Fiduciary liability refers to the legal responsibility of individuals or entities who act as fiduciaries to act in the best interests of the parties they represent, such as beneficiaries, and the potential financial consequences of failing to meet those obligations. This can include breaching fiduciary duties such as acting with loyalty, care, and disclosure, and can result in lawsuits, fines, beneficiaries, and reputational damage. Fiduciary liability is an essential aspect of financial management that concerns the legal responsibility of individuals or entities who manage assets on behalf of others. These individuals, known as fiduciaries, are held to a high standard of care and loyalty due to their entrusted positions. Fiduciaries are obligated to act in the best interest of their beneficiaries, ensuring that their actions and decisions align with the beneficiaries' needs and objectives. The main fiduciary duties include the duty of loyalty, duty of care, duty of disclosure, and the duty to diversify investments. Fiduciaries must always prioritize the beneficiaries' interests over their own or any third party's interests. This entails avoiding conflicts of interest and acting impartially when making decisions that may impact the beneficiaries. Fiduciaries are expected to exercise a high level of prudence and care when making decisions on behalf of their beneficiaries. This includes diligently researching and analyzing investment options, as well as regularly monitoring and reviewing investments to ensure their continued suitability. Fiduciaries must provide accurate, comprehensive, and timely information to beneficiaries, ensuring transparency in their decision-making processes. This duty encompasses disclosing any potential conflicts of interest, as well as communicating investment strategies, risks, and performance. Fiduciaries are required to diversify investments to minimize risk and optimize returns, striking a balance between the two. This involves adhering to established investment guidelines and policies that outline the types of investments that can be made and their respective allocations. Fiduciary liability can arise from different sources, and the potential consequences of such liability can be severe. One source of fiduciary liability is the breach of fiduciary duties, which can include acting in one's self-interest or failing to act in the best interest of beneficiaries, failing to avoid conflicts of interest, mismanaging assets, and failing to monitor investments. Another source of fiduciary liability is the violation of applicable laws and regulations, such as the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) and securities laws. Negligence or mismanagement in carrying out fiduciary duties can also result in fiduciary liability. To mitigate these sources of liability, fiduciaries must establish proper policies and procedures, perform regular audits and reviews, and obtain fiduciary liability insurance. Fiduciaries must also stay informed of the legal and regulatory landscape, industry-specific guidelines, and evolving trends and developments in fiduciary liability to avoid potential liabilities. Fiduciary liability is governed by a complex legal and regulatory framework that varies depending on the jurisdiction and industry. Some of the key components of this framework include: ERISA is a federal law that governs private-sector employee benefit plans, including pension and retirement plans. It establishes standards for fiduciaries who manage these plans, with the aim of protecting plan participants and beneficiaries. The SEC regulates the securities industry and enforces federal securities laws, including those that pertain to investment advisors and broker-dealers who act as fiduciaries. The SEC's rules and regulations help ensure that these professionals adhere to their fiduciary duties. State laws also govern fiduciary relationships, with each state having its own unique statutes and regulations. Fiduciaries must be familiar with the laws in the jurisdictions where they operate to ensure compliance. Certain industries have their own specific regulations and guidelines that govern fiduciary relationships. For example, the financial services industry has a myriad of rules and regulations that impact fiduciary responsibilities. Fiduciaries can employ several strategies to manage and mitigate their liability risks, including: Implementing a strong governance structure that clearly defines roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes can help minimize fiduciary liability risks. Fiduciaries should receive ongoing training and education to stay informed about the latest laws, regulations, and best practices that affect their fiduciary responsibilities. This helps ensure that they remain knowledgeable and competent in fulfilling their duties. Establishing internal controls and monitoring systems can help identify and address potential issues early on, thereby reducing the risk of fiduciary liability. This may involve regular audits, performance evaluations, and the establishment of risk management committees. Maintaining detailed and accurate records of decisions, actions, and communications can provide evidence of fiduciary compliance and help protect against liability claims. Proper documentation also helps facilitate transparency and disclosure to beneficiaries. Fiduciary liability insurance can provide financial protection for fiduciaries in the event of a claim or lawsuit. This type of insurance typically covers legal defense costs, settlement expenses, and damages resulting from alleged breaches of fiduciary duty. Understanding and managing fiduciary liability is crucial for those entrusted with the responsibility of managing assets on behalf of others. By adhering to their fiduciary duties, staying informed about the legal and regulatory landscape, and implementing effective risk management strategies, fiduciaries can minimize their liability risks while providing the best possible service to their beneficiaries. As the financial landscape continues to evolve, staying abreast of trends and developments in fiduciary liability will be increasingly important for both fiduciaries and beneficiaries alike.What Is Fiduciary Liability?
Fiduciary Duties
Duty of Loyalty
Duty of Care
Duty of Disclosure
Duty to Diversify Investments
Sources of Fiduciary Liability
Legal and Regulatory Framework
ERISA (Employee Retirement Income Security Act)
SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission)
State Fiduciary Laws
Industry-Specific Regulations and Guidelines
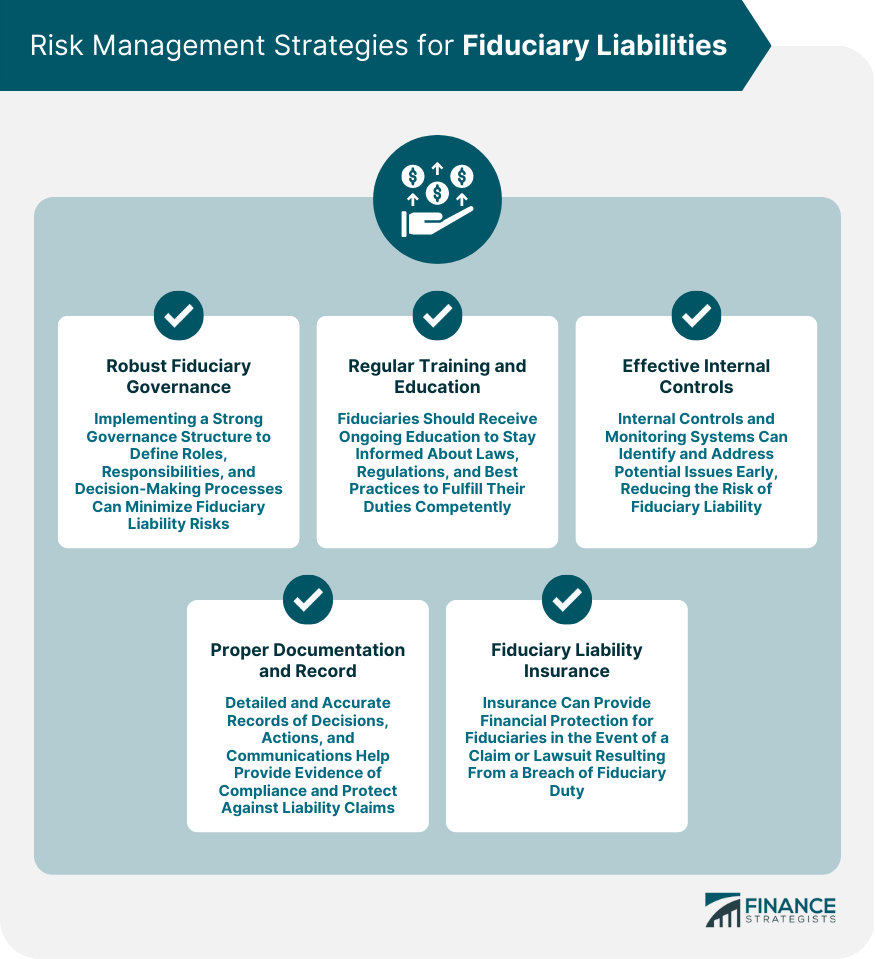
Risk Management Strategies
Development of a Robust Fiduciary Governance Structure
Regular Training and Education for Fiduciaries
Implementation of Effective Internal Controls and Monitoring Systems
Proper Documentation and Record-Keeping
Obtaining Fiduciary Liability Insurance
Conclusion
Fiduciary Liability FAQs
Fiduciary liability refers to the legal obligation of individuals or entities who act as fiduciaries to act in the best interests of the parties they represent, and the potential financial consequences of failing to meet those obligations.
Anyone who serves as a fiduciary, such as trustees, plan administrators, or investment advisors, can be held liable for fiduciary breaches if they fail to meet their legal obligations.
Some common examples of fiduciary breaches include failing to properly disclose conflicts of interest, mismanaging assets, and failing to properly monitor investments.
Fiduciary liability can be managed or mitigated by implementing proper policies and procedures, performing regular audits and reviews, and obtaining fiduciary liability insurance.
The potential consequences of fiduciary breaches can include lawsuits, fines, penalties, and reputational damage, as well as personal liability for fiduciaries who are found to have breached their duties.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











