The fiduciary rule is a set of regulations that requires financial professionals to act in the best interest of their clients when providing investment advice or selling financial products for retirement accounts. The rule aims to ensure that financial advisors, brokers, and other professionals put their clients' interests ahead of their own financial gain. The fiduciary rule is a critical regulation in the financial industry aimed at ensuring that financial professionals act in the best interests of their clients when providing investment advice. The fiduciary rule has its roots in the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) of 1974, which established standards for retirement plan advisors. Over time, the need for broader fiduciary standards in the financial industry became apparent, leading to the introduction of the fiduciary rule in its current form. Fiduciary standards are essential in the financial industry to protect investors from unscrupulous practices and ensure that financial professionals prioritize their clients' interests above their own. These standards help prevent conflicts of interest, increase transparency, and ultimately promote trust in the financial services sector. The Department of Labor (DOL) is the main governing body responsible for establishing and enforcing the fiduciary rule. However, other regulatory organizations like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) also have a role in regulating financial professionals and upholding fiduciary standards. These organizations work to ensure that financial professionals are held accountable for any breaches of fiduciary duty and that investors are protected from potential harm. The fiduciary standard comprises two primary duties: the duty of loyalty and the duty of care. The duty of loyalty requires financial professionals to act in their clients' best interests, while the duty of care necessitates that they provide well-informed, prudent advice. The fiduciary rule affects various financial professionals, including financial advisors, brokers and dealers, retirement plan consultants, and insurance agents. These professionals must adhere to the fiduciary standard when providing investment advice to clients. The fiduciary rule applies to several types of accounts, including retirement accounts, Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs), brokerage accounts, and other advisory accounts. The rule is particularly important for retirement accounts, as it helps protect investors' long-term financial security. The fiduciary rule imposes three impartial conduct standards on financial professionals: the best interest standard, reasonable compensation, and prohibition of misleading statements. These standards ensure that professionals provide unbiased advice, charge fair fees, and communicate honestly with clients. Financial professionals must disclose information about their fees, potential conflicts of interest, and any other relevant information to help clients make informed decisions. These disclosures promote transparency and help clients understand the implications of their investment choices. The fiduciary rule mandates financial professionals to develop and implement policies and procedures to ensure compliance, provide training and education to their staff, and maintain comprehensive records of their adherence to the rule. The fiduciary rule provides for several exemptions and exceptions, such as the Best Interest Contract (BIC) Exemption, Prohibited Transaction Exemption, and other specific circumstances. These exemptions allow financial professionals to engage in certain transactions or arrangements that would otherwise be prohibited under the fiduciary rule. The fiduciary rule offers several benefits for investors, including enhanced investor protection, greater transparency, and better investment outcomes. By ensuring that financial professionals prioritize clients' interests, the rule helps investors make well-informed decisions and safeguard their financial well-being. The fiduciary rule presents challenges for financial professionals, such as increased compliance costs, shifts in business models, and potential for increased litigation. To adhere to the rule, financial professionals must invest in systems, training, and resources, which can lead to higher operational costs. Additionally, some professionals may need to modify their business models to minimize conflicts of interest and prioritize their clients' best interests. The fiduciary rule has several implications for the financial industry, including the evolution of fee structures, a shift toward passive investment strategies, and changes in product offerings. As a result of the rule, many financial professionals have moved toward fee-based models instead of commission-based compensation. Furthermore, the increased focus on clients' best interests has led to a preference for low-cost, passive investment strategies and a decrease in the promotion of high-cost, actively managed funds. The fiduciary rule has faced legal challenges and court rulings questioning its validity and scope. Various industry groups and organizations have argued against the rule, asserting that it is overly burdensome and that it stifles innovation in the financial industry. While some court rulings have upheld the rule, others have called for modifications or struck down certain provisions. In response to legal challenges and industry feedback, regulatory authorities have proposed and implemented changes to the fiduciary rule. These changes aim to address concerns raised by stakeholders while maintaining the core principles of investor protection and transparency. Several states have implemented their own fiduciary rules to supplement federal regulations. These state-level rules often impose additional requirements on financial professionals and may vary in scope and stringency. Financial professionals must navigate this complex regulatory landscape to ensure compliance at both the federal and state levels. The fiduciary rule is likely to continue evolving in response to ongoing debates, legal challenges, and industry developments. Future trends may include further regulatory changes, increased harmonization between federal and state-level rules, and the adoption of international best practices to enhance investor protection. The fiduciary rule is a set of regulations that require financial professionals to act in the best interest of their clients when providing investment advice or selling financial products for retirement accounts. The rule aims to ensure that financial advisors, brokers, and other professionals prioritize their clients' interests over their own financial gain. The rule has its roots in the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA) of 1974 and is critical in the financial industry to protect investors from unscrupulous practices, increase transparency, prevent conflicts of interest, and promote trust in the financial services sector. The fiduciary rule framework includes the fiduciary standard, types of financial professionals affected, types of accounts covered, impartial conduct standards, disclosures, compliance requirements, exemptions, and exceptions. The rule offers benefits for investors, like enhanced investor protection, greater transparency, and better investment outcomes. However, it also presents challenges for financial professionals, such as increased compliance costs, shifts in business models, and potential for increased litigation. The fiduciary rule has several implications for the financial industry, including the evolution of fee structures, a shift toward passive investment strategies, and changes in product offerings. The rule has faced legal challenges and court rulings questioning its validity and scope, and regulatory authorities have proposed and implemented changes to address concerns raised by stakeholders. In summary, the fiduciary rule is an important regulatory standard that establishes a duty of loyalty and care for financial professionals when providing investment advice. As an investor, it is important to work with professionals who adhere to this standard to protect your best interests. As a financial professional, it is crucial to stay informed and educated about the fiduciary rule and other regulatory changes to maintain compliance and uphold ethical practices. Remember, always prioritize your clients' best interests.Fiduciary Rule: Definition
Background
Historical Context of the Fiduciary Rule
Need for Fiduciary Standards in the Financial Industry
Key Players and Organizations Involved
The Fiduciary Rule Framework
The Fiduciary Standard
Types of Financial Professionals Affected
Types of Accounts Covered
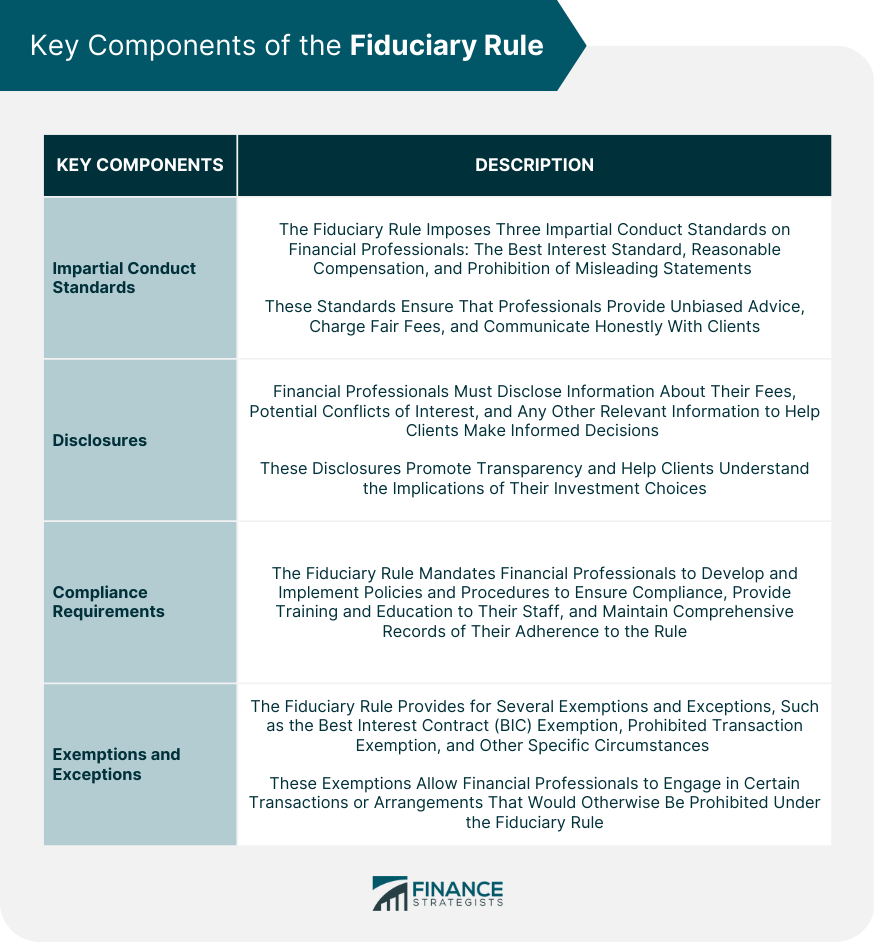
Key Components of the Fiduciary Rule
Impartial Conduct Standards
Disclosures
Compliance Requirements
Exemptions and Exceptions
Impact of the Fiduciary Rule
Benefits for Investors
Challenges for Financial Professionals
Effects on the Financial Industry
Fiduciary Rule Controversies and Developments
Legal Challenges and Court Rulings
Regulatory Changes and Proposals
State-Level Fiduciary Rules
Future Trends and Potential Modifications
Conclusion
Fiduciary Rule FAQs
The fiduciary rule is a set of regulations that requires financial advisors to act in the best interests of their clients when providing investment advice for retirement accounts.
The fiduciary rule applies to financial advisors and brokers who provide investment advice for retirement accounts, including 401(k) plans and IRAs.
The fiduciary rule is designed to protect investors from potential conflicts of interest and ensure that financial advisors act in the best interests of their clients.
The suitability standard requires financial advisors to recommend investments that are suitable for their clients based on their financial situation, while the fiduciary rule requires advisors to act in their clients' best interests.
The fiduciary rule was initially implemented in 2016, but it faced legal challenges and was ultimately vacated in 2018. However, some states have enacted their own fiduciary rules for financial advisors.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











