Financial gerontology is an emerging field that focuses on the unique financial challenges that older adults face. It recognizes that as people age, their financial needs, goals, and behaviors change, and that financial planning must be adapted to meet these changing needs. Financial gerontology is an interdisciplinary field that draws on principles and theories from economics, psychology, sociology, and gerontology to better understand the financial aspects of aging. Some of the key topics studied in financial gerontology include retirement planning, wealth management, investment strategies, financial decision-making, and the impact of financial well-being on the physical and mental health of older adults. Financial gerontology also examines the role of public policy in promoting financial security for older adults, as well as the potential benefits and risks of financial innovations and new technologies. The world's population is rapidly aging due to a combination of factors such as increased life expectancy, declining birth rates, and advancements in healthcare. This demographic shift has significant implications for financial gerontology, as it creates an increasing demand for financial planning services tailored to older adults. As medical technology and healthcare improve, life expectancy continues to rise. Longer lifespans mean that individuals need to plan for a longer retirement period, which requires more resources and careful financial planning. With birth rates declining in many countries, there is a smaller proportion of the working-age population supporting retirees. This places additional strain on social security systems and pension funds, making individual financial planning even more critical. The aging population brings about economic and social challenges, such as increased healthcare costs, strains on social security systems, and a need for more long-term care facilities. Financial gerontology plays a crucial role in addressing these challenges by helping older adults navigate their financial needs and plan for their future. Effective retirement planning starts with developing a saving strategy. Older adults need to consider various factors such as their current financial situation, retirement goals, and risk tolerance when devising a savings plan. Investment options for retirement can include stocks, bonds, mutual funds, real estate, and annuities. A well-diversified portfolio can help minimize risk and maximize returns over time. Understanding the role of social security benefits and pension plans is vital for retirement planning. Financial gerontologists can help older adults navigate the complexities of these systems and ensure they maximize their benefits. Long-term care encompasses various services, including assisted living, nursing home care, home health care, and adult day care. Planning for long-term care is essential as it can be a significant expense during retirement. The costs of long-term care can be substantial, and financing options may include personal savings, long-term care insurance, government programs, and reverse mortgages. Long-term care insurance is a policy designed to cover the costs of long-term care services. Purchasing such a policy can help protect older adults' assets and ensure they have access to quality care when needed. Estate planning is an essential aspect of financial gerontology, as it allows individuals to determine how their assets will be distributed upon their death. Wills and trusts are common tools used in estate planning to designate beneficiaries and manage assets. Understanding the tax implications of estate planning is crucial, as various taxes can impact the value of the estate and the beneficiaries' inheritance. A well-structured estate plan can ensure a smooth and fair distribution of assets among heirs and beneficiaries, minimizing potential conflicts and legal issues. Inflation and the rising cost of living can significantly impact older adults' financial stability. Fixed incomes and limited earning potential make it challenging for retirees to maintain their purchasing power and quality of life. Healthcare costs are a significant concern for older adults, as they often increase with age. Financial gerontologists can help individuals plan for these expenses through various strategies, such as saving, insurance, and government programs. Older adults are often targets of financial scams and abuse. Financial gerontologists play a crucial role in educating and advising older adults on how to protect themselves from such threats. Cognitive decline is a common issue among older adults, which can impair their ability to make sound financial decisions. Financial gerontologists can provide guidance and support to help individuals and their families navigate these challenges. Financial gerontology professionals specialize in providing financial advice and planning services to older adults. They can help individuals navigate retirement, long-term care planning, estate planning, and other financial challenges specific to aging. Financial gerontologists typically have a background in finance, economics, or a related field. Many professionals also hold certifications such as the Certified Financial Planner (CFP) or the Chartered Financial Consultant (ChFC) designation. As the global population continues to age, the demand for financial gerontology professionals is expected to grow. This presents excellent job prospects and opportunities for professionals interested in specializing in this niche field. Governments worldwide are implementing various policies and programs to support older adults, such as retirement benefits, healthcare services, and housing assistance. These initiatives aim to improve the financial well-being and quality of life for older individuals. Many countries are undergoing reforms to their retirement and pension systems to ensure their sustainability amid the aging population. These reforms may include changes to retirement ages, benefit calculations, and funding mechanisms. Financial literacy programs targeted at older adults can help improve their understanding of financial concepts and decision-making. These initiatives are crucial for empowering individuals to take control of their financial future and mitigate potential challenges. Financial gerontology plays a crucial role in addressing the needs of an aging population by helping individuals plan for retirement, long-term care, and other financial challenges that come with aging. The field has significant potential for growth and innovation as demographic trends, technological advancements, and public policy developments continue to evolve. The need for ongoing research and policy development is vital to ensure that financial gerontology remains an essential and effective resource for older adults and their families.What Is Financial Gerontology?
Demographic Trends and Their Impact on Financial Gerontology
Global Aging Population
Increasing Life Expectancy
Declining Birth Rates
Economic and Social Implications
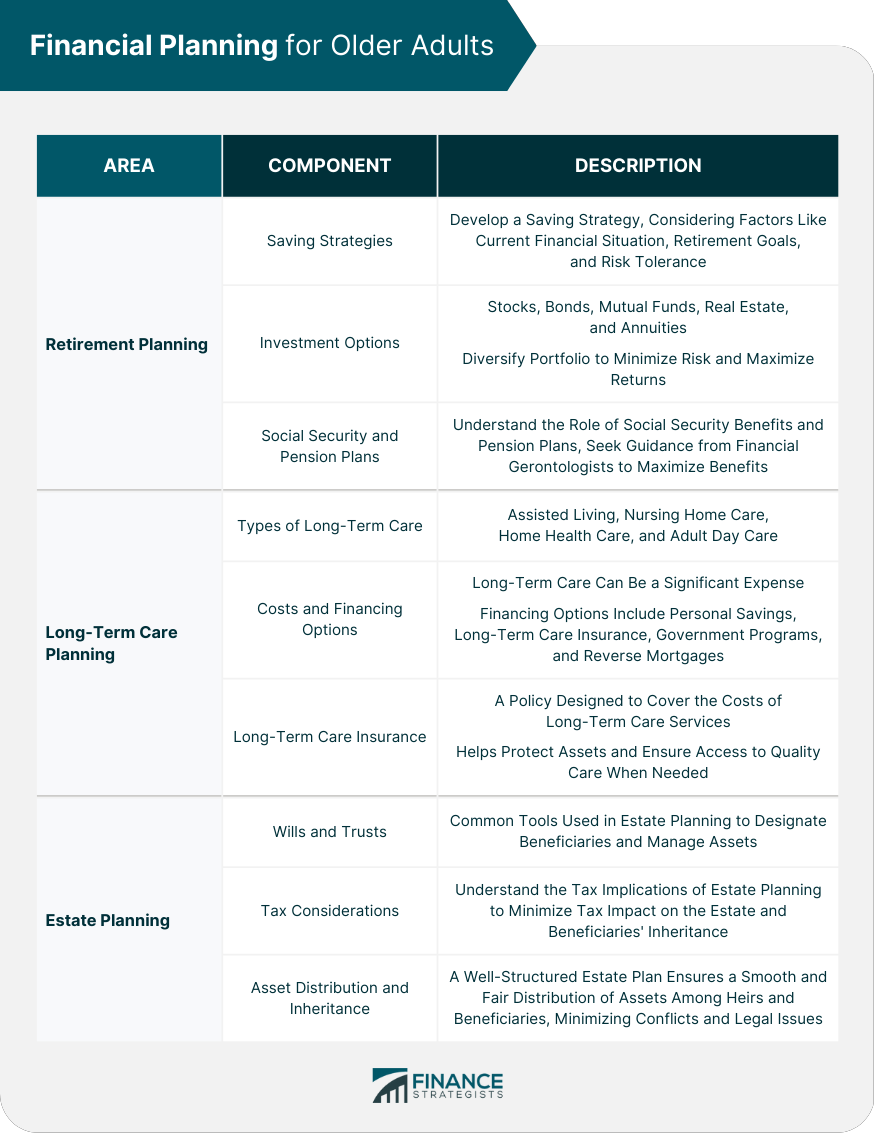
Financial Planning for Older Adults
Retirement Planning
Saving Strategies
Investment Options
Social Security and Pension Plans
Long-Term Care Planning
Types of Long-Term Care
Costs and Financing Options
Long-Term Care Insurance
Estate Planning
Wills and Trusts
Tax Considerations
Asset Distribution and Inheritance
Financial Challenges Facing Older Adults
Inflation and Cost of Living
Healthcare Costs
Elder Fraud and Financial Abuse
Cognitive Decline and Financial Decision-Making

Financial Gerontology Professionals
Roles and Responsibilities
Required Education and Certifications
Job Prospects and Growth in the Field
Public Policies and Initiatives
Government Support for Older Adults
Retirement and Pension System Reforms
Programs to Increase Financial Literacy and Awareness
Conclusion
Financial Gerontology FAQs
Financial gerontology is the study of how aging and retirement impact financial planning, investment, and decision-making. It is concerned with understanding how people's financial needs and behaviors change as they grow older.
Financial gerontology is important because it recognizes that as people age, their financial needs and behaviors change. By understanding these changes, financial professionals can better serve their clients and help them prepare for retirement and old age.
Working with a financial gerontologist can provide many benefits, such as tailored financial advice that considers an individual's unique situation and goals, assistance with navigating complex financial systems, and support in making informed decisions that can help protect their financial well-being in their later years.
By addressing the financial challenges that older adults face, financial gerontology can help improve the quality of life for older adults by providing them with greater financial security, independence, and peace of mind. This can lead to a better overall quality of life and improved physical and mental health.
Financial gerontology can help with estate planning by providing guidance on the distribution of assets, minimizing potential conflicts, and ensuring that beneficiaries receive their inheritance. Financial gerontologists can also assist with drafting wills and trusts, managing assets, and understanding the tax implications of estate planning.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











