The journey to becoming a financial advisor often begins with a bachelor's degree in a field such as finance, economics, accounting, or business. Courses in these fields provide a foundation in financial principles, accounting practices, and economic theory. Some aspiring advisors also pursue a master's degree in finance or a related field to further their understanding of complex financial concepts. Financial advisors need a combination of hard and soft skills. They require a strong understanding of financial markets and investment strategies, as well as skills in data analysis and financial forecasting. Soft skills include communication and listening abilities, as they often have to explain complex financial concepts to clients and understand their needs and goals. Empathy, patience, and integrity are also crucial as they build trusting relationships with their clients. Most financial advisors also need to obtain licenses or certifications. For example, selling securities typically require licenses such as Series 6, Series 7, or Series 63. Many advisors also seek certification as a Certified Financial Planner (CFP) or Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) to boost their credibility and enhance their professional standing. Practical experience is another key aspect of becoming a financial advisor. This often involves internships or entry-level roles at financial institutions or advisory firms. Such experiences can help aspiring advisors gain a real-world understanding of the industry and develop the skills they need to succeed. Continuing education is crucial in the financial advisory field. This could mean seeking additional certifications, attending industry conferences, or enrolling in advanced degree programs. Success as a financial advisor relies heavily on strong client relationships. Advisors need to consistently provide excellent service, maintain open and honest communication, and show genuine interest in their clients' financial goals. The financial industry is continually evolving. Staying informed about market trends, changes in financial regulations, and economic shifts is crucial for providing accurate and timely advice. Financial advisors are entrusted with sensitive financial information and tasked with guiding important financial decisions. Upholding high ethical standards and maintaining client trust is paramount for a successful career. There are several types of financial advisors, each specializing in different aspects of financial planning and investment management. A CFP specializes in comprehensive financial planning. They provide advice on a wide range of financial matters, from retirement planning to tax management, estate planning, and insurance. A CFA is an investment management specialist. They possess expert knowledge in portfolio management and investment analysis, making them ideal for individuals and organizations seeking investment advice. A PFS is a type of financial advisor who has a broad range of financial planning knowledge but also has a solid background in accounting. These advisors are ideal for those with complex tax situations or those who require a more in-depth analysis of their finances. While a CPA is not traditionally seen as a financial advisor, many CPAs offer financial advisory services, particularly in the realm of tax planning and strategy. They are ideal for individuals or businesses with complex tax situations. One of the most rewarding aspects of being a financial advisor is the ability to help individuals and families reach their financial goals. This could mean helping a young couple plan for their first home purchase, aiding an individual in managing their retirement savings, or guiding a family as they navigate estate planning. The financial advisory field offers significant flexibility. Advisors often have the option to work in various settings, from large financial institutions to small independent firms or even self-employment. There's also ample room for growth and specialization in areas such as retirement planning, wealth management, or estate planning. Financial advisors can earn a good income, especially as they gain experience and build a larger client base. They typically earn a fee or commission based on the services they provide or the assets they manage, which can lead to substantial earnings for successful advisors. The financial world is constantly changing, and advisors must stay up-to-date with the latest trends, regulations, and strategies. This offers the opportunity for continuous learning and professional development. The pathway to becoming a financial advisor requires significant educational and licensing commitments. This includes obtaining a bachelor's degree, completing specific coursework, passing licensing exams, and potentially pursuing further certifications. The field is highly competitive, and advisors must constantly strive to stay ahead. They also need to be able to handle the pressure and stress that can come from managing significant amounts of money and making critical financial decisions. Being a financial advisor carries significant responsibility. Advisors are responsible for helping clients navigate their financial futures, which can be a source of stress, especially during uncertain economic times. The financial industry is heavily regulated, and these regulations can change frequently. Advisors need to stay informed about these changes to provide accurate advice and ensure compliance. Becoming a financial advisor requires a strong educational foundation, necessary skills, and often, obtaining licenses and certifications. Sustaining a successful career involves continuous education, building strong client relationships, staying informed about market trends, and upholding ethical standards. There are different types of financial advisors, each specializing in various aspects of financial planning and investment management. Benefits of this career include the ability to help others achieve their financial goals, career flexibility, potential for high income, and continuous learning opportunities. However, drawbacks include the rigorous education and licensing requirements, the competitive and demanding nature of the field, high responsibility and stress levels, and the need to stay updated with changing financial laws and regulations. Overall, aspiring financial advisors should be prepared for both the rewards and challenges that come with this fulfilling career.Pathway to Become a Financial Advisor
Educational Requirements
Necessary Skills and Qualities
License and Certification
Work Experience and Internships

Sustain a Successful Career as a Financial Advisor
Continue Education and Professional Development
Build and Maintain Client Relationships
Stay Informed About Financial Market Trends
Uphold Ethical Standards and Trust

Different Types of Financial Advisors
Certified Financial Planner (CFP)
Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA)
Personal Financial Specialist (PFS)
Certified Public Accountant (CPA)

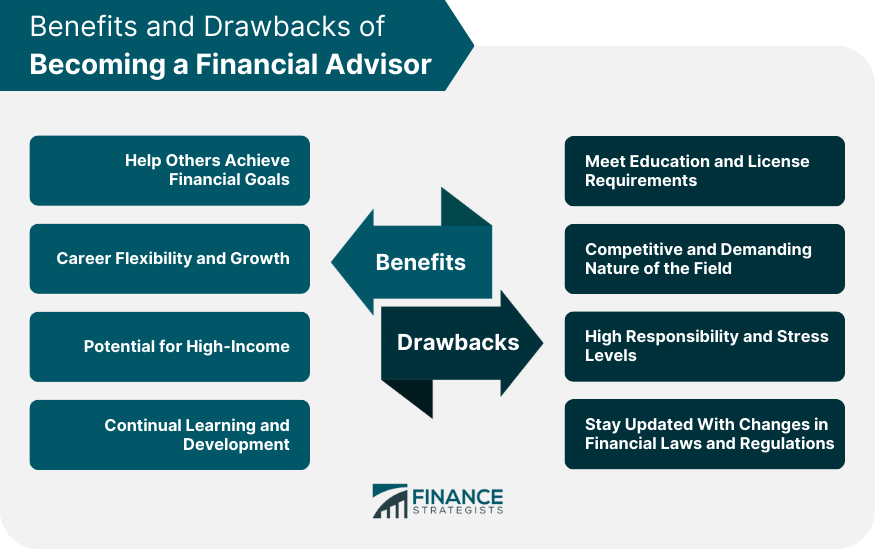
Benefits of Becoming a Financial Advisor
Help Others Achieve Their Financial Goals
Career Flexibility and Growth
Potential for High Income
Continual Learning and Development
Drawbacks of Becoming a Financial Advisor
Meet Education and License Requirements
Competitive and Demanding Nature of the Field
High Responsibility and Stress Levels
Stay Updated With Changes in Financial Laws and Regulations
Conclusion
How to Become a Financial Advisor FAQs
To become a financial advisor, one typically needs a bachelor's degree in finance, economics, accounting, or business. Some professionals may also pursue a master's degree in a related field to further enhance their knowledge and skills.
Financial advisors need a combination of hard and soft skills. Hard skills include a strong understanding of financial markets and investment strategies, while soft skills such as communication, empathy, patience, and integrity are essential for building trusting relationships with clients.
Financial advisors often obtain certifications such as Certified Financial Planner (CFP), Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA), Personal Financial Specialist (PFS), or Certified Public Accountant (CPA). These certifications enhance credibility and can be beneficial in career progression.
Benefits include the ability to help individuals and families achieve their financial goals, significant career flexibility, potential for high income, and continuous opportunities for learning and professional development.
Challenges include meeting the educational and licensing requirements, dealing with the competitive nature of the field, managing high-stress levels that come with significant responsibility, and staying updated with frequently changing financial laws and regulations.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











