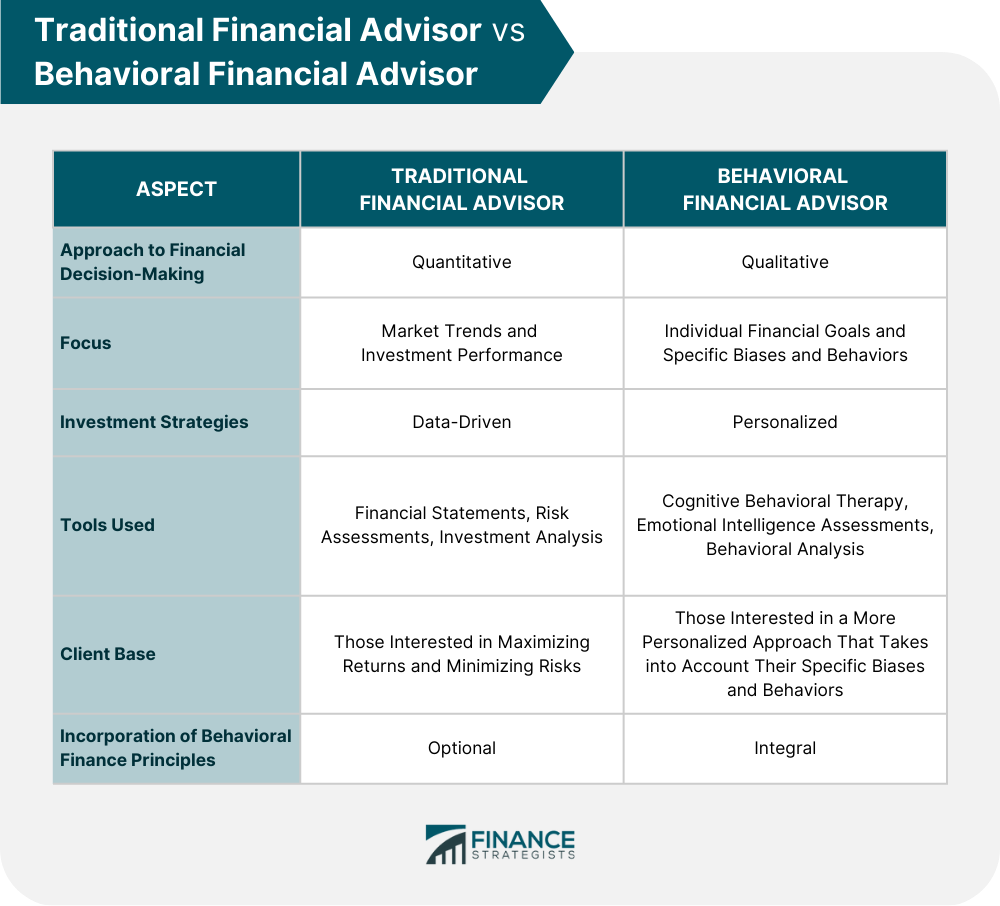
Behavioral financial advisors are financial professionals who specialize in the intersection of psychology and finance. They are trained to identify and analyze the behavioral biases and patterns of clients. It equips them to understand the impact of those biases on financial decision-making. Further, they are able to develop strategies to mitigate those biases and help clients achieve their objectives. Behavioral finance studies the psychology of financial decision-making. It emerged in the 1980s as a response to traditional finance, which assumed that investors are always rational and have perfect information. It recognizes that humans are not always rational and that emotions and cognitive biases can impact financial decision-making. Further, it combines psychology and economics to understand how individuals make financial decisions and how those decisions impact financial markets. Listed below are the importance of a behavioral financial advisor: Behavioral financial advisors are important because they help individuals understand their behavioral biases. These biases can impact financial decisions, leading to suboptimal outcomes. Some common biases that behavioral financial advisors address include overconfidence, loss aversion, anchoring, and confirmation bias. Overconfidence, for example, can lead investors to overestimate their ability to pick winning stocks or predict market trends. On the other hand, loss aversion can cause investors to hold onto losing investments for too long, hoping that the market will recover. Behavioral financial advisors help their clients reduce the negative impact of behavioral biases by developing strategies to mitigate them. These strategies include developing investment plans based on long-term goals rather than short-term market trends or diversifying investments to reduce risk. They may also help their clients to avoid impulsive decisions, such as buying or selling investments based on emotions rather than sound investment principles. By understanding the behavioral biases of their clients and developing strategies to mitigate those biases, behavioral financial advisors help their clients make better financial decisions. This, in turn, helps their clients to achieve their financial goals, such as saving for retirement, funding their children's education, or starting a business. Listed below are some of the services that behavioral financial advisors provide: Behavioral financial advisors help their clients to identify their behavioral biases in investment decision-making and develop strategies to mitigate those biases. For example, a behavioral financial advisor may help a client avoid the temptation to buy or sell investments based on short-term market trends instead of focusing on long-term goals. They may also help their clients build diversified investment portfolios reflecting their goals and risk appetite. This may include developing a diversified portfolio with stocks, bonds, and other investment vehicles. Similarly, they may help their clients avoid cognitive biases, such as overconfidence or confirmation bias, by taking a data-driven approach to investment decision-making. They help their clients to analyze their behavioral biases when it comes to retirement planning and design plans that account for those biases. For example, a behavioral financial advisor may help a client to understand the impact of loss aversion when it comes to retirement planning. Loss aversion can cause individuals to take on more risk than they should to achieve higher returns, which can be detrimental to their long-term financial health. A behavioral financial advisor may also help clients understand the importance of saving for retirement and provide guidance on how to do so effectively. This may include developing a retirement income plan based on the client's specific goals and lifestyle, such as the desired retirement age, expected expenses, and expected income. Behavioral financial advisors help clients manage their wealth based on behavioral finance principles. This may include developing strategies to optimize wealth creation and preservation, as well as building long-term financial plans to achieve clients' objectives. They may also help their clients to avoid emotional biases, such as fear or greed, by taking a systematic approach to wealth management. For example, a behavioral financial advisor may help a client to avoid the temptation to invest in risky or speculative investments, instead focusing on proven investment vehicles. To become a behavioral financial advisor, one must have a degree in finance, economics, psychology, or a related field. Many behavioral financial advisors also have advanced degrees, such as a master's or Ph.D. in finance or psychology. In addition, behavioral financial advisors must have specialized training in behavioral finance and must be able to apply those principles in practice. Behavioral financial advisors must also be able to communicate effectively with clients, as well as have strong analytical skills and attention to detail. They must be able to identify patterns and trends in financial data and develop strategies to mitigate biases and achieve clients' objectives. Traditional and behavioral financial advisors differ in their financial decision-making approaches. While traditional financial advisors focus on maximizing returns and minimizing risks, behavioral financial advisors specialize in understanding and mitigating the impact of human behavior and emotions on financial decision-making. Traditional financial advisors use a quantitative approach to financial decision-making, focusing on market trends and investment performance. They use data-driven models to analyze market trends and develop investment strategies that maximize returns while minimizing risks. They may use financial statements, risk assessments, and investment analysis tools to evaluate investment opportunities. Typically, they work with clients with specific financial goals, such as retirement planning, wealth creation, or risk management. Based on the client's risk tolerance and financial objectives, they may recommend particular investment vehicles, such as mutual funds, stocks, or bonds. In contrast, behavioral financial advisors take a qualitative approach to financial decision-making. They are experts in recognizing and mitigating the effects of human behavior and emotions on financial decision-making. Identifying behavioral biases, developing strategies to minimize them, and achieving their financial goals are their most crucial assistance. Such professionals focus on the client's financial goals rather than market trends or investment performance. They help clients develop investment strategies that reflect their needs and financial objectives. In their practice, they often use cognitive behavioral therapy, emotional intelligence assessments, and behavioral analysis to help clients overcome cognitive, emotional, and social biases that may impact their financial decision-making. Choosing between a traditional and a behavioral financial advisor depends on your financial goals and needs. A traditional financial advisor may be a good fit for you if you are primarily interested in maximizing returns and minimizing risks. On the other hand, if you want to develop a more personalized approach to financial decision-making that considers your specific biases and behaviors, a behavioral financial advisor may be a better choice. It is important to note that the two types of financial advisors are not mutually exclusive. Some financial advisors may incorporate behavioral finance principles into their practice, while others may use a more quantitative approach. When choosing a financial advisor, it is important to ask questions about their approach to financial decision-making and their qualifications and experience. This will help you find an advisor that fits your specific financial goals and needs well. A behavioral financial advisor specializes in understanding and mitigating the impact of biases and emotions on financial decision-making. By helping individuals and businesses understand their behavioral biases and develop strategies to overcome them, behavioral financial advisors help their clients achieve their financial objectives. Through investment planning, retirement planning, and wealth management, behavioral financial advisors can optimize wealth creation and preservation and achieve long-term financial success. Therefore, if you want to achieve your financial goals and avoid costly mistakes, consider hiring the services of a behavioral financial advisor. With their specialized training in behavioral finance, analytical skills, and attention to detail, a behavioral financial advisor can help you make sound financial decisions and navigate the complex world of finance. Contact a behavioral financial advisor today and take the first step toward achieving your financial objectives.What Is a Behavioral Financial Advisor?
Introduction to Behavioral Finance
Importance of Behavioral Financial Advisor
Understanding Behavioral Biases
Reducing Negative Impact of Behavioral Biases
Helping Clients Achieve Financial Goals
Services Offered by a Behavioral Financial Advisor

Investment Planning
Retirement Planning
Wealth Management
Qualifications and Requirements for a Behavioral Financial Advisor
Traditional Financial Advisor vs Behavioral Financial Advisor
Traditional Financial Advisor
Behavioral Financial Advisor
Which One to Choose?
Final Thoughts
Behavioral Financial Advisor FAQs
A behavioral financial advisor is a financial professional who specializes in the intersection of psychology and finance. They help their clients identify their behavioral biases, understand the impact of those biases on financial decision-making, and develop strategies to mitigate those biases. If you want to achieve your financial goals and avoid costly mistakes, consider hiring one.
Some common biases that behavioral financial advisors can help you overcome include overconfidence, loss aversion, anchoring, and confirmation bias. These biases can lead to suboptimal financial decisions, harming your long-term financial health.
A behavioral financial advisor's services include investment planning, retirement planning, and wealth management. Each service helps individuals and businesses optimize wealth creation and preservation and achieve long-term financial success.
To become a behavioral financial advisor, one must have a degree in finance, economics, psychology, or a related field. Additionally, behavioral financial advisors must have specialized training in behavioral finance and be able to apply those principles in practice. Strong communication, analytical, and attention to detail are also essential for a successful career as a behavioral financial advisor.
While traditional financial advisors focus on maximizing returns and minimizing risks, behavioral financial advisors specialize in understanding and mitigating the impact of human behavior and emotions on financial decision-making. They help clients identify their behavioral biases, develop strategies to mitigate them and achieve their financial goals. Behavioral financial advisors use a data-driven approach to financial decision-making, while traditional financial advisors focus on market trends and investment performance.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











