Prepaid tuition plans are a type of college savings plan that allows individuals to pay for future tuition expenses at today's rates. They can help families lock in current tuition costs and avoid the impact of rising college expenses. The primary purpose of prepaid tuition plans is to provide a secure and affordable way for families to save for their children's higher education. Benefits include guaranteed tuition coverage, protection against tuition inflation, and potential tax advantages. Since their inception in the late 20th century, prepaid tuition plans have grown in popularity as a viable college savings option. Many states now offer these plans, providing families with an accessible way to save for higher education costs. Prepaid tuition units are a type of prepaid tuition plan that allows participants to purchase a fixed amount of college credits at current rates. These units can be redeemed in the future to cover tuition expenses at participating institutions. The main advantage of prepaid tuition units is the ability to lock in current tuition rates. However, they may be less flexible than other college savings options, as they are typically limited to in-state public colleges and universities. Prepaid tuition contracts involve a binding agreement between the account owner and the plan provider, in which the owner agrees to pay a fixed amount upfront or in installments. In return, the plan provider guarantees to cover future tuition costs at participating institutions. Prepaid tuition contracts offer the benefit of guaranteed tuition coverage, providing peace of mind to families. Disadvantages may include limited investment choices and restrictions on eligible institutions, as well as potential penalties for non-qualified withdrawals. To qualify for a prepaid tuition plan, the beneficiary must typically be a resident of the state offering the plan or attending an eligible institution. Age and grade restrictions may also apply, depending on the specific plan. Account owners of prepaid tuition plans are typically required to be U.S. citizens or legal residents. Some plans may impose additional requirements, such as residency or a minimum age for the account owner. Enrolling in a prepaid tuition plan typically involve completing an application form and providing necessary documentation, such as proof of residency, identification, and beneficiary information. Some plans may also require a social security number or tax identification number. Prepaid tuition plans usually have specific enrollment periods, which may be annual or more frequent. Potential participants should check with their state's plan provider for exact dates and deadlines. Lump-sum payments are one funding method for prepaid tuition plans, allowing account owners to pay the entire cost of the plan upfront. This option may provide the greatest savings, as it locks in current tuition rates for the entire plan duration. Installment plans offer another funding method, allowing account owners to make regular payments over a specified period. This option provides more flexibility but may result in higher overall costs due to interest and fees. Prepaid tuition plans often have administrative fees, which may be assessed annually or as a percentage of the total plan cost. These fees cover the management and operation of the plan and may vary depending on the provider. Enrollment fees are typically required when joining a prepaid tuition plan. These one-time fees may vary depending on the plan provider and help cover the costs associated with establishing and managing the account. Prepaid tuition plans offer federal tax benefits, such as tax-deferred growth and tax-free withdrawals for qualified higher education expenses. These benefits can help families save on taxes while funding their child's education. In addition to federal tax benefits, many states offer tax incentives for participating in prepaid tuition plans, such as state income tax deductions or credits. These benefits vary by state and may be subject to certain limitations and restrictions. While prepaid tuition plans provide some protection against rising tuition costs, they may still be subject to market fluctuations. Changes in the financial markets can impact the plan's investments and overall value. Inflation is another investment risk associated with prepaid tuition plans, as it can erode the purchasing power of the funds saved. However, prepaid plans typically provide some degree of inflation protection by locking in current tuition rates. One limitation of prepaid tuition plans is that they are often restricted to in-state public colleges and universities. This can limit the beneficiary's choices for higher education institutions. Prepaid tuition plans generally do not cover non-tuition expenses, such as room and board, books, or other fees. Families may need to rely on additional savings or financial aid to cover these costs. To mitigate the risks and limitations of prepaid tuition plans, families can diversify their college savings strategy by combining prepaid plans with other savings vehicles, researching plan options carefully, and consulting with a financial advisor. A 529 savings plan is a tax-advantaged investment vehicle designed to help families save for future education costs. These plans offer more investment options and flexibility than prepaid tuition plans. Compared to prepaid tuition plans, 529 savings plans offer greater flexibility in investment choices and eligible institutions but do not provide the same level of tuition inflation protection. Coverdell Education Savings Accounts are tax-advantaged investment accounts designed for education savings, including K-12 expenses. They offer investment flexibility and tax-free withdrawals for qualified expenses. Coverdell ESAs provide greater flexibility in investment options and eligible expenses but have lower contribution limits and stricter income restrictions compared to prepaid tuition plans. Traditional savings accounts and investments, such as CDs or mutual funds, can also be used for college savings but do not offer the same tax advantages as prepaid tuition plans or other education-specific savings vehicles. While traditional savings options offer more flexibility and control over investments, they lack the tax benefits and tuition inflation protection of prepaid tuition plans. Prepaid tuition plans offer a unique way for families to save for higher education by locking in current tuition rates and providing protection against inflation. However, they also come with certain limitations and risks that should be considered when choosing a college savings strategy. As the cost of higher education continues to rise, prepaid tuition plans are likely to remain a popular college savings option. Future trends may include increased plan flexibility, expanded eligibility for participating institutions, and additional state tax benefits. To make the most informed decision about college savings options, including prepaid tuition plans, it is recommended that families consult with a financial advisor. These professionals can help assess individual needs, risks, and goals to develop a tailored college savings strategy.What Are Prepaid Tuition Plans?
Types of Prepaid Tuition Plans
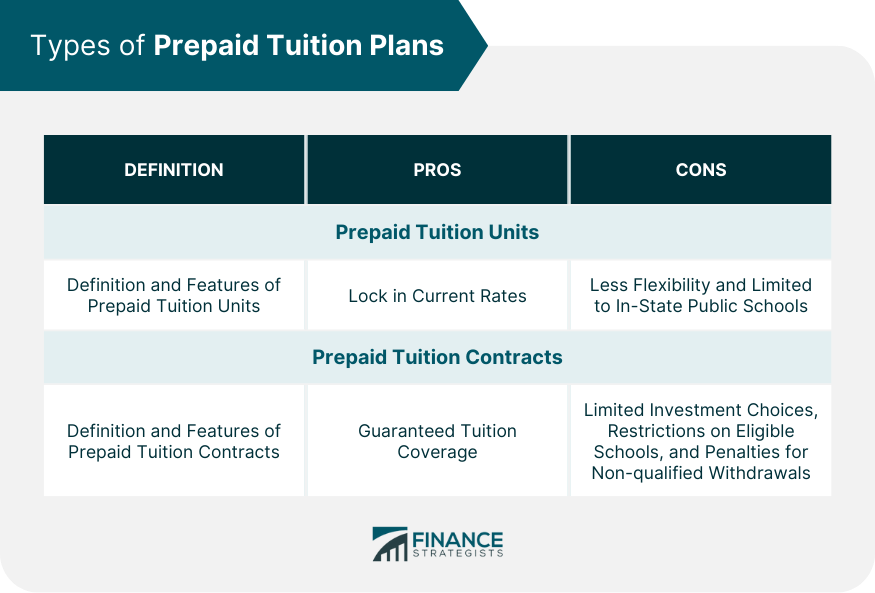
Prepaid Tuition Units
Prepaid Tuition Contracts
Eligibility and Enrollment of Prepaid Tuition Plans
Eligibility Requirements
Beneficiary Qualifications
Account Owner Qualifications
Enrollment Process
Application and Documentation
Enrollment Periods
Financial Aspects of Prepaid Tuition Plans
Funding Methods
Lump-Sum Payments
Installment Plans
Plan Costs and Fees
Administrative Fees
Enrollment Fees
Tax Benefits
Federal Tax Benefits
State Tax Benefits

Risks and Limitations of Prepaid Tuition Plans
Investment Risks
Market Fluctuations
Inflation
Limitations
Restricted to In-State Public Colleges and Universities
Non-Tuition Expenses Not Covered
Strategies to Mitigate Risks and Limitations
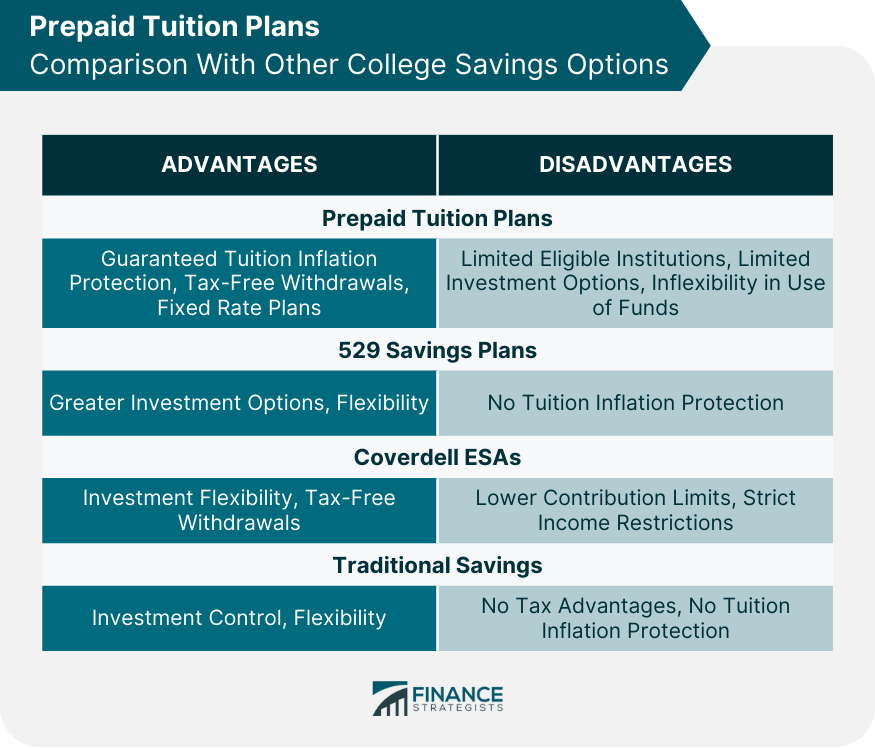
Prepaid Tuition Plans Comparison with Other College Savings Options
529 Savings Plans
Coverdell Education Savings Accounts (ESAs)
Traditional Savings Accounts and Investments
Final Thoughts
Prepaid Tuition Plans FAQs
Prepaid tuition plans offer several benefits, including locking in current tuition rates, protecting against tuition inflation, and providing potential tax advantages at both federal and state levels.
Prepaid tuition plans focus on prepaying tuition expenses at current rates, whereas 529 savings plans offer a more flexible investment vehicle for college savings. Prepaid tuition plans generally have more restrictions on eligible institutions, while 529 plans can be used for a wider range of schools and expenses.
Prepaid tuition plans are primarily designed for in-state public colleges and universities. However, some plans may allow for the transfer of funds to out-of-state or private institutions, though the benefits may be reduced or limited.
Prepaid tuition plans generally do not cover non-tuition expenses like room and board, books, or other fees. Families may need to rely on additional savings, financial aid, or other college savings options to cover these costs.
To mitigate the risks and limitations of prepaid tuition plans, families can diversify their college savings strategy by combining prepaid plans with other savings vehicles, researching plan options carefully, and consulting with a financial advisor to tailor their approach to their unique needs and goals.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











