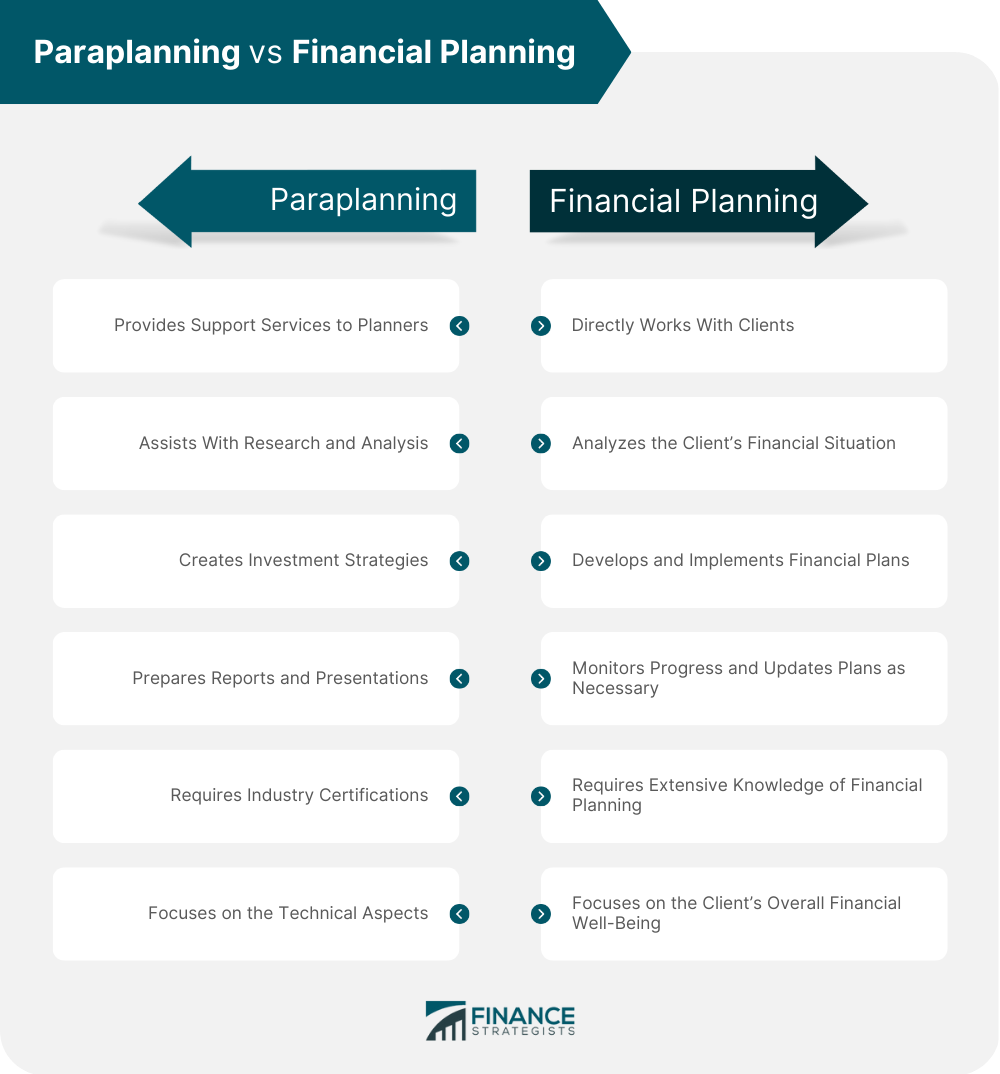
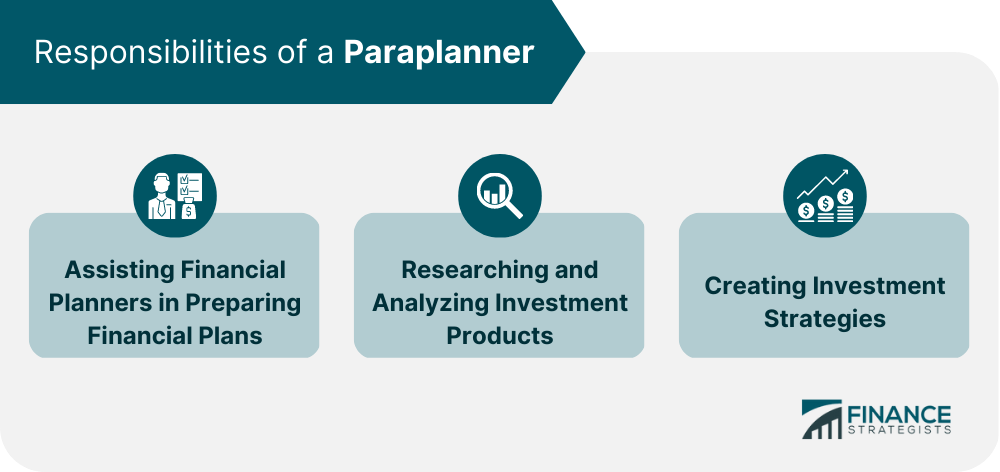
Paraplanning is a critical component of financial planning. It involves providing support services to financial planners, such as research, analysis, and the preparation of financial plans and investment strategies. While both paraplanning and financial planning play important roles in the field of finance, there are distinct differences between the two. Paraplanning involves supporting financial planners, such as conducting research and analysis, creating long-term and short-term investment strategies, and preparing reports and presentations. Financial planning involves working directly with clients, analyzing their current financial situation, developing and implementing comprehensive financial plans, and monitoring progress over time. While both require industry certifications, paraplanning focuses on the technical aspects of finance, while financial planning focuses on the overall financial well-being of the client. The table below further illustrates the difference between paraplanning and financial planning. Paraplanners use a variety of software tools to assist them in their work. Some of the most popular software tools include financial planning, investment analysis, and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software. Financial planning software is designed to help financial planners and paraplanners develop and present financial plans to clients. These tools typically include calculators for retirement planning, investment analysis, and tax planning. They also allow paraplanners to input data and generate reports for clients. Paraplanners use investment analysis software to research and analyze investment options. These tools provide data on market trends, investment performance, and risk analysis. They also allow paraplanners to evaluate the suitability of investments for clients. Paraplanners use CRM software to manage client relationships. These tools help paraplanners keep track of client contact information, financial goals, and investment preferences. They also allow paraplanners to schedule meetings and send reminders to clients. To be successful in paraplanning, it is essential to adhere to best practices. Some of the best practices for paraplanners include: Compliance. Paraplanners must adhere to all regulatory requirements and compliance standards. This includes keeping client information secure and ensuring that all recommendations are in the client's best interest. Communication. Effective communication with clients is essential for success in paraplanning. Paraplanners must be able to explain complex financial information in a way that clients can understand. Continuing Education. The financial planning industry is constantly evolving, and paraplanners must stay up-to-date with the latest trends and regulations. Continuing education is essential for staying current in the field. The primary role of a paraplanner is to assist financial planners in preparing financial plans for their clients. They work closely with the financial planner to gather and analyze data, research investment options, create investment strategies, and prepare reports and presentations. One of the primary responsibilities of a paraplanner is to conduct research and analysis on investment products. They must keep abreast of market trends, evaluate the risks and potential rewards of investment options, and determine the suitability of investments for clients' financial goals. Another responsibility of a paraplanner is to create investment strategies. They must work with the financial planner to determine the most effective investment options for clients and develop a plan to achieve their financial goals. Finally, paraplanners are responsible for preparing reports and presentations. They must be skilled in presenting complex financial data clearly and concisely to clients. These reports may include investment performance reports, portfolio analysis reports, and other financial planning documents. Becoming a paraplanner requires a strong educational background, industry certifications, and soft skills. Most paraplanners have a bachelor's degree in finance, accounting, or a related field. Some may also have a master's degree in business administration or finance. In addition to a strong educational background, paraplanners must also hold industry certifications. These certifications demonstrate a paraplanner's expertise and knowledge of financial planning. Some of the most popular certifications for paraplanners include the Certified Financial Planner (CFP), Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA), and Accredited Wealth Management Advisor (AWMA) certifications. Soft skills are also essential for a successful career in paraplanning. Paraplanners must have excellent communication and interpersonal skills to build and maintain relationships with clients. They must also be detail-oriented, organized, and possess strong analytical skills to effectively conduct research and analysis. Paraplanning is a growing field, and the job outlook for paraplanners is positive. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects that employment in the personal financial advisor field will grow by 15% from 2021 to 2031, which is about as fast as the average for all occupations. This growth is due in part to the increasing demand for financial planning services as the baby boomer generation reaches retirement age and seeks advice on retirement planning and wealth management. Paraplanners can expect their salary range to fluctuate depending on their experience, industry, and location. As per the BLS latest available data, the median annual wage for personal financial advisors is $94,170. However, entry-level paraplanners can expect to earn less than the median wage, while experienced paraplanners can earn significantly more. Paraplanning is an essential aspect of financial planning, providing support services to financial planners that include research, analysis, and preparation of financial plans and investment strategies. A paraplanner's educational background, industry certifications, and soft skills are crucial to their success, while their tools, best practices, and compliance with regulations ensure they provide quality services. The job outlook for paraplanners is positive, and the demand for financial planning services continues to increase. For individuals or businesses seeking sound financial advice, hiring the services of a paraplanner can prove invaluable. With their expertise, clients can achieve their financial goals and secure their financial future.What Is Paraplanning?
Paraplanning vs Financial Planning
Paraplanning
Financial Planning
Paraplanning Tools
Paraplanning Best Practices
Responsibilities of a Paraplanner
Qualifications for a Paraplanner
Career Prospects
Final Thoughts
Paraplanning FAQs
Paraplanning refers to providing support services to financial planners, such as research, analysis, and preparation of financial plans and investment strategies.
Paraplanners typically hold a bachelor's degree in finance, accounting, or a related field, as well as industry certifications such as the Certified Financial Planner (CFP), Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA), and the Accredited Wealth Management Advisor (AWMA) certifications. Soft skills such as communication, organization, and analytical skills are also essential.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that employment in the personal financial advisor field will grow by 15% from 2021 to 2031, which is about as fast as the average for all occupations. This growth is due in part to the increasing demand for financial planning services as the baby boomer generation reaches retirement age and seeks advice on retirement planning and wealth management.
Effective communication with clients, adherence to regulatory requirements and compliance standards, and continuing education to stay current with industry trends and regulations are essential for success in paraplanning.
Paraplanners assist financial planners in creating investment strategies and financial plans that align with clients' financial goals. They conduct research and analysis on investment products, evaluate risks and potential rewards of investment options, and provide reports and presentations that help clients understand their financial situation and make informed decisions. Hiring a paraplanner can help individuals or businesses achieve their financial goals and secure their financial future.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











