Financial advisors are professionals dedicated to helping individuals and organizations make informed decisions about their finances. They assess financial needs, set and monitor financial goals, and offer guidance on topics such as investments, insurance, and retirement. A foundation in formal education is vital for financial advisors. The world of finance is complex and ever-changing, and a robust education ensures advisors are equipped with the knowledge, analytical tools, and expertise to address diverse client needs. A strong academic background provides credibility, fostering trust between advisors and their clientele. It ensures advisors can navigate the intricacies of finance, from understanding market dynamics to deciphering tax laws. Studying finance at the undergraduate level introduces students to the core concepts of money management, investments, financial institutions, and risk management. This foundational knowledge prepares individuals for a wide range of roles in the finance sector, offering them a holistic view of how money moves in the economy and how best to manage and grow wealth. Economics delves into how societies allocate their resources and how markets function. An economics degree fosters critical thinking, equipping students with a macro perspective of financial systems. It offers insights into market behaviors, the role of governments in economies, and how global events can impact financial markets. A degree in Business Administration offers a broad understanding of how businesses operate. It covers various disciplines, including marketing, operations, and, importantly for financial advisors, finance. This multidisciplinary approach ensures that future financial advisors can appreciate the wider business context in which they will operate. An accounting degree equips students with a deep understanding of financial statements, taxation, auditing, and internal financial controls. Financial advisors with an accounting background have an edge, especially when providing advice on tax planning, understanding business financial health, and in-depth financial analysis. A Master's in Finance provides in-depth knowledge of financial theories, quantitative analysis techniques, and the intricacies of financial markets. This degree often delves deeper into specialized topics like derivatives, portfolio management, and mergers and acquisitions, making it ideal for those seeking roles in investment banking or asset management. An MBA, particularly with a specialization in Finance or Wealth Management, is tailored for those seeking leadership roles. It blends financial expertise with management skills, preparing individuals for strategic roles in finance and beyond. This degree is laser-focused on the needs of future financial advisors. It delves into personal finance, estate planning, retirement solutions, and tax strategies, ensuring advisors are well-equipped to offer holistic advice to their clientele. A PhD in Finance is typically pursued by those keen on academic roles or high-level research positions within financial institutions. It represents the pinnacle of understanding in finance, with candidates often contributing original research to the field. A DBA, while similar to a PhD, is often more applied in its focus. It's geared towards professionals seeking to combine academic rigor with practical business applications, making it ideal for high-level consultancy or executive roles in finance. The Certified Financial Planner (CFP) designation is one of the most recognized in the financial advising world. It signifies expertise in comprehensive financial planning, ensuring its holders are well-equipped to guide clients through various financial scenarios. This certification also mandates continuous education, ensuring professionals stay updated with evolving financial landscapes. Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) charter holders are recognized for their expertise in investment management. The rigorous three-level exam covers topics from quantitative analysis to portfolio management, making it one of the most sought-after designations in finance. Their training emphasizes not just knowledge but also the ethical responsibilities of a financial professional. The Chartered Financial Consultant (ChFC) certification focuses on the complexities of financial planning. Its comprehensive curriculum covers diverse topics, from behavioral finance to special needs planning, ensuring a well-rounded approach to wealth management. Continuous updates to the ChFC curriculum ensure that it's always in sync with the latest in financial planning. By taking on internships or snagging an entry-level role, aspiring financial advisors get a firsthand look at the day-to-day operations of the financial world. This on-the-ground experience lets them test their theoretical knowledge, helping them see how theories play out in real situations. It's also an opportunity to learn the practical aspects of client interactions, how financial products are pitched and sold, and how to navigate the challenges that come with managing other people's money. Being a financial advisor is about building and maintaining relationships. A big part of that relationship-building comes from effective communication – breaking down intricate financial concepts into easy-to-understand language for clients. Empathy is another critical skill. It's important to understand where clients are coming from, whether they're anxious about investments, worried about retirement, or just confused about where to start. Lastly, being able to "sell" or convince clients to take specific financial steps is crucial. This doesn't just mean selling products but effectively communicating the value of certain financial strategies or decisions. The best financial advisors have an insatiable appetite for learning. By attending workshops, they can delve deeper into specific topics. Seminars often bring together experts from various fields, offering a comprehensive view of the finance landscape. Conferences are especially invaluable, often featuring thought leaders and innovators who share their insights on the future of finance. These gatherings are not just about absorbing knowledge but also about networking, sharing experiences, and even collaborating on new initiatives or ideas. By prioritizing ongoing education, financial advisors ensure they're always ahead of the curve, ready to offer clients the latest and most informed advice. Financial advisors play a pivotal role in guiding individuals and organizations through the complexities of financial decision-making. Their expertise ensures informed choices in investments, insurance, retirement planning, and more. A solid educational foundation is crucial, with degrees such as Finance, Economics, Business Administration, and Accounting equipping advisors with analytical tools and credibility. Master's degrees, like Finance or Financial Planning, offer specialized knowledge for intricate financial landscapes, while certifications like CFA, CFP, and ChFC validate expertise and ethical responsibility. Education extends beyond degrees. Practical experience, like internships, shapes client interaction and sales insight. Soft skills, communication, empathy, persuasion, and building client relationships. Ongoing learning through workshops, conferences, offers updated insights. In an evolving financial world, education and practical skills are vital for advisors' success in guiding clients effectively.What Is a Financial Advisor?
Essential Degrees for Aspiring Financial Advisors
Bachelor's Degrees
Finance
Economics
Business Administration
Accounting
Master's Degrees
Master's in Finance
MBA With a Focus on Finance or Wealth Management
Master's in Financial Planning
Doctorate Degrees
PhD in Finance
Doctorate in Business Administration (DBA)

Financial Certifications for Financial Advisors
Certified Financial Planner (CFP)
Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA)
Chartered Financial Consultant (ChFC)

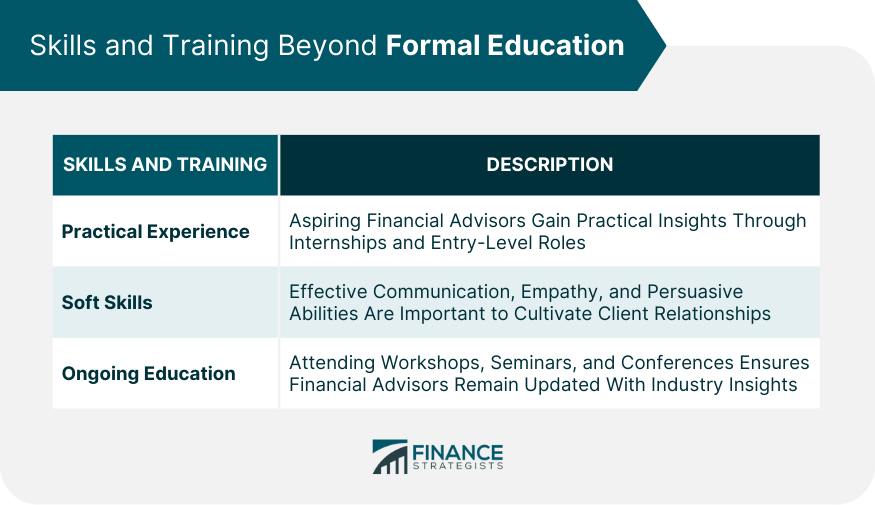
Skills and Training Beyond Formal Education
Practical Experience
Soft Skills
Ongoing Education
Conclusion
Financial Advisor Degree FAQs
A Financial Advisor Degree refers to formal education programs that provide knowledge and skills required to become a financial advisor.
Bachelor's degrees in Finance, Economics, Business Administration, and Accounting are crucial. Master's degrees in Finance, Financial Planning, or an MBA with a finance focus also enhance expertise.
Education equips advisors with analytical tools, credibility, and expertise to navigate complex financial landscapes and provide informed guidance to clients.
Certifications like Certified Financial Planner (CFP), Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA), and Chartered Financial Consultant (ChFC) validate expertise in comprehensive planning, investment management, and financial complexities.
Workshops, seminars, and conferences provide opportunities to deepen expertise and network with peers, ensuring advisors offer clients the most relevant and informed financial advice.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











