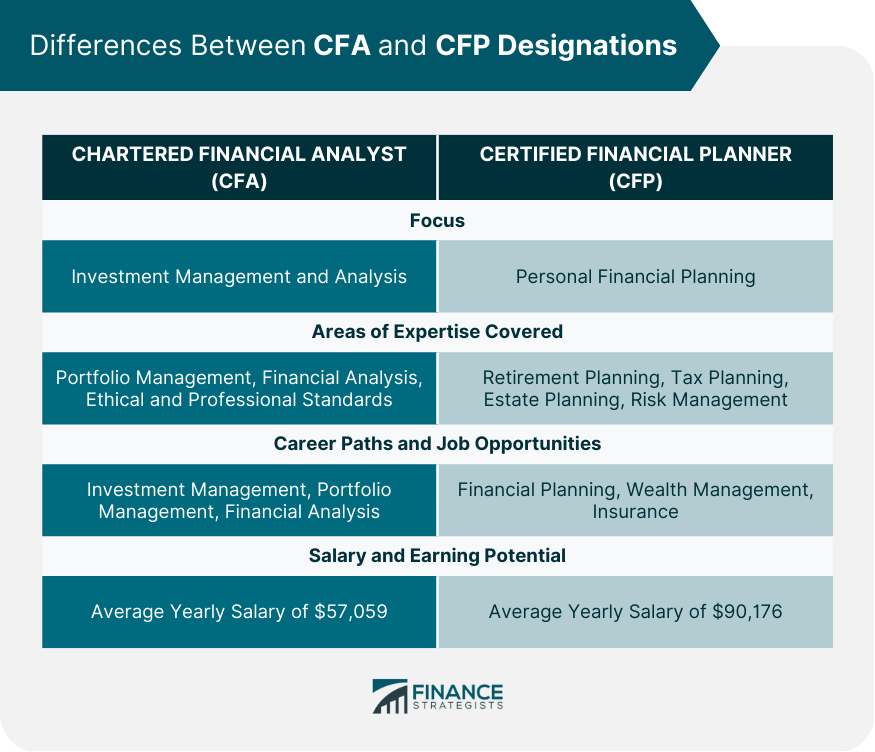
The Certified Financial Planner (CFP) and Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) designations are two professional certifications for individuals working in the financial industry. They demonstrate an individual's expertise in finance and investment management, and are highly respected in the industry. A financial advisor can demonstrate competence and skill by acquiring either designation. The CFA designation is awarded by the CFA Institute, a global association of investment professionals. The CFA program covers a broad range of investment topics, including portfolio management, financial analysis, and ethical and professional standards. The CFP designation, on the other hand, is awarded by the Certified Financial Planner Board of Standards, Inc. The CFP program focuses on personal financial planning, including retirement planning, tax planning, and estate planning. Understanding the differences can help individuals determine which certification is best suited for their career goals and interests. Second, it can help individuals make informed decisions about their education and professional development. Finally, it can help employers and clients understand the qualifications and expertise of the individuals they are working with. Have a financial question? Click here. The Chartered Financial Analyst designation is a globally recognized professional certification that demonstrates an individual's expertise in finance and investment management. The CFA program covers a broad range of investment topics, including portfolio management, financial analysis, and ethical and professional standards. The CFA designation is highly respected in the industry and is often considered the "gold standard" for investment professionals. To obtain the CFA designation, individuals must complete the CFA program, which consists of three levels of exams. The exams cover a wide range of investment topics, including ethics, economics, portfolio management, and financial analysis. In addition to passing the exams, individuals must also meet certain work experience requirements. To become a CFA charterholder, individuals must have at least four years of professional work experience in the investment industry, including experience in investment decision-making, supervising others who make investment decisions, or teaching or researching finance. CFA charterholders are highly respected and valued in the finance industry. They are typically employed by investment banks, asset management firms, hedge funds, or other financial institutions. The CFA designation can lead to a variety of career paths, including portfolio management, investment analysis, risk management, and wealth planning. CFA charterholders may also work in academia or for regulatory agencies. The Certified Financial Planner designation is a professional certification that demonstrates an individual's expertise in personal financial planning. The CFP program focuses on a broad range of financial planning topics, including retirement planning, tax planning, estate planning, and risk management. To obtain the CFP designation, individuals must complete the CFP program, which consists of a series of courses that cover the various topics and skills required for personal financial planning. In addition to completing the coursework, individuals must also pass a comprehensive exam that tests their knowledge and understanding of personal financial planning. To be eligible for the CFP program, individuals must have a bachelor's degree from an accredited university or college, or have a minimum of three years of relevant work experience in the financial services industry. They must also meet certain ethics and professionalism requirements. CFP professionals are highly respected and valued in the financial industry. They are typically employed by financial planning firms, wealth management firms, insurance companies, or other financial institutions. The CFP designation can lead to a variety of career paths, including financial planning, investment management, risk management, and estate planning. Below are key differences between the two designations: The CFA and CFP certifications have different focuses. The CFA designation is focused on investment management and analysis, while the CFP designation is focused on personal financial planning. The CFA program covers a broad range of investment topics, including portfolio management, financial analysis, and ethical and professional standards. The CFP program covers a broad range of personal financial planning topics, including retirement planning, tax planning, estate planning, and risk management. CFA charterholders typically work in investment management, portfolio management, and financial analysis. CFP professionals typically work in financial planning, wealth management, and insurance. According to information provided by ZipRecruiter, individuals who hold a CFA charter can expect to earn an average yearly salary of $57,059. Meanwhile, the average yearly salary for a CFP professional in the United States is $90,176. The range of salaries for individuals with these certifications can vary significantly, with some earning as much as $145,000. When choosing between the CFA and CFP designations, there are several factors to consider. These include your career goals, your personal interests, your educational background, and your work experience. You should also consider the job opportunities and salary potential for each designation, as well as the time and cost required to complete the program. Your personal preferences and career goals are important factors to consider when choosing between the CFA and CFP designations. If you are interested in investment management and analysis, the CFA designation may be a better fit for you. If you are interested in personal financial planning and helping individuals and families achieve their financial goals, the CFP designation may be a better fit. Both the CFA and CFP designations have advantages and disadvantages. The CFA designation is highly respected and valued in the finance industry, and can lead to a variety of career paths and job opportunities. However, it is also a challenging program that requires a significant investment of time and money. The CFP designation, on the other hand, is focused on personal financial planning, which may be more rewarding for individuals who enjoy working with clients. It is also possible to obtain both the CFA and CFP certifications, which can enhance your expertise and qualifications in both investment management and personal financial planning. However, obtaining both designations requires a significant investment of time and money, and may not be necessary for all individuals. Knowing the difference between the CFA and CFP certifications is crucial for individuals looking to pursue a career in finance or enhance their skills and credentials in the field. The CFA and CFP designations have different focuses and are designed for different purposes. Understanding the differences between them can help individuals make informed decisions about their education and professional development. The main differences between the CFA and CFP certifications are their areas of expertise and their career paths. The CFA designation is focused on investment management and analysis, while the CFP designation is focused on personal financial planning. CFA charterholders typically work in investment management, portfolio management, and financial analysis. While CFP professionals typically work in financial planning, wealth management, and insurance. By understanding these differences, individuals can determine which designation is best suited for their career goals and interests.Overview of CFA and CFP
What Is a CFA?
What Is a CFP?
Differences Between CFA and CFP
Focus of Each Certification
Areas of Expertise Covered
Career Paths and Job Opportunities
Salary and Earning Potential
Which Certification Is Right for You?
Final Thoughts
CFA vs CFP FAQs
The CFA designation is focused on investment management and analysis, while the CFP designation is focused on personal financial planning.
CFA charterholders typically work in investment management, portfolio management, and financial analysis. CFP professionals typically work in financial planning, wealth management, and insurance.
According to information provided by ZipRecruiter, individuals who hold a CFA charter can expect to earn an average yearly salary of $57,059. Meanwhile, the average salary for a CFP professional in the United States is $90,176. The range of salaries for individuals with these certifications can vary significantly, with some earning as much as $145,000.
Yes, it is possible to obtain both designations, which can enhance your expertise and qualifications in both investment management and personal financial planning.
Factors to consider when choosing between CFA and CFP certifications include career goals, personal interests, educational background, work experience, job opportunities, salary potential, time and cost required to complete the program, and the advantages and disadvantages of each certification.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











