Fee levelization is the process of equalizing or leveling fees across all investors in an investment management product, such as mutual funds, hedge funds, or other pooled investment vehicles. The primary goal of fee levelization is to ensure that investors are charged fair and transparent fees, irrespective of their investment size, tenure, or type of investment. Fee levelization aims to eliminate disparities in fee structures, enhance transparency, and promote fairness among investors. By leveling fees, investment managers can encourage investor confidence, foster competition, and improve the overall performance of their investment products. Management fees are the ongoing fees charged by investment managers for managing the assets in a fund. They are typically calculated as a percentage of the assets under management (AUM) and cover the costs of portfolio management, research, and advisory services. Performance fees are incentive-based fees charged by investment managers when a fund's performance exceeds a predetermined benchmark or hurdle rate. These fees are intended to align the interests of investment managers with those of their investors. Administrative fees cover fund administration costs, including record keeping, accounting, legal, and compliance services. These fees are usually charged as a fixed percentage of the fund's net asset value (NAV). Trading and transaction fees are costs incurred when buying or selling securities within a fund. These fees include brokerage commissions, bid-ask spreads, and other transaction-related costs. Under the pro-rata fee allocation approach, each investor is charged fees in proportion to their investment in the fund. This method ensures that all investors share the costs of managing the fund equally, regardless of their individual investment size. Fee equalization credits involve allocating a portion of the fund's fees back to the investors, effectively reducing their overall fee burden. This method helps equalize fees across all investors, particularly in cases where fee structure disparities exist. Fee offset arrangements allow investors to offset their management fees against other fees they might incur within the fund, such as performance fees. This approach can help equalize fees by ensuring that investors do not pay multiple fees for the same services. Unified fee structures involve consolidating all fees into a single, transparent fee that is charged to all investors. This approach simplifies the fee structure and ensures that all investors pay the same fees for the same services. Fee levelization promotes fairness by ensuring all investors are charged the same fees for services. This approach enhances transparency by making fee structures more understandable and comparing different investment products easier. By implementing fee levelization, investment managers can increase investor confidence in their products. Investors are more likely to trust and invest in funds that have fair and transparent fee structures. As fee levelization becomes more prevalent, investment managers will need to compete on the quality and performance of their investment products rather than relying on complex or opaque fee structures to attract and retain investors. Fee levelization can help improve the performance metrics of investment products by eliminating fee-related distortions. This enables investors to compare investment performance across different funds accurately. Implementing fee levelization can be complex, particularly when dealing with multiple fee structures, investment products, and investor types. Investment managers must develop robust fee calculation methodologies to ensure accurate and consistent fee allocation. Fee levelization may be subject to legal and regulatory requirements, particularly in the context of investor protection and disclosure. Investment managers must ensure that their fee levelization practices comply with applicable laws and regulations. Implementing fee levelization may require significant changes to an investment manager's operational infrastructure, including fee calculation, invoicing, and reporting systems. Investment managers must invest the necessary technology and resources to implement fee levelization. Investment managers must clearly communicate their fee levelization policies and practices to investors. This may involve providing detailed fee disclosure documents, offering investor education materials, and maintaining open lines of communication with investors to address any questions or concerns. Many investment managers have adopted fee levelization practices recently, including BlackRock, Vanguard, and Fidelity. These firms have recognized the benefits of fee levelization and have taken steps to implement it across their product offerings. The adoption of fee levelization is becoming more widespread as investors demand greater transparency and fairness in fee structures. Industry associations, such as the Investment Company Institute (ICI) and the Alternative Investment Management Association (AIMA), have also issued guidance on fee levelization to promote best practices among investment managers. To effectively implement fee levelization, investment managers should consider the following best practices: Develop a comprehensive fee levelization policy outlining the firm's fee allocation and disclosure approach. Regularly review and update the firm's fee levelization practices to ensure they remain consistent with industry standards and regulatory requirements. Invest in technology and resources for accurate and efficient fee calculation and reporting. Clearly communicate the firm's fee levelization policies and practices to investors and other stakeholders. Regulatory requirements and guidance on fee levelization vary by jurisdiction. In the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has issued guidance on fee disclosure and transparency for investment managers. As the investment management industry continues to evolve, regulators may introduce new rules and standards related to fee levelization. Investment managers should stay informed about regulatory developments and ensure that their fee levelization practices remain compliant with applicable laws and regulations. Regulatory requirements and guidance can significantly impact the adoption and implementation of fee levelization practices. Investment managers must proactively understand and comply with these requirements to effectively implement fee levelization and maintain investor confidence. Fee levelization is a critical component of fair and transparent investment management practices. It is the process of equalizing or leveling fees across all investors in an investment management product to promote fairness, transparency, and equality. The implementation of fee levelization can benefit investment managers by increasing investor confidence, promoting competition, and improving the overall performance of investment products. However, implementing fee levelization can be complex and requires investment managers to develop robust fee calculation methodologies, comply with legal and regulatory requirements, and invest in technology and resources for accurate and efficient fee reporting. Despite the challenges, many investment managers have already adopted fee levelization practices, and the adoption of fee levelization is becoming more widespread as investors demand greater transparency and fairness in fee structures. Investment managers should stay informed about regulatory developments and ensure that their fee levelization practices remain compliant with applicable laws and regulations. By implementing fee levelization, investment managers can enhance transparency, promote fairness, and increase investor confidence in their products.What Is Fee Levelization?
Types of Fees in Investment Management
Management Fees
Performance Fees
Administrative Fees
Trading and Transaction Fees
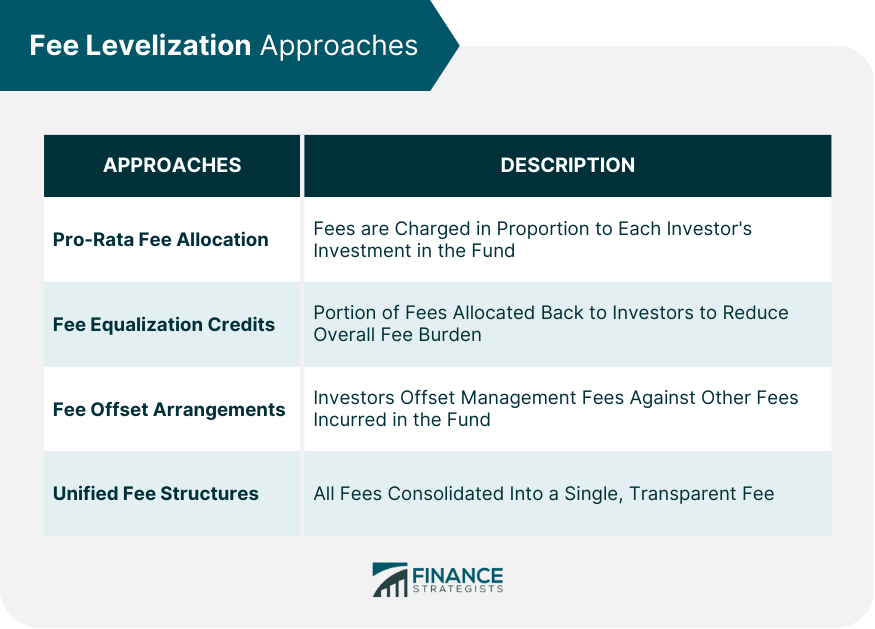
Fee Levelization Approaches
Pro-Rata Fee Allocation
Fee Equalization Credits
Fee Offset Arrangements
Unified Fee Structures
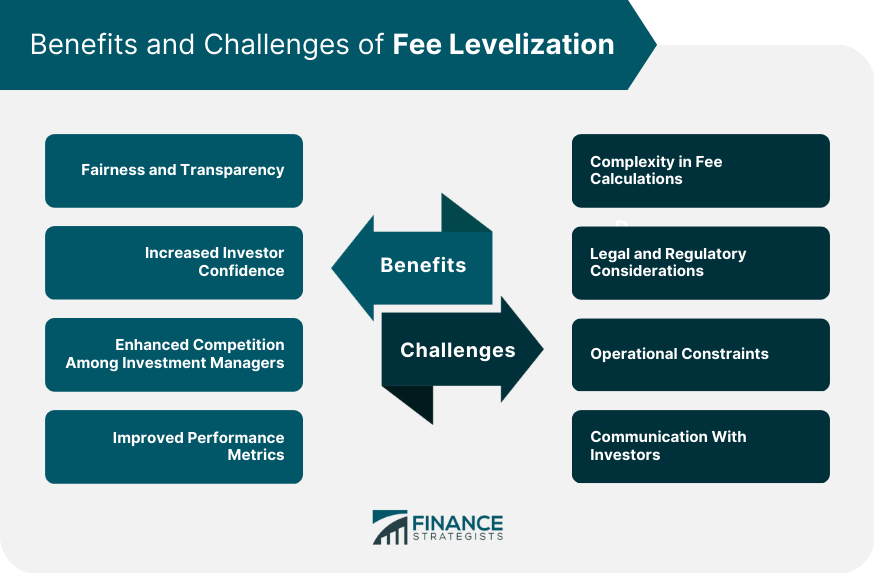
Benefits of Fee Levelization
Fairness and Transparency
Increased Investor Confidence
Enhanced Competition Among Investment Managers
Improved Performance Metrics
Fee Levelization Implementation Challenges
Complexity in Fee Calculations
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Operational Constraints
Communication With Investors
Fee Levelization in Practice
Examples of Investment Managers Adopting Fee Levelization
Industry Trends and Developments
Best Practices and Recommendations
Regulatory Landscape of Fee Levelization
Regulatory Requirements and Guidance
Similarly, the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) has provided guidance on fee transparency for investment funds in the European Union.Evolving Rules and Standards
Impact of Regulations on Fee Levelization
Conclusion
Fee Levelization FAQs
Fee levelization is the process of equalizing fees across different classes or groups within an organization.
Fee levelization helps to promote fairness and equality within an organization. It ensures that everyone pays the same amount for the same services or products, regardless of their membership status or other factors.
Fee levelization works by analyzing the fees charged to different groups or classes within an organization and adjusting them so that they are equal. This may involve increasing fees for some groups or decreasing fees for others.
Some benefits of fee levelization include promoting fairness and equality, simplifying fee structures, reducing administrative costs, and improving member satisfaction.
One potential drawback of fee levelization is that it may result in some members paying more than they did before, which could lead to dissatisfaction. Additionally, it may be difficult to determine which fees should be equalized and how much they should be adjusted.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











