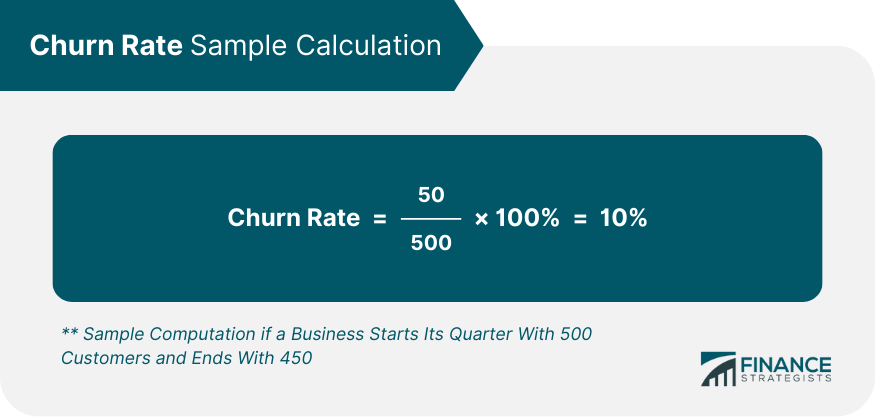
Churn rate, also known as attrition rate, refers to the percentage of subscribers to a service who discontinue their subscriptions within a given time period. For a company to grow its client base, its growth rate (i.e., its new customers) must exceed its churn rate. Understanding churn rate is vital for any business, especially in the sectors such as telecommunications, banking, or any subscription-based service. By determining their churn rate, businesses can identify issues in their customer retention strategies, thereby providing insights into customer dissatisfaction. It also plays a significant role in predicting revenue and is a reflection of customer loyalty and product acceptance. In the context of business finance, churn rate is a critical metric as it directly impacts profitability. Retaining existing customers is often less expensive than acquiring new ones, meaning a lower churn rate can lead to higher profits. Furthermore, a high churn rate may indicate deeper issues with the company's product or service that, if left unaddressed, could negatively impact its financial standing. Customer churn rate refers to the number of customers who stop using a company's product or service over a particular period. This rate is a crucial indicator of customer dissatisfaction, product-market fit, and customer service effectiveness. Revenue churn rate, on the other hand, measures the lost revenue due to customers churning. It's an important metric for businesses with varying customer payment amounts as it provides a clearer picture of the financial impact of customer churn. Gross churn rate represents the total loss of customers or revenue without accounting for growth from existing customers. Net churn rate, however, considers the growth through upselling or cross-selling to existing customers. While gross churn gives an overall churn picture, net churn offers deeper insights into the business' financial status. The basic formula to calculate churn rate is: This formula gives the churn rate as a percentage. Let's break it down to a step-by-step process: 1. Identify the period for which you want to calculate churn rate. 2. Note the number of customers at the beginning of this period. 3. Determine the number of customers at the end of the period. 4. Use the formula to calculate churn rate. For example, if a business starts its quarter with 500 customers and ends with 450, the churn rate would be: The quality of a product or service significantly impacts the churn rate. If customers perceive the quality to be poor, they are more likely to churn. Similarly, a high level of service can boost customer retention and, therefore, decrease the churn rate. Price competitiveness is another key factor. If a company's prices are significantly higher than its competitors without any added value, customers may choose to switch to cheaper alternatives, increasing the churn rate. Customer satisfaction and experience are vital in determining the churn rate. A positive experience can lead to higher customer loyalty and lower churn, while a negative experience can increase churn rate. Finally, market competition affects churn rate. In a highly competitive market, customers have more alternatives, leading to a potentially higher churn rate if businesses fail to differentiate themselves effectively. High churn rate directly impacts a company's revenue stream. If a company continually loses customers, its income decreases unless it can replace the lost customers at a faster rate, which is often more expensive than retaining existing customers. Customer Acquisition Cost is the total cost associated with gaining a new customer. If the churn rate is high, the company will need to spend more on marketing and sales efforts to replace lost customers, thereby increasing the CAC. Churn rate also impacts Customer Lifetime Value, which is the total revenue a company can expect from a single customer. A high churn rate means a lower CLV since customers are not maintaining a relationship with the company for a long period. An effective way to reduce churn rate is by improving customer service. Prompt and effective customer service can solve problems, resolve doubts, and improve overall customer satisfaction, leading to lower churn rates. If the company's pricing is competitive, it can reduce the churn rate. This strategy, however, should be balanced with the need to maintain profitability. A positive user experience can lead to higher customer retention. Companies should focus on improving their products or services and ensure they meet or exceed customer expectations. Onboarding is the process of introducing a new customer to a product or service. A well-executed onboarding process can enhance customer understanding and appreciation of the product or service, thereby reducing the churn rate. High churn rate directly impacts a company's revenue stream. If a company continually loses customers, its income decreases unless it can replace the lost customers at a faster rate, which is often more expensive than retaining existing customers. Customer Acquisition Cost is the total cost associated with gaining a new customer. If the churn rate is high, the company will need to spend more on marketing and sales efforts to replace lost customers, thereby increasing the CAC. Churn rate also impacts Customer Lifetime Value, which is the total revenue a company can expect from a single customer. A high churn rate means a lower CLV since customers are not maintaining a relationship with the company for a long period. An effective way to reduce churn rate is by improving customer service. Prompt and effective customer service can solve problems, resolve doubts, and improve overall customer satisfaction, leading to lower churn rates. If the company's pricing is competitive, it can reduce the churn rate. This strategy, however, should be balanced with the need to maintain profitability. A positive user experience can lead to higher customer retention. Companies should focus on improving their products or services and ensure they meet or exceed customer expectations. Onboarding is the process of introducing a new customer to a product or service. A well-executed onboarding process can enhance customer understanding and appreciation of the product or service, thereby reducing the churn rate. Churn rate is a critical metric in financial modeling, particularly for subscription-based businesses. It helps to predict future revenue, profitability, and growth of the company. Investors see a high churn rate as a risk, as it shows customers are not satisfied with the company's product or service. Thus, a low churn rate could make a company more attractive to investors. In SaaS (Software as a Service) business models, churn rate is a fundamental metric. Since revenue in SaaS companies is earned over time, retaining customers is crucial for business sustainability and growth. Churn rate, an essential business metric, indicates the percentage of customers who stop using a company's product or service over a given time period. This measure provides essential insights into customer satisfaction and loyalty and can significantly impact a business's financial health. There are several types of churn rates that businesses should be aware of. These include customer churn rate, which provides the number of customers lost, and revenue churn rate, which outlines the financial loss resulting from customer churn. Understanding the difference between gross and net churn rate can also provide more nuanced insights into a business's financial status. By taking the number of customers at the start of a period, subtracting the number at the end of the period, and then dividing this by the initial number of customers, businesses can determine their churn rate. This figure is often multiplied by 100% to express it as a percentage. However, managing churn rate can be a complex process, requiring a sound understanding of your customers and market. It might be beneficial for businesses to seek wealth management services to help navigate the challenges associated with high churn rates. Professional wealth managers can provide strategic insights and advice, helping businesses to better manage their churn rate and improve their financial sustainability.What Is a Churn Rate?
Types of Churn Rates
Customer Churn Rate
Revenue Churn Rate
Gross Churn Rate vs Net Churn Rate
How to Calculate the Churn Rate
Formula and Explanation

Step-By-Step Process of Calculation
Practical Examples
Factors Influencing Churn Rates
Product Quality and Service Levels
Price Competitiveness
Customer Satisfaction and Experience
Market Competition
Impact of High Churn Rates on Business Finance
Effect on Revenue
Effect on Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC)
Effect on Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Churn Rate Reduction Strategies
Improving Customer Service
Offering Competitive Pricing
Enhancing User Experience
Implementing Effective Onboarding Processes
Impact of High Churn Rates on Business Finance
Effect on Revenue
Effect on Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC)
Effect on Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Churn Rate Reduction Strategies
Improving Customer Service
Offering Competitive Pricing
Enhancing User Experience
Implementing Effective Onboarding Processes
Role of Churn Rates in Financial Analysis
Churn Rates in Financial Modeling
How Investors Evaluate Churn Rates
Churn Rates in SaaS Business Models
Final Thoughts
Churn Rate FAQs
Churn rate, also known as attrition rate, is the percentage of customers who stop using a company's product or service within a specific time period.
Churn rate is calculated by dividing the number of customers lost during a given period by the number of customers at the start of that period, multiplied by 100% to give a percentage.
Factors that can influence churn rate include product quality, price competitiveness, customer satisfaction, and market competition.
A high churn rate can lead to decreased revenue, increased customer acquisition costs, and a decrease in customer lifetime value, all of which can negatively impact a company's financial situation.
Effective strategies for reducing churn rate include improving customer service, offering competitive pricing, enhancing user experience, and implementing effective onboarding processes.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











