Stock options are contracts that grant the holder the right to buy or sell a specific number of shares of a company's stock at a predetermined price, called the exercise or strike price. They can be a valuable part of an employee's compensation package, providing potential for financial gain if the company's stock price increases. Stock option planning is essential for maximizing the potential benefits of stock options while minimizing associated risks and tax liabilities. By understanding the types of stock options, vesting schedules, tax implications, and developing strategies, employees can make informed decisions about managing and exercising their options. Various strategies can be employed when managing stock options, such as exercising options early, holding options until expiration, or utilizing tax-advantaged strategies. Choosing the right strategy depends on factors like the type of stock options, individual financial goals, and the company's stock performance. Incentive Stock Options (ISOs) are a type of employee stock option that offers favorable tax treatment. They are only available to employees of the company and must meet specific requirements set forth by the Internal Revenue Code. ISOs can help employees reduce their tax liability if certain conditions are met. Non-qualified Stock Options (NSOs) are another type of employee stock option that does not have the same tax advantages as ISOs. They are more flexible and can be offered to both employees and non-employees, such as consultants or board members. NSOs are subject to ordinary income tax when exercised. Employee Stock Purchase Plans (ESPPs) allow employees to purchase company stock at a discounted price, typically through payroll deductions. They can be a valuable benefit for employees, offering an opportunity to invest in the company at a lower cost. ESPPs are subject to specific tax rules depending on the plan's design. Restricted Stock Units (RSUs) are a form of equity compensation that grants employees the right to receive company shares after meeting certain vesting requirements. RSUs can provide employees with a more predictable form of equity compensation compared to stock options, as they are not dependent on the company's stock price. Vesting schedules dictate when employees can exercise their stock options or receive shares from RSUs. They can be based on time, performance, or a combination of both. Understanding the vesting schedule is crucial for planning when to exercise options or sell shares while managing risk and tax implications. The exercise price is the predetermined price at which an employee can purchase company shares through stock options. The fair market value (FMV) is the current price of the company's stock. The difference between the exercise price and the FMV determines the potential profit from exercising stock options. Ordinary income tax applies to the difference between the exercise price and the FMV when exercising NSOs or selling shares acquired through ESPPs. Employees must report this amount as part of their taxable income, which may increase their overall tax liability. Capital gains tax applies to the difference between the FMV at the time of exercise and the sale price of the stock when selling shares acquired through stock options or RSUs. The tax rate depends on the holding period, with long-term capital gains typically being taxed at a lower rate than short-term gains. The Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) may apply to employees who exercise Incentive Stock Options (ISOs) and do not sell the shares in the same year. The AMT is a parallel tax system that ensures high-income earners pay a minimum amount of tax. Exercising ISOs can trigger the AMT, which may result in additional tax liability. Managing risk and diversifying investments is crucial when dealing with stock options. Concentrating too much of one's wealth in a single company's stock can expose investors to significant risk. Diversification across different investments, asset classes, and industries can help mitigate risk and improve long-term returns. Exercising stock options and holding the shares for more than one year can qualify the gains for long-term capital gains tax treatment. Long-term capital gains are generally taxed at a lower rate than short-term gains, providing a tax advantage for those who hold shares longer. The exercise and hold strategy can provide potential tax benefits, but it also carries risks. Holding company stock for an extended period exposes investors to market volatility and potential declines in stock value. It's essential to weigh the potential tax advantages against the risks associated with holding company stock. The exercise and sell strategy involves exercising stock options and immediately selling the shares. This results in short-term capital gains, which are generally taxed at a higher rate than long-term capital gains. The strategy provides immediate liquidity but may result in a higher tax liability. Exercising and selling stock options can provide immediate cash and limit exposure to company stock price fluctuations. However, this strategy may result in a higher tax liability due to short-term capital gains. Investors should consider their financial goals, risk tolerance, and tax situation when deciding on this strategy. The exercise and sell-to-cover strategy involves exercising stock options and immediately selling enough shares to cover the exercise cost and associated taxes. This allows employees to retain some shares for potential future gains while managing their immediate tax liability. Sell-to-cover provides a balance between realizing immediate gains and retaining potential future growth. This strategy allows investors to manage tax liabilities while still participating in the company's future success. However, it still exposes investors to market risk and fluctuations in the company's stock price. Stock option ladders involve exercising stock options in staggered intervals rather than exercising all options at once. This strategy can help manage tax liabilities and reduce the risk of concentrating too much wealth on a single company's stock. Stock option ladders can provide a more balanced approach to exercising stock options, potentially reducing tax liability and market risk. However, this strategy requires careful planning and may result in missed opportunities if the company's stock price declines during the staggered exercise periods. Protective puts involve purchasing put options to protect against potential declines in the value of company stock. This strategy can help reduce downside risk while still allowing employees to participate in potential stock price appreciation. Collars involve combining protective puts with the sale of call options, effectively limiting both the upside potential and downside risk. This strategy can provide a more conservative approach to managing stock options, particularly for risk-averse investors. Hedging strategies can help protect against downside risk while still allowing for potential gains. However, these strategies can be complex and may involve additional costs, such as option premiums. Investors should carefully consider their risk tolerance, financial goals, and investment knowledge before implementing hedging strategies. Job changes and termination can significantly impact stock option planning. Unexercised stock options may be forfeited or subject to accelerated vesting, depending on the terms of the employment agreement. Employees should carefully review their stock option agreements and understand the implications of job changes on their equity compensation. Marriage and divorce can affect stock option planning and ownership, as stock options may be considered marital property. Couples should understand how their stock options will be treated in the event of a divorce and consider the potential tax implications of transferring options between spouses. Retirement planning should take stock options into account, as they can be an important source of income and wealth during retirement. Retirees should develop a strategy for exercising and managing their stock options to maximize their benefits and minimize tax liabilities. Stock options can have significant estate planning implications, particularly for high-net-worth individuals. Careful planning is necessary to ensure that stock options are appropriately included in an estate plan and that beneficiaries understand their rights and responsibilities related to inherited stock options. Employees with stock options must be aware of insider trading rules and regulations, as exercising options or selling company stock while in possession of material non-public information can result in severe penalties. It's essential to understand and comply with insider trading rules to avoid legal and financial repercussions. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) regulates stock options and other equity compensation arrangements, and employees must comply with SEC rules and reporting requirements. Understanding and adhering to these regulations is crucial for avoiding potential fines, penalties, or legal actions. Companies often have their own internal policies and guidelines related to stock options and equity compensation. Employees should familiarize themselves with their company's specific policies to ensure compliance and avoid potential conflicts of interest or other issues. Financial planners and advisors can provide valuable guidance and expertise in stock option planning and strategies. They can help employees understand the potential risks, rewards, and tax implications of their stock options and develop personalized strategies to maximize their benefits. Choosing the right financial professional is crucial for effective stock option planning. Employees should consider factors such as credentials, experience, and communication style when selecting a financial planner or advisor to help them navigate their stock options. Working with a financial professional on an ongoing basis can help employees stay informed about their stock options and make adjustments to their strategies as needed. Regular reviews and updates can ensure that stock option strategies remain aligned with employees' financial goals and changing circumstances. To maximize the benefits of equity compensation and minimize risks and tax liabilities, employees should develop a personalized stock options strategy based on their financial goals, risk tolerance, and tax situation. Understanding the various strategies and factors that impact stock options can help employees make informed decisions and improve their overall financial well-being. It is important to regularly review and update stock option plans as life circumstances and financial goals change to ensure alignment with evolving needs and objectives. Consulting with a financial advisor can provide valuable guidance in navigating the complexities of stock options, managing potential risks, and optimizing equity compensation for long-term financial success. What Are Stock Option Planning and Strategies?
Types of Stock Options
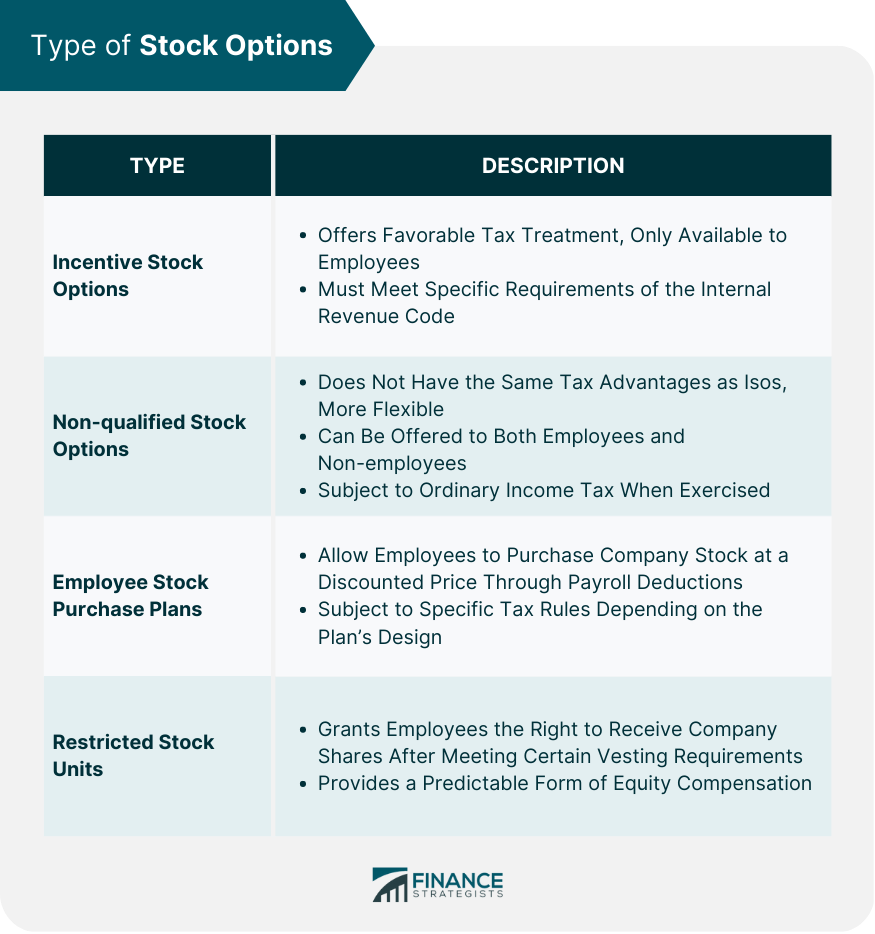
Incentive Stock Options (ISOs)
Non-qualified Stock Options (NSOs)
Employee Stock Purchase Plans (ESPPs)
Restricted Stock Units (RSUs)
Stock Option Planning Basics
Understanding Vesting Schedules
Exercise Price and Fair Market Value
Tax Implications
Ordinary Income Tax
Capital Gains Tax
Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT)
Risk Management and Diversification

Stock Options Strategies
Exercise and Hold
Long-Term Capital Gains
Risks and Benefits
Exercise and Sell
Short-Term Capital Gains
Risks and Benefits
Exercise and Sell-To-Cover
Tax Management Strategy
Risks and Benefits
Stock Option Ladders
Staggered Exercise Strategy
Risks and Benefits
Hedging Strategies
Protective Puts
Collars
Risks and Benefits

Impact of Life Events on Stock Option Planning
Job Changes and Termination
Marriage and Divorce
Retirement
Estate Planning
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
Insider Trading Rules
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) Regulations
Company-Specific Policies
Working With Financial Professionals
Role of Financial Planners and Advisors
Selecting the Right Professional
Ongoing Stock Option Management
Final Thoughts
Stock Option Planning and Strategies FAQs
Stock option planning and strategies involve understanding the types of stock options, vesting schedules, tax implications, and developing personalized strategies to maximize benefits while minimizing risks and tax liabilities associated with stock options.
Effective stock option planning and strategies can help employees make informed decisions about managing and exercising their options, optimizing tax implications, and reducing potential risks related to their equity compensation.
Common stock option strategies include exercise and hold, exercise and sell, exercise and sell-to-cover, stock option ladders, and hedging strategies. The appropriate strategy depends on factors like the type of stock options, individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and the company's stock performance.
Life events, such as job changes, marriage, divorce, retirement, and estate planning, can significantly impact stock option planning and strategies, requiring adjustments to align with changing circumstances and goals. Regulatory considerations, such as insider trading rules, SEC regulations, and company-specific policies, also play a crucial role in stock option planning and compliance.
Working with a financial planner or advisor can provide valuable expertise and guidance in stock option planning and strategies. Financial professionals can help employees understand the potential risks, rewards, and tax implications of their stock options and develop personalized strategies tailored to their specific needs and goals.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











