Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II) is an integrated approach to managing the resources, materials, and processes in a manufacturing organization. This holistic method streamlines operations, reduces waste, and optimizes production efficiency. MRP II has become a crucial component in the modern manufacturing landscape, as it enables organizations to adapt to changing market demands and remain competitive. By leveraging the power of MRP II, manufacturers can make better decisions, minimize delays, and improve customer satisfaction. The concept of MRP II evolved from the earlier Material Requirements Planning (MRP) system. While MRP focused primarily on material planning and inventory control, MRP II expanded its scope to include all aspects of manufacturing, such as capacity planning, production scheduling, and financial management. The Master Production Schedule is a critical element of MRP II, as it outlines the production plan for a specified period. It considers factors such as customer demand, production capacity, and inventory levels to determine the optimal production quantities and timings. The Bill of Materials is a comprehensive list of raw materials, components, and assemblies required to produce a finished product. By providing a detailed breakdown of product composition, BOMs help manufacturers accurately plan their material requirements, manage costs, and streamline production. Effective inventory management is essential in MRP II systems to maintain optimal stock levels, reduce carrying costs, and avoid stockouts. MRP II helps organizations monitor and control their inventory levels through automated tracking, demand forecasting, and real-time data analysis. Capacity planning in MRP II ensures that organizations have the right resources and capabilities to meet production demands. This process involves assessing equipment, labor, and material availability, as well as evaluating production constraints to optimize resource utilization. MRP II systems utilize production scheduling to establish a detailed timeline for manufacturing operations. This includes allocating resources, setting priorities, and sequencing production tasks to minimize lead times, improve productivity, and ensure timely order fulfillment. Shop floor control in MRP II systems refers to the real-time monitoring and management of production processes. By providing visibility into shop floor activities, MRP II allows manufacturers to identify bottlenecks, track progress, and make informed decisions to optimize production performance. MRP II systems facilitate effective purchasing and procurement processes by automating material requirements planning, generating purchase orders, and tracking supplier performance. This leads to more efficient procurement, better supplier relationships, and improved cost control. Financial management in MRP II systems provides a comprehensive view of the organization's financial performance. By integrating financial data with production and inventory information, MRP II enables better cost analysis, budgeting, and decision-making to support overall business objectives. Implementing MRP II systems can significantly improve production efficiency by streamlining processes, reducing waste, and optimizing resource utilization. This, in turn, leads to cost savings, increased productivity, and higher profitability. MRP II systems help organizations maintain optimal inventory levels, preventing stockouts and reducing carrying costs. This results in better inventory control, reduced waste, and improved cash flow management. By leveraging historical data and advanced analytics, MRP II systems enable manufacturers to forecast demand more accurately. This allows organizations to plan production schedules more effectively, reduce lead times, and respond quickly to changing market conditions. MRP II systems contribute to reduced lead times by optimizing production schedules, streamlining processes, and facilitating better communication. Shorter lead times improve customer satisfaction, increase operational efficiency, and provide a competitive advantage in the market. By providing a comprehensive view of resources, MRP II systems enable better decision-making and resource allocation. Manufacturers can identify bottlenecks, prioritize tasks, and allocate resources more effectively, leading to increased productivity and cost savings. MRP II systems foster communication and collaboration across departments, suppliers, and customers. This results in a more cohesive and efficient organization, as stakeholders have access to real-time information and can work together to achieve common goals. Implementing MRP II systems can lead to increased customer satisfaction by ensuring timely delivery of high-quality products. By providing better demand forecasting, reducing lead times, and improving production efficiency, MRP II helps manufacturers meet customer expectations more consistently. MRP II systems can be expensive to implement, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises. These costs include software licensing, hardware upgrades, employee training, and ongoing maintenance, which may present financial challenges for some organizations. Employees may resist the implementation of an MRP II system, particularly if they perceive it as a threat to their job security or if it requires significant changes to established processes. Addressing these concerns through effective change management and communication is crucial for successful adoption. The effectiveness of MRP II systems depends on the quality and accuracy of the data they use. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to suboptimal decisions and inefficiencies, making it essential for organizations to invest in data quality and validation processes. MRP II systems can be complex and require a steep learning curve for employees. This complexity may result in initial productivity losses and frustration among users, making it essential for organizations to provide adequate training and support during implementation. Some MRP II systems may struggle to adapt to rapidly changing business environments or accommodate significant growth. Organizations must carefully evaluate their chosen system's scalability and flexibility to ensure it can meet their evolving needs. Integrating MRP II systems with other organizational systems can be challenging, particularly if those systems use different data formats or communication protocols. Ensuring seamless integration is essential for maximizing the benefits of MRP II implementation. Numerous MRP II software solutions are available in the market, offering a wide range of features and capabilities. These systems can help manufacturers streamline their operations, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in the industry. MRP II systems can be integrated with ERP systems to create a comprehensive business management solution. This integration enables seamless data sharing and communication between various departments, improving overall organizational efficiency and decision-making. Some MRP II software solutions are designed specifically for certain industries, offering customized features and functionalities to meet unique requirements. These industry-specific solutions can help manufacturers address the challenges and needs of their particular sector more effectively. MRP II software can be deployed either on-premises or through cloud-based platforms. While on-premises solutions offer more control and customization, cloud-based options provide greater flexibility, scalability, and reduced upfront costs. AI and ML technologies are increasingly being integrated into MRP II systems, enhancing their capabilities and efficiency. These advanced technologies can help manufacturers automate processes, improve demand forecasting, and optimize production scheduling, among other benefits. Before implementing an MRP II system, organizations must assess their readiness by evaluating their current processes, infrastructure, and culture. This assessment helps identify potential challenges and opportunities for improvement, laying the foundation for a successful implementation. Defining the project scope and objectives is crucial for a successful MRP II implementation. This involves identifying the desired outcomes, setting priorities, and establishing a clear vision for the project, ensuring all stakeholders are aligned with the project goals. Choosing the right MRP II software is critical, as it will directly impact the organization's ability to achieve its objectives. Factors to consider include industry-specific requirements, integration capabilities, scalability, and ease of use, among others. Effective project management and a dedicated implementation team are essential for a successful MRP II implementation. The team should consist of cross-functional members with the necessary skills and expertise to ensure a smooth transition and minimize potential risks. Migrating data from existing systems to the new MRP II software and integrating it with other organizational systems is a critical step in the implementation process. This ensures data consistency, facilitates communication, and enables seamless operations across the organization. Employee training and change management are essential for successful MRP II adoption. Organizations must invest in comprehensive training programs and support employees throughout the transition to ensure they understand and can effectively use the new system, minimizing resistance and maximizing benefits. After implementing an MRP II system, organizations should conduct regular evaluations to measure its effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. This continuous improvement approach ensures that the system remains aligned with the organization's objectives and adapts to evolving business needs. Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II) is a holistic approach that helps manage resources, materials, and processes in manufacturing organizations. It has evolved from Material Requirements Planning and expanded its scope to include capacity planning, production scheduling, and financial management. MRP II offers several benefits, including improved production efficiency, better inventory management, enhanced demand forecasting, reduced lead times, improved resource allocation, streamlined communication, and increased customer satisfaction. However, there are challenges to consider, such as high implementation costs, resistance to change, data quality, system complexity, scalability limitations, and integration with other systems. MRP II software solutions provide various features and can integrate with Enterprise Resource Planning systems. Industry-specific solutions, cloud-based deployment options, and the integration of AI and ML technologies further enhance the capabilities of MRP II. Implementing MRP II requires assessing organizational readiness, establishing project scope and objectives, selecting the right software, effective project management, data migration and integration, training and change management, and post-implementation evaluation.What Is Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II)?
Key Components of MRP II
Master Production Schedule (MPS)
Bill of Materials (BOM)
Inventory Management
Capacity Planning
Production Scheduling
Shop Floor Control
Purchasing and Procurement
Financial Management

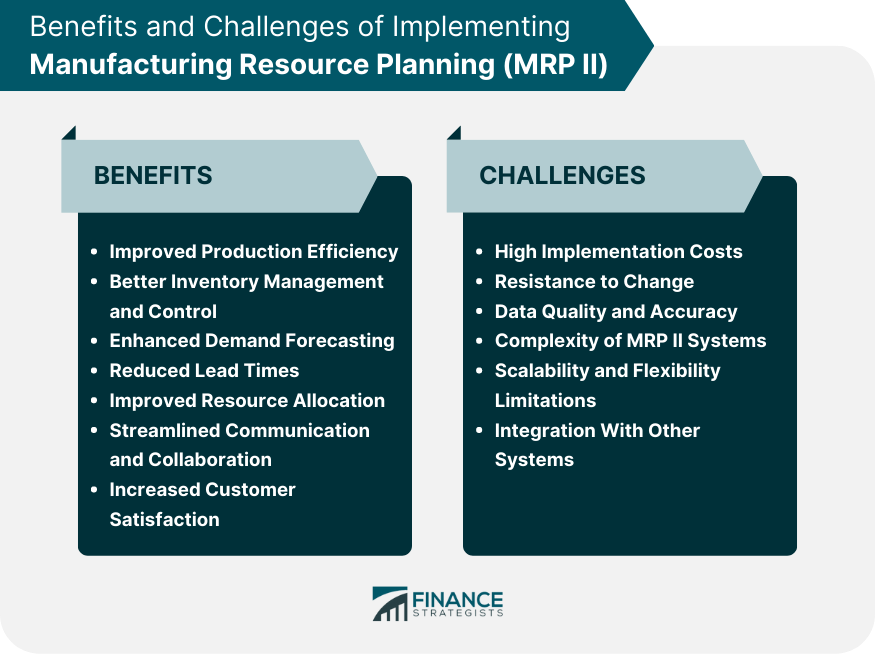
Benefits of Implementing MRP II
Improved Production Efficiency
Better Inventory Management and Control
Enhanced Demand Forecasting
Reduced Lead Times
Improved Resource Allocation
Streamlined Communication and Collaboration
Increased Customer Satisfaction
Challenges and Limitations of MRP II
High Implementation Costs
Resistance to Change
Data Quality and Accuracy
Complexity of MRP II Systems
Scalability and Flexibility Limitations
Integration With Other Systems
MRP II Software and Technologies
Overview of MRP II Software Solutions
Integration With Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
Industry-Specific MRP II Solutions
Cloud-Based and On-Premises Deployment Options
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in MRP II Systems
MRP II Implementation Strategies

Assessing Organizational Readiness
Establishing Project Scope and Objectives
Selecting the Right MRP II Software
Project Management and Team Formation
Data Migration and System Integration
Training and Change Management
Post-implementation Evaluation and Continuous Improvement
Final Thoughts
Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II) FAQs
Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II) is an integrated approach to managing resources, materials, and processes in a manufacturing organization. While Material Requirements Planning (MRP) focuses primarily on material planning and inventory control, MRP II expands its scope to include all aspects of manufacturing, such as capacity planning, production scheduling, and financial management.
MRP II systems can significantly improve production efficiency by streamlining processes, reducing waste, and optimizing resource utilization. They enable better decision-making, improved resource allocation, and real-time monitoring of production processes, which can lead to cost savings, increased productivity, and higher profitability.
The key components of MRP II systems include the Master Production Schedule (MPS), Bill of Materials (BOM), inventory management, capacity planning, production scheduling, shop floor control, purchasing and procurement, and financial management. These components work together to provide a comprehensive view of an organization's manufacturing operations and facilitate better decision-making.
Some of the main benefits of implementing MRP II systems include improved production efficiency, better inventory management and control, enhanced demand forecasting, reduced lead times, improved resource allocation, streamlined communication and collaboration, and increased customer satisfaction.
Organizations should be aware of challenges and limitations such as high implementation costs, resistance to change, data quality and accuracy issues, complexity of MRP II systems, scalability and flexibility limitations, and potential difficulties with integrating MRP II systems with other organizational systems. Proper planning, training, and support can help organizations overcome these challenges and maximize the benefits of MRP II implementation.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











