The Debt Snowball Method is a debt repayment strategy that helps individuals pay off their debts in a systematic and organized manner. The method involves paying off debts in order of smallest to largest, regardless of the interest rate. This approach is different from other debt repayment strategies that focus on paying off debts with the highest interest rate first, which may not necessarily be the debt with the smallest balance. The debt snowball method gained widespread recognition through personal finance expert Dave Ramsey, who popularized the concept in his book, "The Total Money Makeover." The method has since become a go-to approach for individuals seeking to eliminate their debts. The debt snowball method involves listing all debts from the smallest balance to the largest, making minimum payments on each, and allocating any extra funds toward the smallest debt. Once the smallest debt is paid off, the process is repeated with the next smallest debt, effectively "snowballing" payments until all debts are eliminated. 1. List All Debts from Smallest to Largest Balance: Begin by organizing debts from the smallest balance to the largest, regardless of interest rates. 2. Determine Minimum Payments for Each Debt: Identify the minimum required payment for each debt to ensure all payments are made on time. 3. Allocate Extra Funds Toward the Smallest Debt: Apply any additional funds to the smallest debt, accelerating its repayment. 4. Celebrate Milestones and Maintain Motivation: Recognize achievements in debt repayment to stay motivated throughout the process. 5. Roll Over Payments to the Next Smallest Debt: Once the smallest debt is paid off, roll over its payment to the next smallest debt, continuing the "snowball" effect. 6. Repeat the Process Until All Debts Are Eliminated: Continue the debt snowball method until all debts have been successfully repaid. The debt avalanche method prioritizes debts with the highest interest rates, paying them off first to save money on interest payments. While the debt avalanche method may save individuals money on interest payments, it may not provide the same psychological benefits and motivation as the debt snowball method. Debt consolidation involves combining multiple debts into a single loan, typically with a lower interest rate, to simplify and streamline the repayment process. Debt consolidation can make managing debts easier and potentially save money on interest payments, but it may not address the root causes of debt or foster the same positive financial habits as the debt snowball method. The debt snowball method offers quick wins by focusing on the smallest debts first, providing motivation to continue the debt repayment process. By maintaining a consistent repayment schedule, individuals using the debt snowball method can build strong financial habits that last beyond debt elimination. The debt snowball method is relatively simple and easy to follow, making it an appealing option for those who may be overwhelmed by their debts. By targeting the smallest debts first, the debt snowball method can help individuals reduce the total number of debts more quickly than other repayment strategies. As debts are paid off, individuals may see improvements in their credit scores, which can lead to better financial opportunities in the future. The debt snowball method does not prioritize debts with higher interest rates, which can result in individuals paying more in total interest over time. For those with high-interest debts, the debt snowball method may not be the most efficient strategy, as it does not take interest rates into account when prioritizing debt repayment. The success of the debt snowball method depends on an individual's ability to maintain discipline and make consistent payments. It's essential to consider personal financial situations and preferences when selecting a debt repayment strategy. Some individuals may prefer the psychological benefits of the debt snowball method, while others may prioritize saving money on interest payments through the debt avalanche method or debt consolidation. The debt snowball method offers several advantages, including psychological benefits, simplicity, and the potential to reduce the total number of debts quickly. However, it may result in higher total interest payments and may not be the best option for those with significantly higher interest rate debts. The debt snowball method can be an effective debt repayment strategy for many individuals, but it's essential to consider personal financial circumstances and preferences when choosing the most suitable approach. By carefully evaluating various debt repayment strategies, individuals can make informed decisions that best align with their goals and financial situations.What Is Debt Snowball Method?
Origin and Popularity
Process Overview
Steps to Implement the Debt Snowball Method

Comparison to Other Debt Repayment Strategies
Debt Avalanche Method
Debt Consolidation
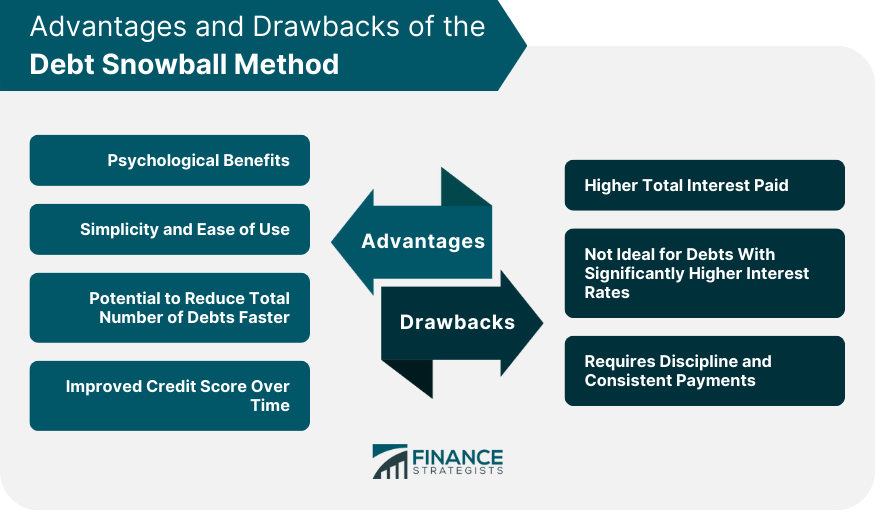
Advantages of the Debt Snowball Method
Psychological Benefits
Quick Wins and Motivation
Encourages Habit-Building
Simplicity and Ease of Use
Reducing the Total Number of Debts Faster
Improved Credit Score Over Time
Drawbacks of the Debt Snowball Method
Higher Total Interest Paid
Not Ideal for Debts with Significantly Higher Interest Rates
Requires Discipline and Consistent Payments
Choosing the Best Strategy for Individual Circumstances
Conclusion
Debt Snowball Method FAQs
The debt snowball method is a debt repayment strategy that focuses on paying off debts in ascending order of their balances, starting with the smallest debt. This method involves listing all debts from the smallest to the largest balance, making minimum payments on each, and allocating any extra funds toward the smallest debt. The process is repeated until all debts are eliminated, creating a "snowball" effect as payments roll over from one debt to the next.
The debt snowball method offers several advantages, including psychological benefits such as quick wins and motivation, simplicity, and ease of use, the potential to reduce the total number of debts faster, and improved credit scores over time.
Yes, there are some downsides to the debt snowball method. It may result in higher total interest payments, as it does not prioritize debts with higher interest rates. Additionally, it may not be the most efficient strategy for individuals with significantly higher interest-rate debts and requires discipline and consistent payments to be effective.
The debt snowball method prioritizes paying off debts in ascending order of their balances, while the debt avalanche method focuses on paying off debts with the highest interest rates first. The debt avalanche method may save more money on interest payments but may not provide the same psychological benefits as the debt snowball method. On the other hand, debt consolidation involves combining multiple debts into a single loan with a lower interest rate, which simplifies the repayment process but may not address the root causes of debt or foster positive financial habits.
The debt snowball method can be an effective debt repayment strategy for many individuals. However, it's essential to consider your personal financial circumstances and preferences when choosing the most suitable approach. If saving money on interest payments is a higher priority or you have debts with significantly higher interest rates, other strategies like the debt avalanche method or debt consolidation may be more appropriate.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











