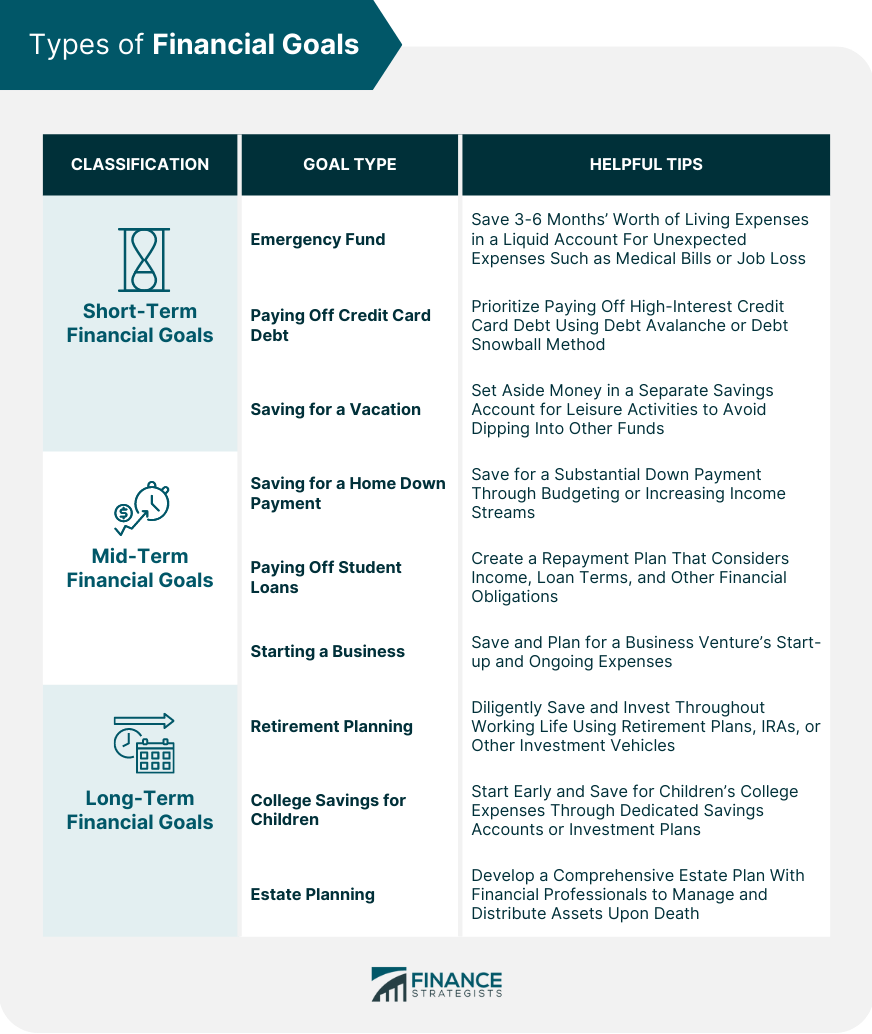
Financial goals are the specific objectives that individuals or businesses set for themselves to achieve financial success. They represent the desired financial state or outcome and provide a sense of direction and focus towards achieving that state. Financial goals can be short-term or long-term, and they can vary depending on the individual's or business's financial circumstances, priorities, and aspirations. Examples of financial goals may include saving for a down payment on a home, paying off debt, building an emergency fund, saving for retirement, or investing in the stock market to build long-term wealth. An emergency fund is a financial safety net to cover unexpected expenses, such as medical bills, car repairs, or job loss. Aim to save 3-6 months' worth of living expenses in a liquid, easily accessible account. Paying off high-interest credit card debt should be a priority, as it can quickly accumulate and negatively impact credit scores. Consider using strategies such as the debt avalanche or debt snowball method. Set aside money for vacations or other short-term goals in a separate savings account. This approach prevents dipping into other funds and promotes mindful spending on leisure activities. Buying a home often requires a substantial down payment. Saving for this expense is a common mid-term financial goal, and it may involve budgeting, cutting expenses, or increasing income streams. Reducing or eliminating student loan debt can significantly improve financial well-being. Develop a repayment plan that considers income, loan terms, and other financial obligations. Entrepreneurship requires capital for start-up costs and ongoing expenses. Saving and planning for a business venture is a crucial mid-term financial goal for aspiring entrepreneurs. A comfortable retirement requires diligent saving and investment strategies throughout one's working life. Utilize employer-sponsored retirement plans, IRAs, or other investment vehicles to grow wealth over time. Higher education costs continue to rise. Start saving early for children's college expenses through dedicated savings accounts or investment plans, such as 529 plans. Estate planning involves managing and distributing assets upon death, minimizing tax liabilities, and ensuring loved ones are cared for. Consult with financial professionals to develop a comprehensive estate plan. Determine net worth by subtracting total liabilities from total assets. This calculation provides a snapshot of overall financial health and serves as a starting point for goal-setting. Review income and expenses to understand cash flow and identify areas for improvement. This evaluation is crucial for creating a realistic financial plan. Establish goals using the SMART criteria: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. This approach ensures that goals are well-defined and attainable. Prioritize financial goals based on importance, time horizon, and personal values. Strive for a balance between short-term and long-term objectives. Develop a budget that allocates income towards financial goals, necessary expenses, and discretionary spending. Regularly review and adjust the budget as needed. Implement debt repayment strategies that accelerate progress towards becoming debt-free. Consider interest rates, loan terms, and available resources when selecting a strategy. Invest in various assets to grow wealth and achieve long-term financial goals. Diversify investments to reduce risk and optimize returns. Monitor financial goal progress by conducting regular assessments of net worth, savings, and investments. Reviewing progress helps identify areas for improvement and maintain motivation. Adjust financial goals as life circumstances change, such as career advancements, marriage, or the birth of a child. Adapting to these changes ensures that financial goals remain relevant and achievable. Reevaluate and revise financial goals periodically to ensure alignment with current priorities and financial circumstances. This practice allows for continuous improvement and keeps financial plans on track. Leverage technology to streamline financial planning and goal-setting. Use budgeting apps, investment trackers, and financial planning software to simplify the process and stay organized. Consult with financial professionals to develop personalized financial plans and receive expert guidance on achieving financial goals. These experts can provide valuable insights and recommendations based on their experience and knowledge. Access a wealth of information online, including blogs, podcasts, webinars, and online courses, to improve financial literacy and develop effective goal-setting strategies. Many resources are available for free or at a low cost. Achieving financial goals provides a sense of accomplishment, financial stability, and freedom. It requires financial discipline, patience, and a commitment to continuous learning and growth. By setting SMART financial goals, creating a comprehensive plan, and regularly monitoring progress, individuals and families can work towards a secure financial future and enjoy the benefits that come with it.What Are Financial Goals?
Types of Financial Goals
Short-Term Financial Goals
Emergency Fund
Paying Off Credit Card Debt
Saving for a Vacation
Mid-Term Financial Goals
Saving for a Home Down Payment
Paying Off Student Loans
Starting a Business
Long-Term Financial Goals
Retirement Planning
College Savings for Children
Estate Planning
Steps to Set Financial Goals
Assessing Current Financial Situation
Net Worth Calculation
Evaluating Income and Expenses
Identifying and Prioritizing Goals
SMART Goal-Setting Criteria
Balancing Multiple Financial Goals
Creating a Financial Plan
Budgeting
Debt Repayment Strategies
Investment Strategies

Monitoring and Adjusting Financial Goals
Regularly Reviewing Progress
Adapting to Changes in Financial Situation
Revising Goals as Needed
Financial Goal-Setting Tools and Resources
Financial Planning Software and Apps
Financial Advisors and Planners
Online Resources and Courses
Conclusion
Financial Goals FAQs
Financial goals refer to the objectives or targets that individuals or businesses set for their financial future. These goals can be short-term, such as paying off a credit card debt, or long-term, such as saving for retirement.
Setting financial goals helps individuals or businesses prioritize their spending and savings, as well as make strategic financial decisions. It provides a sense of direction and focus, helping to achieve financial stability and security.
Setting financial goals involves assessing your current financial situation, determining what you want to achieve, and creating a plan of action to achieve those goals. This can involve creating a budget, saving a certain amount of money each month, or investing in a specific asset class.
Yes, financial goals should be adjusted over time as your priorities and circumstances change. Reassessing your goals regularly ensures that you remain on track and continue to make progress towards your financial objectives.
Common financial goals include saving for a down payment on a home, paying off debt, building an emergency fund, saving for retirement, and investing in the stock market or other asset classes to build long-term wealth.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











