A professional risk manager (PRM) is a financial professional who specializes in identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks within an organization. PRMs work in a variety of industries, including banking, insurance, investment, and consulting. They use their expertise to help organizations manage risks related to market fluctuations, regulatory compliance, operational failures, and other potential threats to the organization's financial stability and reputation. The PRM certification is a well-respected credential for risk management professionals and is designed to help those professionals develop a detailed understanding of financial risk management. The designation can be helpful for all types of risk managers, financial analysts, and CEOs since the program prepares candidates with skills considered important by business professionals. PRMs work with other professionals in the organization to identify potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them. They monitor market and industry trends to identify potential risks and opportunities for the organization. PRMs also collaborate with other departments, such as finance, legal, and operations, to implement risk management initiatives and ensure that the organization is compliant with regulations and industry standards. As a professional risk manager, there are several key job responsibilities that you will be expected to fulfill. These include: One of the primary responsibilities of a PRM is to identify and assess potential risks that could affect the organization. This includes analyzing financial data, market trends, and other relevant information to determine various risks' likelihood and potential impact. PRMs must be able to think critically and strategically to anticipate and mitigate potential threats to the organization. Once potential risks have been identified and assessed, PRMs must work with other departments within the organization to develop risk management strategies and policies. This may involve creating risk management plans, implementing risk mitigation measures, and developing policies and procedures to minimize the impact of potential risks. PRMs must stay up-to-date on market and industry trends that could impact the organization's financial stability and long-term success. This involves monitoring economic indicators, industry developments, and other relevant information to identify potential risks and opportunities. PRMs must be able to interpret and analyze complex data to make informed decisions about risk management. Risk management is a cross-functional activity that requires collaboration with other departments within the organization. PRMs must work closely with other professionals, such as finance, legal, and operations, to implement risk management initiatives and ensure that the organization complies with regulations and industry standards. This may involve communicating risk management strategies and policies, providing training to employees, and coordinating risk management activities across departments. To become a professional risk manager, several educational and professional requirements must be met. Professional Risk Managers’ International Association (PRMIA) requires candidates to have a graduate degree, a Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) designation, a bachelor's degree, and two years of full-time work experience in the financial services industry or any industry's risk management department. Candidates can also have four years of full-time work experience in these fields. Candidates must also have a current PRMIA membership. Membership can be obtained by visiting the PRMIA website and submitting an application. To become a successful PRM, candidates should possess strong analytical and problem-solving skills. They should also have excellent communication and interpersonal skills, as they will be working with individuals from different departments and backgrounds. In addition, PRMs should have a strong understanding of financial markets, instruments, and products. They should be familiar with financial modeling techniques like Monte Carlo simulations and value-at-risk (VaR) models. Knowledge of regulatory requirements and industry standards is also important. To become a PRM, candidates must complete the PRM Designation program offered by PRMIA. The program consists of two exams covering a wide range of topics related to financial risk management. The exams can be taken in any order, and candidates have three years to complete the program. In addition to the PRM designation, candidates can also obtain other risk management certifications, such as the Certified Risk Manager (CRM), Financial Risk Manager (FRM), Certified Risk Management Professional (CRMP), and Associate Risk Management Professional (ARMP). These certifications may be valuable for individuals looking to specialize in a particular area of risk management or advance their careers. To become a professional risk manager, candidates must complete the PRM Designation program, which includes two exams that cover a wide range of topics related to financial risk management. Here is an overview of the PRM certification process: The PRM Designation program is offered by the Professional Risk Managers' International Association. The program is designed to provide candidates with the knowledge and skills needed to manage financial risk in a variety of industries. The program consists of two exams that cover a wide range of topics related to financial risk management. Candidates have three years to complete the PRM Designation program. The enrollment period begins the day the candidate's successful PRM application is submitted, and candidates are given 9-12 months of study time before attempting the exams. The PRM exams were recently updated and now consist of two exams instead of four. Candidates who are qualified CFAs or in a PRMIA-accredited university program may be able to skip Exam 1. Exam 1 has 60 multiple-choice questions and tests candidates' knowledge of finance theory, instruments, and markets and their ability to apply the mathematical foundations of risk measurement. Exam 2 has 84 multiple-choice questions and tests candidates' knowledge of risk management frameworks, asset liability management, funds transfer pricing, the specific risk areas of operational risk, credit risk, counter-party credit risk, and market risk, as well as the PRMIA standards and governance. Exam 2 also includes a Practicum Assessment that assesses the ability to apply lessons learned from the PRMIA case studies using knowledge from across the PRM syllabus. Earning the PRM certification requires passing two rigorous exams that test candidates on their knowledge of finance theory, risk management frameworks, and more. Here are some tips to help you prepare for and pass the PRM exams: The PRM exams are 100% multiple-choice questions. Exam 1 has 60 questions, and Exam 2 has 84 questions. Exam 1 tests candidates on their knowledge of finance theory, instruments, and markets and their ability to apply the mathematical foundations of risk measurement. Exam 2 tests candidates on their knowledge of risk management frameworks, asset liability management, funds transfer pricing, specific areas of operational risk, credit risk, counter-party credit risk, and market risk, as well as the PRMIA standards and governance. Give yourself plenty of time to prepare for the exams by creating a study plan that includes regular study sessions and practice exams. Use study materials provided by PRMIA or other reputable sources, and focus on areas where you need the most improvement. The PRMIA provides a range of study resources, including online courses, practice exams, and study guides. Take advantage of these resources to help you prepare for the exams. Practice answering sample questions to understand the exam format and content. This will help you identify areas where you need to focus your studying. Seek feedback from others who have taken the PRM exams or have experience in risk management. This can help you identify areas where you may need more practice or clarification. During the exams, manage your time wisely by allocating enough time to answer each question thoroughly. If you are unsure about a question, move on to the next one and come back to it later. Finally, stay calm and focused during the exams. Do not let anxiety or stress get the best of you. Take deep breaths, stay hydrated, and stay focused on answering each question to the best of your ability. By following these tips and dedicating enough time and effort to prepare, you can increase your chances of passing the PRM exams and earning this prestigious certification. Earning the professional risk manager certification can open up a wide range of career opportunities in the financial services industry and beyond. Here are some common job titles and positions for PRMs: Risk Manager Risk Analyst Chief Risk Officer (CRO) Quantitative Analyst Portfolio Manager Compliance Officer Internal Auditor Credit Risk Manager Operational Risk Manager These positions are typically found in banks, insurance companies, consulting firms, and other financial services organizations. However, many non-financial organizations also employ PRMs to manage various types of risk. PRMs can follow various career paths depending on their interests and skills. Some common career paths for PRMs include: Risk Management: Many PRMs start their careers in risk management and progress to more senior positions, such as risk manager or chief risk officer. Quantitative Analysis: PRMs with a strong background in mathematics and statistics may choose to specialize in quantitative analysis, which involves using advanced analytical techniques to identify and manage risk. Portfolio Management: PRMs with experience in investment management may choose to specialize in portfolio management, which involves selecting and managing a portfolio of investments to achieve specific financial goals. Consulting: PRMs with strong communication and problem-solving skills may choose to work as consultants, helping organizations manage their risk and improve their overall financial performance. According to Salary.com, the median salary for a risk manager in the United States is $128,618 per year, with salaries ranging from $110,446 to $138,535 depending on location, experience, and other factors. However, PRMs with more experience and specialized skills may earn significantly more. In addition to base salary, many PRMs receive bonuses, stock options, and other forms of compensation based on their organization's performance and overall financial performance. PRMs who work in consulting may earn higher salaries and more variable compensation depending on the projects they work on. A professional risk manager is a financial professional who specializes in identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks within an organization. PRMs work in a variety of industries and use their expertise to help organizations manage risks related to market fluctuations, regulatory compliance, operational failures, and other potential threats to the organization's financial stability and reputation. To become a PRM, candidates must meet educational and professional requirements and complete the PRM Designation program, which includes passing two rigorous exams. PRMs possess strong analytical and problem-solving skills, have excellent communication and interpersonal skills, and understand financial markets, products, and regulatory requirements. Obtaining the PRM certification can open up a wide range of career opportunities and paths, with average salaries ranging from $110,446 to $138,535 depending on experience, skills, and location. If you are interested in becoming a PRM, it is recommended to seek help from a financial advisor to guide you through the process and enhance your chances of success.What Is a Professional Risk Manager (PRM)?
Job Responsibilities of Professional Risk Manager (PRM)
Identifying and Assessing Potential Risks
Developing Risk Management Strategies and Policies
Monitoring and Analyzing Market and Industry Trends
Collaborating With Other Departments to Implement Risk Management Initiatives

How to Become a Professional Risk Manager (PRM)
Educational and Professional Requirements
Key Skills and Competencies Needed for a Career in Risk Management
Relevant Certifications and Training Programs

Professional Risk Manager (PRM) Exams
Overview of the PRM Certification Process
Exam Format and Content
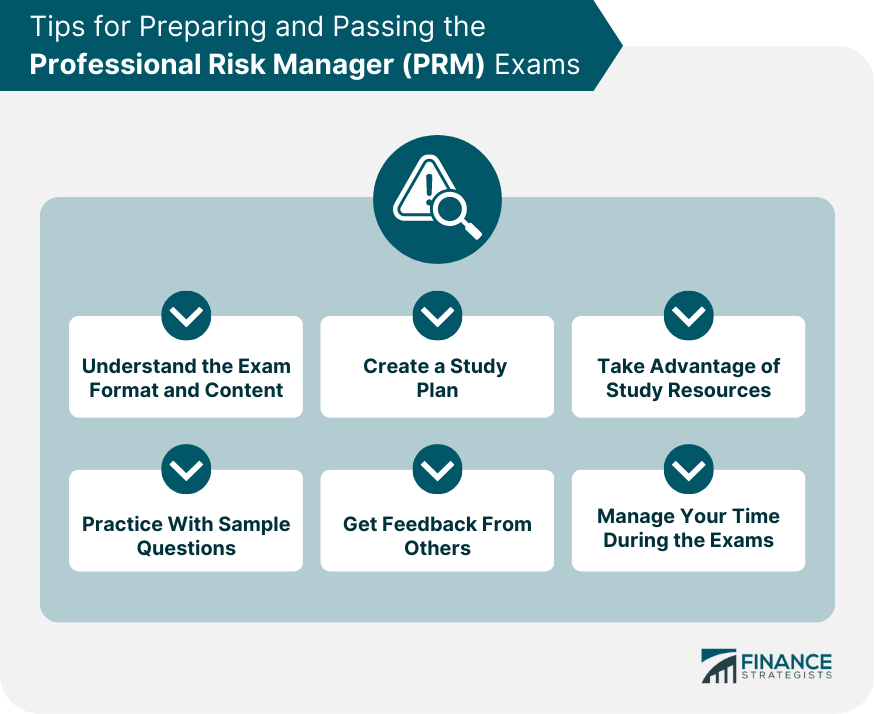
Tips for Preparing and Passing the Exams
Understand the Exam Format and Content
Create a Study Plan
Take Advantage of Study Resources
Practice With Sample Questions
Get Feedback From Others
Manage Your Time During the Exams
Stay Calm and Focused
Professional Risk Manager (PRM) Career Opportunities and Advancement
Career Paths and Progression
Salary and Compensation Information
Final Thoughts
Professional Risk Manager (PRM) FAQs
A Professional Risk Manager (PRM) is a financial professional who specializes in identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks within an organization.
The primary responsibilities of a PRM include identifying and assessing potential risks, developing risk management strategies and policies, monitoring and analyzing market and industry trends, and collaborating with other departments to implement risk management initiatives.
To become a PRM, candidates must complete the PRM Designation program offered by the Professional Risk Managers' International Association (PRMIA). Candidates are required to have a graduate degree, a chartered financial analyst (CFA) designation, a bachelor's degree, and two years of full-time work experience in the financial services industry or any industry's risk management department.
To become a successful PRM, candidates should possess strong analytical and problem-solving skills, excellent communication and interpersonal skills, and a strong understanding of financial markets, instruments, and products.
PRMs can follow various career paths depending on their interests and skills. Some common career paths for PRMs include risk management, quantitative analysis, portfolio management, and consulting. PRMs typically work in banks, insurance companies, consulting firms, and other financial services organizations.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











