Bankruptcy is a legal procedure that can provide relief to individuals and businesses struggling with overwhelming debt. There are several types of bankruptcy filings, but the two most common types are Chapter 7 and Chapter 13. Chapter 7 bankruptcy, or “liquidation” bankruptcy, requires selling off the debtor’s assets to repay the creditors. Under Chapter 7 bankruptcy, a trustee is appointed to oversee the liquidation of the debtor’s assets, and the proceeds are distributed to creditors by a predetermined priority system. Chapter 13 bankruptcy is sometimes referred to as “reorganization” bankruptcy, as it involves the reorganization of the debtor’s debts into a repayment plan. Under Chapter 13 bankruptcy, the debtor is allowed to keep their assets but must use their disposable income to make regular payments to creditors over three to five years. Several key differences between Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 bankruptcy should be considered when deciding which option is right for you. The following are some main differences: Under Chapter 7 bankruptcy, the debtor’s assets are liquidated to pay off creditors. Under Chapter 13 bankruptcy, the debtor can keep their assets but must use their disposable income to pay creditors over three to five years. Chapter 7 bankruptcy does not involve a repayment plan, as the debtor is not required to make ongoing payments to creditors. On the other hand, Chapter 13 bankruptcy demands the debtor to present a repayment plan to the court that must be accepted by the trustee and the creditors. The debtor has to make regular payments to the trustee, who then distributes the money to the creditors following the plan. Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 bankruptcy allow for the release of particular types of debts, such as personal loans, credit card debt, and medical bills. However, some debts can only be discharged under Chapter 13 bankruptcy, such as from willful or malicious injury to another person or property and debts incurred while driving under the influence of drugs or alcohol. The time it takes to receive a discharge of debts varies between Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 bankruptcy. In a Chapter 7 case, discharge is typically granted within a few months of filing. In a Chapter 13 case, the discharge is granted after the repayment plan, which can take three to five years. When deciding which type of bankruptcy to file, it is important to consider several factors that may influence the outcome of your case. The following are some of the main factors to consider: Chapter 7 bankruptcy is generally better suited for individuals with a large amount of unsecured debt, such as credit card debt and medical bills. In contrast, Chapter 13 bankruptcy may be a better option for individuals with a lower level of debt or secured debts, such as a mortgage or car loan, that they wish to keep current. The type of debt you have may also influence your decision to file for Chapter 7 or Chapter 13 bankruptcy. As mentioned earlier, some debts can only be discharged under Chapter 13 bankruptcy, such as debts arising from willful or malicious injury to another person or property. The eligibility requirements for Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 bankruptcy differ. If you do not pass the means test for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, or if your debts exceed the threshold for Chapter 13 bankruptcy, you may not be eligible to file under that chapter. It is essential to consider your objectives for filing for bankruptcy. If your primary goal is to discharge your debts and start fresh, Chapter 7 bankruptcy may be the better option. If you are primarily concerned with keeping your assets or catching up on missed mortgage or car payments, Chapter 13 bankruptcy may be more appropriate. Bankruptcy is a legal process that can relieve those struggling with overwhelming debt. The two most common types of bankruptcy are Chapter 7 and Chapter 13. Chapter 7 involves liquidating assets to pay off creditors, while Chapter 13 involves creating a repayment plan over three to five years. The decision to file for bankruptcy depends on several factors, including the level and type of debt, eligibility requirements, and goals for bankruptcy filing. Chapter 7 bankruptcy is suitable for those with a large amount of unsecured debt, while Chapter 13 is better for those with a lower level of debt or secured debts they wish to keep current. If you are struggling with debt and considering bankruptcy, it is essential to make an informed decision. Hiring a financial advisor can be a valuable investment in your financial future. They can help you understand your options, navigate the complex legal process, and develop a plan for rebuilding your financial future.Overview of Chapter 7 and 13 Bankruptcy
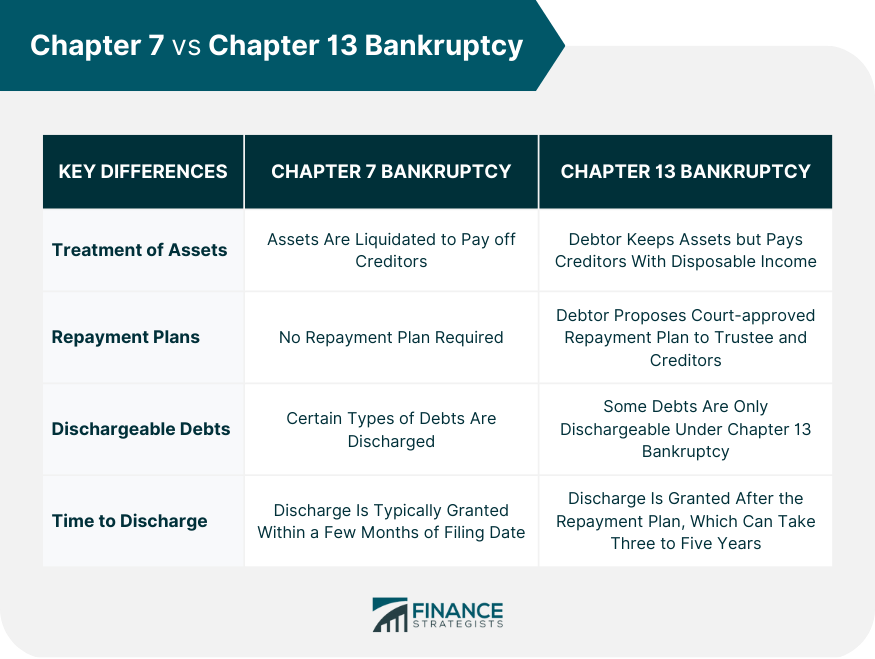
Key Differences Between Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
Treatment of Assets
Repayment Plans
Dischargeable Debts
Time to Discharge
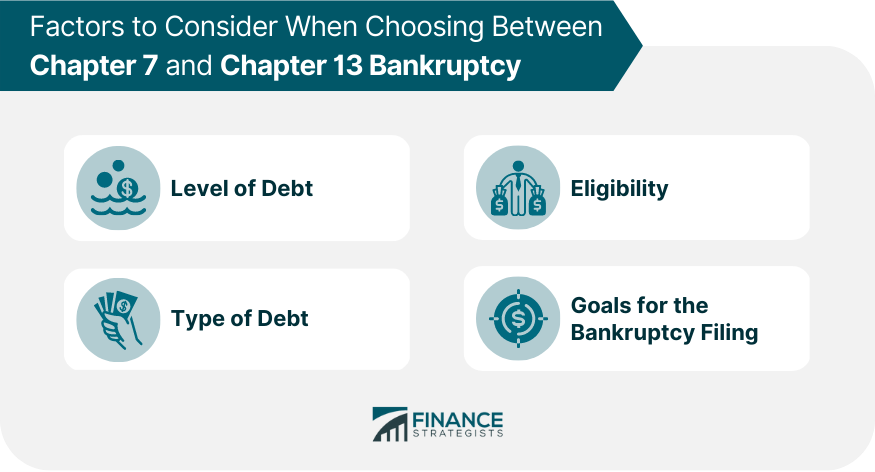
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
Level of Debt
Type of Debt
Eligibility
Goals for the Bankruptcy Filing
Conclusion
What Is the Difference Between Chapter 7 and Chapter 13 Bankruptcy? FAQs
Chapter 7 bankruptcy involves liquidating assets to pay off creditors, while Chapter 13 involves creating a repayment plan over three to five years.
To be eligible for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, the debtor must pass a means test comparing their income to the median income in their state.
To qualify for Chapter 13 bankruptcy, the debtor must have a regular income and unsecured debts below a certain threshold.
Factors to consider include the level and type of debt, eligibility requirements, and goals for the bankruptcy filing.
A financial advisor can provide guidance and support throughout the bankruptcy process, helping you understand your options, navigate the complex legal process, and develop a plan for rebuilding your financial future.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











