Financial planning for startups refers to the strategic process of designing and managing a comprehensive financial framework tailored specifically to the needs and goals of a new and emerging business. This process involves forecasting future financial requirements, determining potential revenue streams, and assessing the costs associated with various business operations. It encompasses activities like budgeting, expense projection, revenue forecasting, and capital structure planning, all aimed at ensuring that the startup's financial resources are utilized optimally to achieve sustainable growth and success. Unlike established businesses, startups often operate with limited resources and face higher levels of uncertainty, making effective financial planning a critical aspect of their survival and progress. By incorporating proactive financial management practices from the outset, startups can establish a strong foundation for sustainable growth while navigating the dynamic and often unpredictable business landscape. Financial planning for startups is a multi-faceted process that involves a series of strategic steps designed to manage the startup's financial resources effectively and achieve its business objectives. • Identify Fixed and Variable Costs: Start by compiling a detailed list of both fixed and variable costs associated with running the business. Fixed costs include rent, salaries, and insurance, which remain relatively constant over time. Variable costs, on the other hand, fluctuate with the level of production or sales and include expenses like raw materials and shipping fees. • Allocate Resources for Different Business Functions: Allocate financial resources to various aspects of the business, such as marketing, research and development, operations, and customer support. This allocation ensures that funds are distributed optimally to support all vital functions and prevent overspending in any one area. • Project Sales and Revenue Streams: Conduct a thorough market analysis to estimate potential sales and revenue streams. Consider factors such as the target market's size, demand for your product or service, and pricing strategies. This projection provides a baseline for understanding the startup's revenue potential and helps in setting achievable financial goals. • Estimate Operating and Non-operating Expenses: Outline all operating expenses required to maintain day-to-day operations, including costs for materials, labor, and overhead. Additionally, consider non-operating expenses like interest on loans and taxes. Accurate estimation of both operating and non-operating expenses ensures that your budget aligns with the reality of running the business. • Determine the Optimal Mix of Equity and Debt: Equity financing involves selling ownership shares in exchange for funds, while debt financing involves borrowing money that must be repaid with interest. Finding the right balance between equity and debt is crucial for maintaining financial stability and controlling ownership dilution. • Evaluate Funding Options: Explore funding options available to startups (Angel Investors, Venture Capital, Loans, etc.). Angel investors and venture capital firms provide equity funding, often in exchange for a stake in the company. Loans, whether from banks or alternative lenders, offer debt financing. Analyze the terms, interest rates, and potential implications of each funding source before making a decision. A well-structured financial plan is essential for guiding a startup's financial decisions and ensuring its long-term success. Here are the key components that make up a comprehensive startup financial plan: Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement): This component provides an overview of the startup's revenues, costs, and expenses over a specific period, typically a month, quarter, or year. Cash Flow Statement: The cash flow statement tracks the inflows and outflows of cash within a defined timeframe. It categorizes cash movements into operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities. Balance Sheet: The balance sheet lists the company's assets, liabilities, and shareholders' equity. The balance sheet helps assess the startup's solvency, liquidity, and overall financial stability. Financial Ratios and Metrics: Common ratios include the liquidity ratio, which assesses the ability to meet short-term obligations, and the profitability ratio, which measures the ability to generate profits relative to its revenue and assets. Sales Forecast: Outlines the expected revenue the startup aims to generate over a specific period. This is a critical component for planning resource allocation, setting sales targets, and assessing the viability of expansion plans. Expense Budget: Outlines the anticipated costs and expenditures across various categories such as salaries, marketing, research and development, overhead, and more. Capital Expenditure Plan: This plan outlines the startup's intended investments in long-term assets, such as equipment, facilities, and technology infrastructure. It also provides a roadmap for managing capital expenditures. Funding Strategy: Outlines how the startup plans to secure the necessary capital to fuel its growth. It may detail equity funding from founders and investors, debt financing from loans, or other sources of funding. Contingency Plans: These plans outline how the startup will navigate unexpected financial challenges, market fluctuations, or disruptive events. Risk Assessment and Management: This component involves analyzing both internal and external factors that could affect revenue, expenses, and funding availability. Financial planning equips startups with data-driven insights, allowing founders to make informed decisions about resource allocation, expansion opportunities, and strategic direction. By having a clear overview of their financial health, startups can avoid hasty choices and prioritize actions that align with their long-term goals. Through proactive financial planning, startups can identify potential financial challenges and risks early on. By anticipating these challenges, they can develop contingency plans to navigate uncertainties, ensuring that the business remains resilient in the face of unexpected obstacles. A well-structured financial plan enhances a startup's credibility and attractiveness to potential investors and lenders. Investors seek evidence of responsible financial management and a clear path to profitability. A solid financial plan demonstrates that the startup's founders are committed to achieving sustainable growth, making it more likely to secure funding. Financial planning enables startups to allocate resources more efficiently by prioritizing expenditures based on business goals and revenue potential. This prevents wastage and ensures that every dollar spent contributes to the company's growth and success. Establishing a comprehensive financial plan fosters a culture of financial discipline and accountability within the startup. By maintaining a focus on financial health from the outset, startups are better positioned to weather challenges and achieve long-term sustainability, avoiding the pitfalls that can lead to premature failure. Developing a detailed financial plan requires significant time and effort, diverting the attention of founders and key team members from core business activities. This can slow down operational progress, especially in startups where resources are already limited. Startups often operate in dynamic and unpredictable markets, making accurate financial projections challenging. Overly optimistic projections can lead to unrealistic expectations, while conservative projections might hinder growth opportunities. Striking the right balance is essential but can be difficult. Financial plans are based on assumptions and predictions made at a specific point in time. If market conditions change rapidly, the startup might find it challenging to adapt its financial plan to accommodate new realities, potentially limiting its agility and responsiveness. Developing a robust financial plan requires a thorough understanding of financial principles, accounting practices, and market dynamics. Founders might lack the necessary financial expertise, leading to misinterpretation of data and potentially flawed decisions. Startups often lack the financial resources to hire dedicated financial experts or purchase sophisticated financial planning software. This can hinder the accuracy and effectiveness of the financial planning process, potentially leading to suboptimal outcomes. Financial planning for startups is a pivotal process that underpins their success in the competitive business landscape. It involves creating a comprehensive budget that considers fixed and variable costs while allocating resources strategically across different business functions. Forecasting revenue and expenses, coupled with capital structure planning, helps establish a strong financial foundation. The key components of a startup's financial plan, including income statements, cash flow statements, balance sheets, and various financial ratios, provide crucial insights for informed decision-making. While financial planning offers numerous benefits, including risk mitigation, investor confidence, efficient resource allocation, and long-term sustainability, it's not without its challenges. The time-consuming nature, uncertainty of projections, potential rigidity, complexity, and resource constraints can all pose hurdles. Balancing the pros and cons is essential for startups to chart a path to success.What Is Financial Planning for Startups?
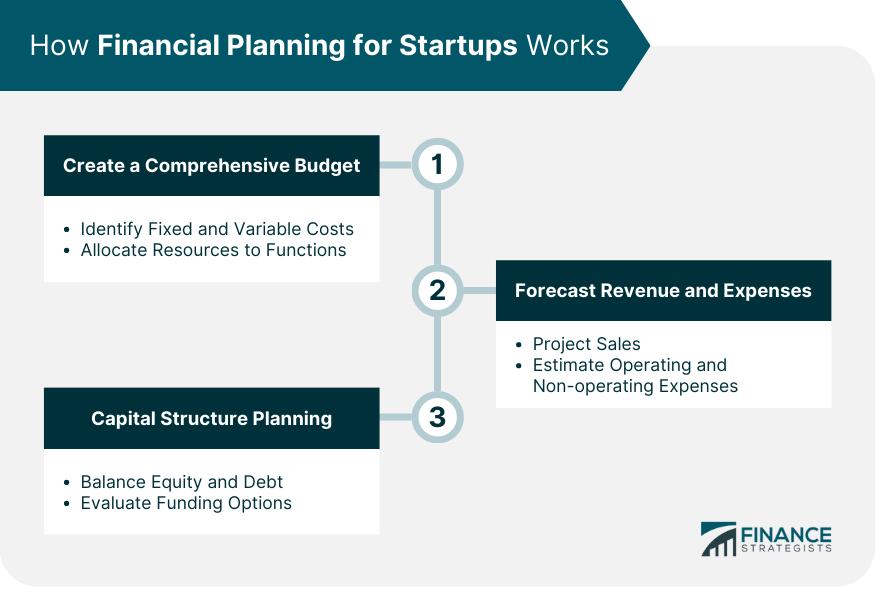
How Financial Planning for Startups Works
Create a Comprehensive Budget
Forecast Revenue and Expenses
Capital Structure Planning
Key Components of a Startup Financial Plan

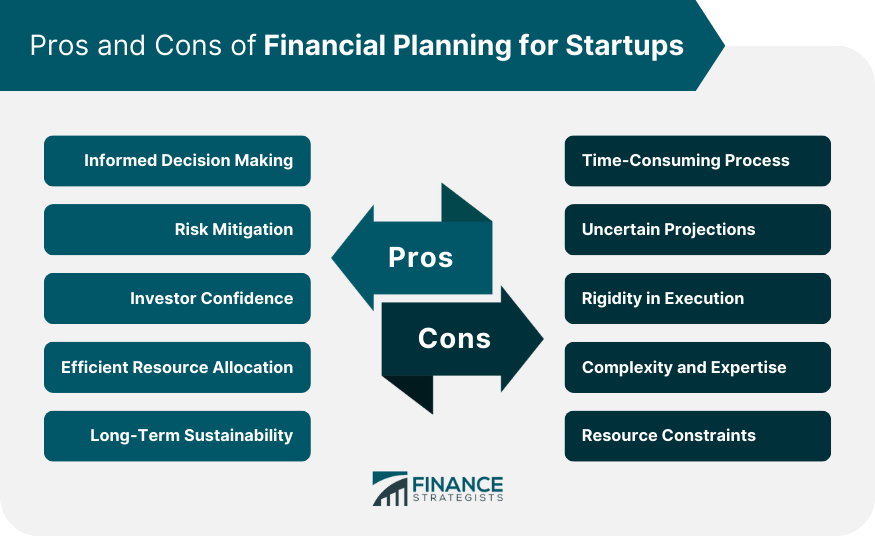
Pros of Financial Planning for Startups
Informed Decision Making
Risk Mitigation
Investor Confidence
Efficient Resource Allocation
Long-Term Sustainability
Cons of Financial Planning for Startups
Time-Consuming Process
Uncertain Projections
Rigidity in Execution
Complexity and Expertise
Resource Constraints
Conclusion
Financial Planning for Startups FAQs
Financial planning for startups is the strategic process of designing and managing a tailored financial framework to meet the needs and goals of new businesses.
Financial planning helps allocate funds wisely, make informed decisions, and navigate challenges. A well-structured plan enhances credibility for investors and fosters long-term sustainability.
A comprehensive startup financial plan includes an income statement, cash flow statement, balance sheet, financial ratios, sales forecast, expense budget, capital expenditure plan, funding strategy, contingency plans, and risk assessment.
Financial planning empowers startups with informed decision-making, risk mitigation, investor confidence, efficient resource allocation, and a focus on long-term sustainability.
Startups encounter challenges such as the time-consuming nature of detailed planning, uncertain market projections, potential rigidity in execution, complexity requiring financial expertise, and resource constraints for hiring financial experts or software.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











