Assisted living is a type of residential care option designed to provide older adults with a combination of housing, personal care services, and health-related support. These communities are intended for individuals who may need assistance with activities of daily living (ADLs) such as bathing, dressing, grooming, and medication management, but who do not require the level of medical care provided in a nursing home. These facilities aim to promote independence, dignity, and quality of life for residents while offering a safe and supportive environment. Independent living communities cater to seniors who can largely manage their daily activities without assistance but prefer a community setting with access to amenities and social opportunities. These communities often provide maintenance-free living and various recreational activities for residents. Assisted living communities provide a higher level of care than independent living communities, offering assistance with daily tasks such as bathing, dressing, and medication management. Residents typically live in private apartments or rooms and have access to common areas, dining services, and various activities. Memory care communities are specifically designed for seniors with Alzheimer's disease or other forms of dementia. These facilities provide a secure environment with specialized care, structured activities, and trained staff to address the unique needs of residents with cognitive impairments. CCRCs offer a comprehensive range of care options, from independent living to skilled nursing care, on a single campus. As residents' needs change over time, they can transition between different levels of care within the community, ensuring continuity and familiarity. SNFs provide 24-hour medical care and rehabilitation services for seniors recovering from illness or injury or those with complex medical needs. While not strictly an assisted living option, SNFs may be a necessary step in a senior's care journey. Assisted living facilities provide help with activities of daily living (ADLs), such as bathing, dressing, grooming, and mobility assistance. Staff members work with residents to ensure they maintain their dignity and independence while receiving the support they need. Residents in assisted living facilities often receive assistance with medication administration and management, ensuring they take their medications correctly and on time. This service reduces the risk of medication errors and related health complications. Assisted living communities typically offer communal dining options, providing residents with nutritious meals and an opportunity for social interaction. Some facilities also offer private dining areas and specialized meal plans to accommodate individual preferences and dietary needs. Assisted living facilities handle housekeeping and laundry tasks, allowing residents to enjoy a clean, comfortable living environment without the burden of these chores. Many assisted living communities offer transportation services for residents to attend medical appointments, shopping trips, and recreational outings, promoting independence and engagement in the community. Assisted living facilities often provide a wide range of activities and events, including fitness classes, art workshops, social gatherings, and educational programs, to encourage resident engagement and promote overall well-being. Assisted living communities offer a secure environment with 24-hour staff presence, emergency call systems, and safety features to reduce the risk of falls and other accidents. By providing opportunities for social interaction and recreational activities, assisted living communities help seniors build relationships and avoid the isolation often experienced in aging. Assisted living facilities often have medical staff on-site or on-call, providing residents with access to timely healthcare and monitoring of chronic conditions. Residents in assisted living communities maintain their independence and receive personalized care tailored to their specific needs, promoting a higher quality of life and a sense of autonomy. Assisted living communities provide relief for family caregivers, allowing them to rest and recharge while knowing their loved one is receiving professional care and support. Before selecting an assisted living facility, it's essential to evaluate the senior's needs, preferences, and budget. Consider factors such as required level of care, desired amenities, location, and size of the community. Visit multiple assisted living facilities to compare the quality of care, atmosphere, and services offered. Observe staff interactions with residents, cleanliness, and the overall environment to ensure the facility is a good fit for the senior. Assisted living costs can vary widely based on location, services, and amenities. Explore financial options such as long-term care insurance, veterans benefits, and Medicaid waivers to help cover costs. Some facilities may also offer financial assistance programs or sliding scale fees. Familiarize yourself with state regulations and licensing requirements for assisted living facilities. Ensure the facility you choose complies with these standards and maintains a positive reputation in the community. Assisted living facilities are increasingly adopting innovative technologies to improve resident care, safety, and engagement. Examples include telemedicine, remote monitoring systems, and virtual reality experiences for cognitive stimulation. Modern assisted living communities are embracing person-centered care models that prioritize the individual's needs, preferences, and goals. This approach fosters a sense of belonging and purpose among residents. Some assisted living facilities are implementing intergenerational programs that connect seniors with younger generations, promoting mutual understanding, shared learning, and a sense of community. Assisted living communities are increasingly adopting sustainable practices, such as energy-efficient buildings, water conservation, and waste reduction, to minimize their environmental impact and promote healthier living spaces. As the global population ages, the demand for assisted living services will continue to grow. The industry must adapt to accommodate this growing need by expanding capacity and developing innovative care models. The high cost of assisted living remains a significant barrier for many seniors and their families. Policymakers and industry leaders must work together to develop solutions that ensure assisted living services are accessible to all who need them. Assisted living facilities face challenges in recruiting and retaining qualified staff to meet the complex needs of an aging population. Investing in staff training, competitive wages, and supportive work environments will be crucial for maintaining high-quality care. As the senior population becomes more diverse, assisted living facilities must adapt their services to cater to a broader range of cultural, social, and medical needs. This may include offering specialized care programs, language support, and culturally sensitive environments. Assisted living plays a critical role in providing seniors with a supportive, safe, and engaging environment as they age. By understanding the different types of facilities, services, and benefits available, families can make informed decisions to ensure their loved ones receive the care they need. The industry continues to evolve, with new trends and innovations shaping the future of senior care. By addressing the challenges and seizing the opportunities presented by a rapidly aging population, assisted living communities can promote a high quality of life for seniors and their families.Assisted Living: Definition
Types of Assisted Living Facilities
Independent Living Communities
Assisted Living Communities
Memory Care Communities
Continuing Care Retirement Communities (CCRCs)
Skilled Nursing Facilities (SNFs)
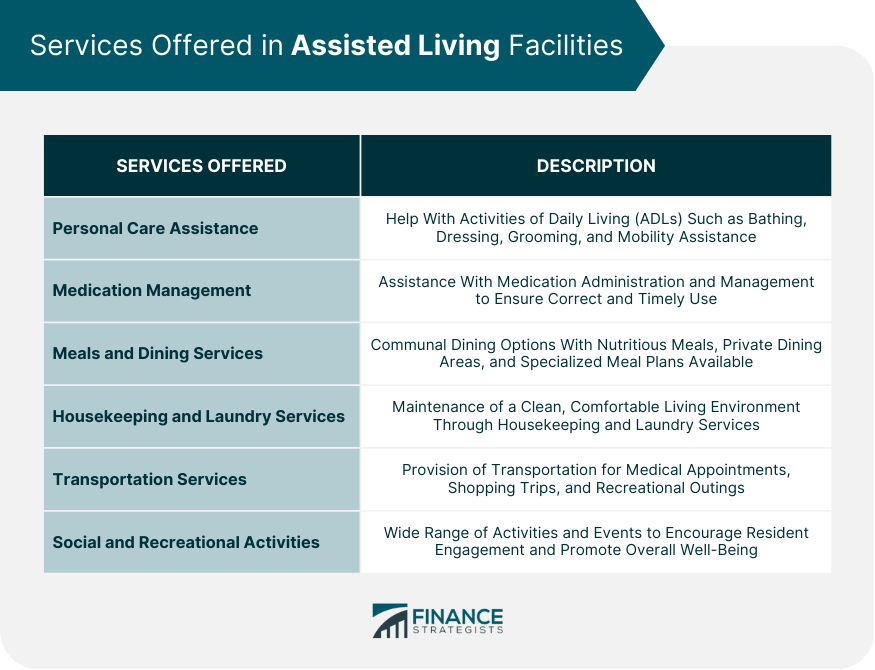
Services Offered in Assisted Living Facilities
Personal Care Assistance
Medication Management
Meals and Dining Services
Housekeeping and Laundry Services
Transportation Services
Social and Recreational Activities
Benefits of Assisted Living
Increased Safety and Security
Social Engagement and Companionship
Access to Medical and Health Care
Independence and Personalized Care
Respite for Family Caregivers
Choosing an Assisted Living Facility
Assessing Individual Needs
Touring and Evaluating Facilities
Evaluating Costs and Financial Options
Understanding Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Trends and Innovations in Assisted Living
Technological Advancements
Holistic and Person-Centered Care
Intergenerational Programs
Sustainable and Environmentally-Friendly Practices
Challenges and Future Outlook
Addressing the Growing Demand for Assisted Living
Ensuring Affordability and Accessibility
Maintaining Quality of Care and Staff Retention
Adapting to Changing Needs and Demographics
Conclusion
Assisted Living FAQs
Assisted living is a type of long-term care that provides support and assistance with daily activities, such as bathing, dressing, and medication management, to seniors or individuals with disabilities who are unable to live independently.
The cost of assisted living varies depending on several factors such as location, level of care required, and amenities offered. On average, the cost can range from $3,500 to $5,000 per month.
Assisted living services typically include meals, housekeeping, laundry, transportation, social activities, and assistance with activities of daily living (ADLs) such as bathing, dressing, and grooming.
When choosing an assisted living facility, it is important to consider factors such as location, cost, level of care, available amenities, staff qualifications, and reputation. It's recommended to tour multiple facilities and ask questions to ensure the facility meets your needs.
Medicare typically does not cover the cost of assisted living. However, some long-term care insurance policies may cover a portion of the cost. Medicaid may also provide assistance for those who meet the eligibility requirements.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











