often involve specialized knowledge and the development of tailored strategies to address the client's unique needs and objectives. Financial advisors and their fees are subject to various regulations and disclosure requirements to protect clients and promote transparency in the industry. Advisors are required to disclose their fees and any potential conflicts of interest in documents like Form ADV and the Client Relationship Summary (CRS). This ensures that clients clearly understand the costs associated with their advisory services. Regulations aim to minimize conflicts of interest in the financial industry, such as instances where an advisor may recommend products or services that generate higher fees or commissions for themselves instead of prioritizing the client's best interests. Financial advisors have a fiduciary duty to act in their client's best interests, which includes ensuring that their fees are reasonable and transparent. Regulation Best Interest (Reg BI) is a rule from the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) that requires broker-dealers to act in the best interests of their clients, including disclosing and mitigating potential conflicts of interest related to fees and commissions. When choosing a financial advisor, it's essential to consider their fee structures, costs, qualifications, and services. Transparent fee structures helps clients understand the costs associated with their advisory services and enable them to make informed decisions about the value they are receiving. Clients should carefully evaluate different fee structures and consider the overall cost-effectiveness of the advisory services, taking into account factors such as the advisor's experience, qualifications, and the scope of services provided. While fees are an important consideration, clients should also focus on the quality of service provided by an advisor. Sometimes, paying higher fees for an experienced and knowledgeable advisor may lead to better long-term outcomes. In some cases, clients may be able to negotiate fees with their advisors, particularly if they have a large investment portfolio or are engaging the advisor for multiple services. Understanding advisory fees is crucial for clients seeking financial advice, as it helps them make informed decisions about the cost and value of the services they receive. By examining different fee structures, regulatory requirements, and industry trends, clients can better evaluate and compare advisors, ensuring they choose the right professional to meet their financial goals. Ultimately, careful consideration of fees, alongside the quality of service and advisor qualifications, will help clients make the most of their investment in financial advice. Don't hesitate to seek the guidance of a financial advisor who aligns with your needs and preferences. Taking action today can put you on the path to a more secure and prosperous financial future.What Are Advisory Fees?
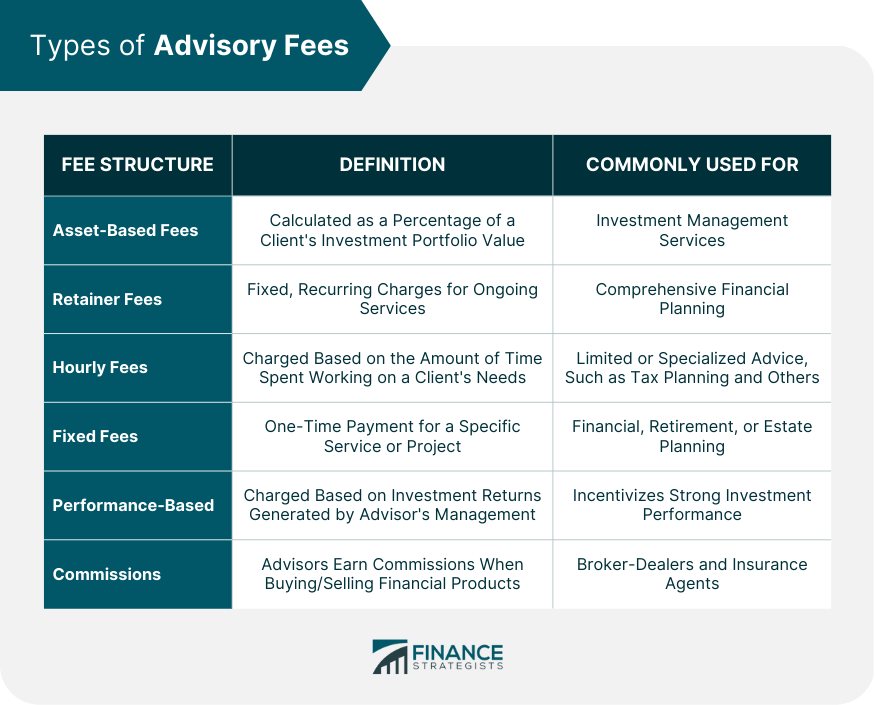
Types of Advisory Fees
Asset-Based Fees
Retainer Fees
Hourly Fees
Fixed Fees
Performance-Based Fees
Commissions
Factors Influencing Advisory Fees
Client's Financial Situation and Needs
Scope and Complexity of Services Provided
Advisor's Experience and Qualifications
Geographic Location
Size and Type of Advisory Firm

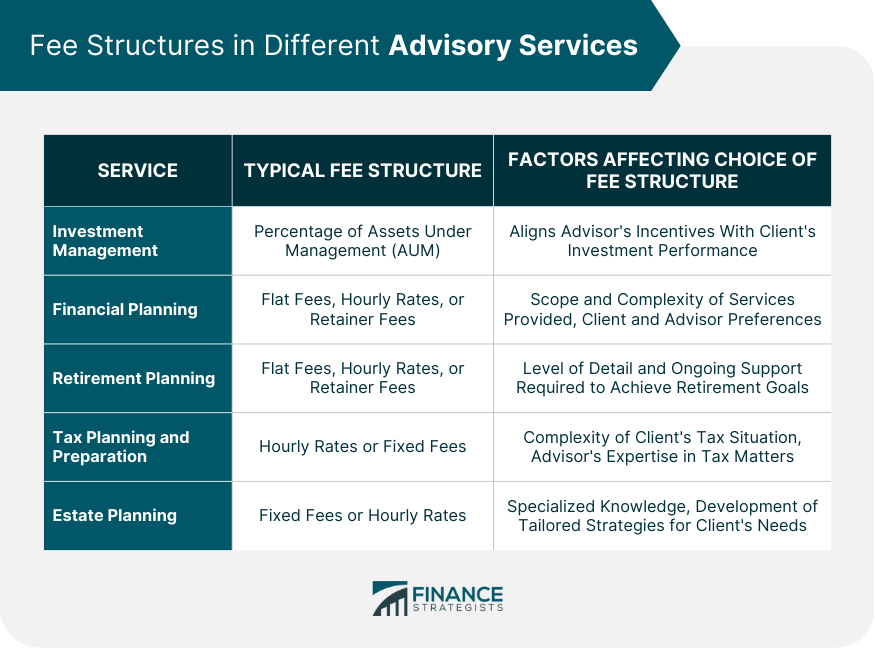
Fee Structures in Different Advisory Services
Investment Management
Financial Planning
Retirement Planning
Tax Planning and Preparation
Estate Planning
Regulatory Aspects of Advisory Fees
Fee Disclosure Requirements
Conflicts of Interest
Fiduciary Responsibility
Regulation Best Interest (Reg BI)
Comparing and Selecting Advisors Based on Fees
Importance of Fee Transparency
Evaluating Fee Structures and Cost-Effectiveness
Balancing Fees With Quality of Service
Negotiating Fees
Final Thoughts
Advisory Fees FAQs
Advisory fees are charges that financial advisors, planners, and other professionals charge their clients for the advice and services they provide.
The common types of advisory fees are asset-based fees, retainer fees, hourly fees, fixed fees, performance-based fees, and commissions.
Advisory fees can be influenced by factors such as the client's financial situation and needs, the scope and complexity of services provided, the advisor's experience and qualifications, the geographic location, and the size and type of advisory firm.
Financial advisors and their fees are subject to various regulations and disclosure requirements to protect clients and promote transparency in the industry, including fee disclosure requirements, minimizing conflicts of interest, fiduciary responsibility, and Regulation Best Interest (Reg BI).
Clients can compare and select advisors based on fees by considering the importance of fee transparency, evaluating fee structures and cost-effectiveness, balancing fees with quality of service, and negotiating fees when possible. They should also consider recent trends and developments in advisory fees, such as fee compression and competition, the impact of technology on fees, the emergence of robo-advisors, and the shift towards fee-only advisors.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











