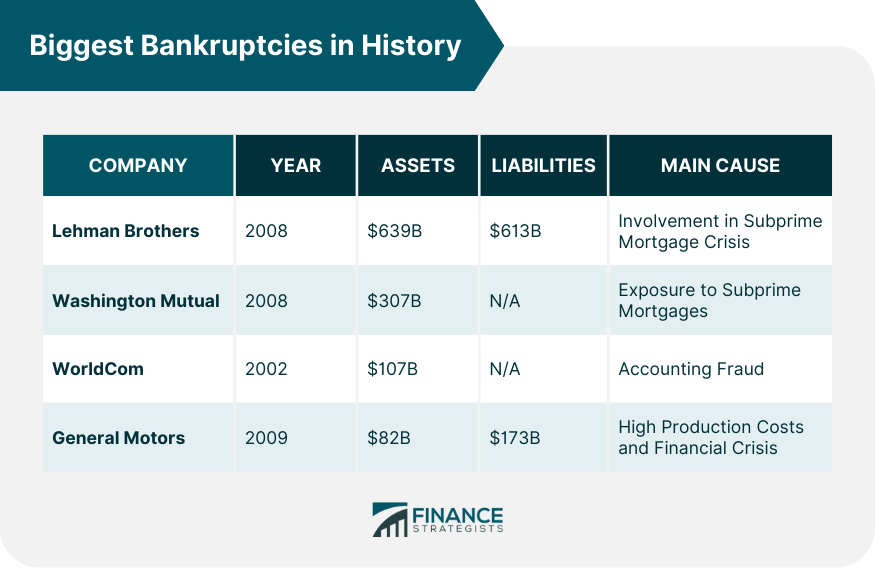
Lehman Brothers, a global financial services firm, filed for bankruptcy in 2008 with $639 billion in assets and $613 billion in liabilities. This bankruptcy is the largest in U.S. history and was a key event in the subprime mortgage crisis that led to the Great Recession. The bankruptcy was primarily caused by Lehman Brothers' involvement in the subprime mortgage crisis, where they had significant exposure. When the housing market collapsed, the firm found itself holding a vast amount of worthless assets. The fall of Lehman Brothers sent shockwaves around the globe. It exacerbated the financial crisis of 2008 and led to the most severe global recession since the Great Depression. Washington Mutual, a savings bank holding company and the former owner of Washington Mutual Bank went into receivership in 2008. With over $307 billion in assets, it was the largest bank failure in American history. Washington Mutual's failure was largely due to its exposure to subprime mortgages. It experienced significant losses when the value of its mortgage-backed securities plummeted as a result of the housing market crash. The bank was seized by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) and sold to JPMorgan Chase. This event marked a critical point in the financial crisis. Telecommunications company WorldCom filed for bankruptcy in 2002 after a series of accounting scandals. At the time, with $107 billion in assets, it was the largest bankruptcy in U.S. history. WorldCom's bankruptcy was primarily caused by fraudulent accounting practices that inflated the company's assets by billions of dollars. WorldCom's downfall led to stricter regulations in accounting practices. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act, designed to protect investors from fraudulent financial reporting by corporations, was passed in response. General Motors (GM), one of the world's largest automakers, filed for bankruptcy in 2009. At the time, GM had $82 billion in assets and $173 billion in liabilities. Several factors led to GM's bankruptcy, including high production costs, an overemphasis on SUVs and trucks despite rising fuel costs, and the 2008 financial crisis, which resulted in a massive drop in auto sales. After restructuring, a leaner, more focused GM emerged from bankruptcy and returned to profitability. The U.S. government supported the process with a massive bailout to protect jobs and the overall economy. Major bankruptcies have had far-reaching impacts on global economies, leading to significant societal and regulatory changes. They affect financial markets and investor confidence, disrupt supply chains, lead to job losses, and often trigger regulatory changes to prevent similar incidents in the future. Bankruptcies of major corporations can have profound effects on global economies. The bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers, for example, triggered a global financial crisis. Major bankruptcies often expose regulatory weaknesses and lead to significant changes in laws and regulations. For instance, the Enron and WorldCom scandals led to the enactment of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act to improve corporate governance and accountability. Bankruptcies can lead to significant losses for shareholders and employees. Shareholders may lose most or all of their investments, and employees may lose their jobs, pensions, or both. Significant bankruptcies in history provide crucial lessons about the importance of financial transparency, the consequences of financial mismanagement, and the vital role of risk management and corporate governance. These bankruptcies underscore the importance of sound risk management and robust corporate governance in maintaining financial stability. Companies that ignore these principles are often more prone to failure. Transparency in financial reporting is critical to maintaining investor trust. Fraudulent practices like those at WorldCom can lead to catastrophic outcomes. Financial mismanagement can lead to severe consequences, including bankruptcy. This lesson is vividly illustrated by the bankruptcy of GM, which was largely due to financial mismanagement. Bankruptcy laws and regulations, the bankruptcy process itself, and the roles of creditors and stakeholders in the process are all essential elements of the bankruptcy system. Bankruptcy laws and regulations provide the framework within which bankruptcies are handled. These laws protect the rights of both the debtor and creditors and ensure an orderly process. The bankruptcy process is designed to provide a fair mechanism for dealing with insolvent entities. It ensures that assets are distributed to creditors in an orderly and equitable manner. Creditors and stakeholders play a crucial role in the bankruptcy process. They are involved in negotiating repayment plans, and their cooperation is crucial for a successful outcome. Throughout history, significant corporate bankruptcies such as Lehman Brothers, Washington Mutual, WorldCom, and General Motors have not only reshaped industries but also triggered major financial and societal shifts. These financial collapses underscore the crucial importance of financial transparency, risk management, and robust corporate governance. Fraudulent practices and financial mismanagement can lead to catastrophic outcomes, inflicting substantial losses on shareholders and employees while also impacting global economies. On the regulatory front, such failures have often exposed systemic weaknesses, catalyzing changes to enhance corporate accountability and governance. Overall, these episodes serve as stark reminders of the potential repercussions of financial instability, emphasizing the vital role of bankruptcy laws, the insolvency process, and stakeholders in preserving economic order. Thus, the lessons from these events are pivotal, providing insights to avert future financial calamities.What Are the Biggest Bankruptcies in History?
Lehman Brothers
Washington Mutual
WorldCom
General Motors
Economic and Societal Impact of Major Bankruptcies
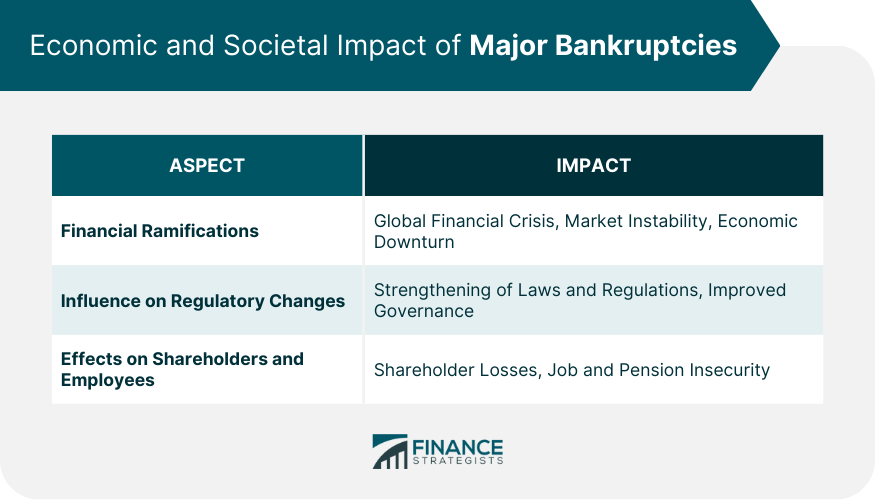
Financial Ramifications on the Global Economy
Influence on Regulatory Changes
Effects on Shareholders and Employees
Critical Lessons From the Biggest Bankruptcies in History
Role of Risk Management and Corporate Governance
Importance of Financial Transparency
Consequences of Financial Mismanagement
Role of Legal and Financial Systems in Bankruptcies
Bankruptcy Laws and Regulations
Bankruptcy Process
Role of Creditors and Stakeholders in the Process
Final Thoughts
Biggest Bankruptcies in History FAQs
The largest bankruptcy in history was that of Lehman Brothers, a global financial services firm. In 2008, it filed for bankruptcy with $639 billion in assets and $619 billion in debt.
The fall of Lehman Brothers sent shockwaves around the world, exacerbating the financial crisis of 2008 and leading to the most severe global recession since the Great Depression.
The biggest bankruptcies in history underscore the importance of sound risk management, robust corporate governance, and financial transparency. They also highlight the severe consequences of financial mismanagement.
Washington Mutual's bankruptcy was largely due to its heavy exposure to subprime mortgages. When the housing market crashed, the bank experienced significant losses as the value of its mortgage-backed securities plummeted.
The bankruptcy process is designed to provide a fair mechanism for dealing with insolvent entities. Bankruptcy laws and regulations protect the rights of both the debtor and creditors, and ensure that assets are distributed to creditors in an orderly and equitable manner.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











