Accessible income is an important concept relevant to individuals, households, and families when it comes to an understanding of their financial health. Accessible income refers to the income that is available to an individual or household after taxes, deductions, and other expenses have been taken into account. It is how much money a person or family can use for their daily living expenses and discretionary spending. To calculate accessible income, one needs to take into account all the sources of income and the expenses that are necessary for daily living. The following is a breakdown of how to calculate accessible income: Pre-tax income refers to the income that an individual or household earns before taxes and other deductions are taken out. It includes all sources of income, such as salary, commissions, bonuses, and investment income. This is the amount of money that a person or household can expect to earn in a year. Taxes and deductions are expenses that reduce a person's or household's income. Taxes are mandatory contributions to the government, while deductions include expenses such as healthcare premiums, retirement contributions, and union dues. Taxes and deductions can vary based on a person's or household's income level, employment status, and other factors. Necessary expenses are expenses that are required for daily living. These expenses include rent or mortgage payments, utilities, food, transportation, and healthcare. These expenses vary depending on a person's or household's location, family size, and lifestyle. Discretionary expenses are not required for daily living but are considered desirable or enjoyable. These expenses can include travel, entertainment, hobbies, and luxury items. Discretionary expenses can vary depending on a person's or household's income level, lifestyle, and financial goals. Several factors can affect a person's or household's accessible income. These factors include: Employment status refers to whether a person is employed full-time, part-time, or self-employed. Full-time employees generally have a higher income than part-time employees, while self-employed individuals have more control over their income but may have more financial uncertainty. Income sources refer to the types of income that a person or household earns, such as salary, commissions, investments, and government benefits. Different income sources can have different tax implications and can affect a person's or household's accessible income. Location and cost of living can have a significant impact on a person's or household's accessible income. For example, individuals living in urban areas with a high cost of living may have a higher accessible income than those living in rural areas with a lower cost of living, even if their pre-tax income is the same. Family size and dependents can also affect accessible income. Expenses such as housing, food, and healthcare can increase with more family members, reducing accessible income. Government benefits and assistance programs can increase accessible income for eligible people. Programs such as Medicaid, SNAP (Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program), and TANF (Temporary Assistance for Needy Families) can assist individuals and families who meet certain income requirements. There are several strategies that individuals and households can use to increase their accessible income. These strategies include: Negotiating a raise or promotion at work can increase a person's pre-tax income, thereby increasing their accessible income. This can involve discussing salary with an employer, demonstrating the value of one's contributions, and seeking out opportunities for career growth and advancement. Pursuing additional income sources can also increase accessible income. This can involve taking on a part-time job, starting a side hustle, or investing in rental properties or other income-generating assets. Reducing expenses is another way to increase accessible income. This can involve cutting unnecessary expenses such as dining out or subscription services, downsizing to a smaller living space, or negotiating lower rates for services such as utilities or insurance. Investing and saving for the future can also increase accessible income over the long term. By investing in assets such as stocks, bonds, or real estate, individuals and households can earn passive income and grow their net worth. Additionally, saving money in a retirement account such as an IRA or 401(k) can provide tax benefits and help ensure financial security in the future. Accessible income can serve as a useful tool for evaluating one's financial health and making informed financial decisions. By understanding their accessible income, individuals and households can: Setting financial goals is an important part of personal finance, and accessible income can help individuals and households understand what is realistic and achievable. By setting financial goals that align with their accessible income, individuals and households can progress toward financial security and stability. Accessible income can also serve as a useful tool for financial planning. By understanding how much money is available for living expenses and discretionary spending, individuals and households can create a budget that is realistic and sustainable. Additionally, accessible income can help individuals and households determine how much they can afford to save or invest for the future. Finally, accessible income can be used as a metric for evaluating overall financial health. By comparing their accessible income to their expenses and financial goals, individuals and households can determine whether they are living within their means and progressing toward their financial objectives. In conclusion, accessible income is an important concept that can have a significant impact on an individual's or household's financial health. By understanding how to calculate accessible income, factors that affect it, strategies for increasing it, and how to use it as a tool for financial planning, individuals and households can make informed financial decisions and work towards their financial goals. By taking action to increase their accessible income and manage their finances effectively, individuals and households can achieve financial security, stability, and peace of mind. For further guidance on managing your accessible income and overall financial health, consider speaking with a financial advisor who can provide personalized advice and help you create a plan to achieve your financial goals.What Is Accessible Income?
How to Calculate Accessible Income
Pre-tax Income
Taxes and Deductions
Necessary Expenses
Discretionary Expenses
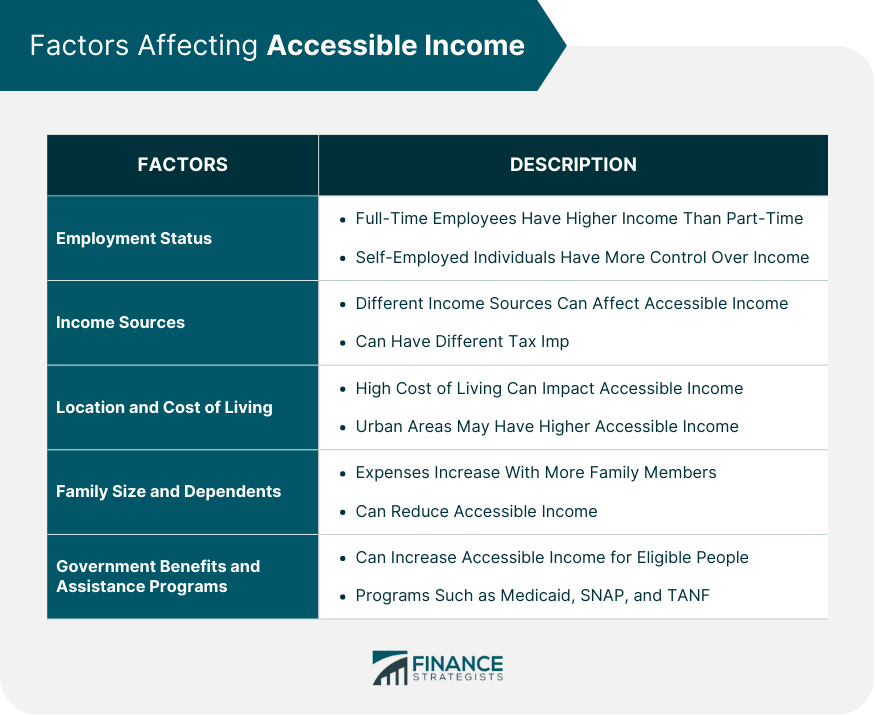
Factors Affecting Accessible Income
Employment Status
Income Sources
Location and Cost of Living
Family Size and Dependents
Government Benefits and Assistance Programs
Strategies for Increasing Accessible Income
Negotiating a Raise or Promotion at Work
Pursuing Additional Income Sources
Reducing Expenses
Investing and Saving for the Future
Evaluating Your Financial Health Based on Accessible Income
Understand the Relationship Between Accessible Income and Financial Goals
Use Accessible Income as a Tool for Financial Planning
Evaluate Overall Financial Health Based on Accessible Income
Final Thoughts
Accessible Income FAQs
Accessible income is the income that is available to an individual or household after taxes, deductions, and other expenses have been taken into account. It is the amount of money that a person or family can use for their daily living expenses and discretionary spending.
Accessible income can be calculated by considering pre-tax income, taxes and deductions, necessary expenses, and discretionary expenses.
Factors that affect accessible income include employment status, income sources, location and cost of living, family size and dependents, and government benefits and assistance programs.
There are several strategies for increasing accessible income, including negotiating a raise or promotion at work, pursuing additional income sources, reducing expenses, and investing and saving for the future.
Accessible income can be used as a tool for evaluating financial health by understanding the relationship between accessible income and financial goals, using it as a tool for financial planning, and evaluating overall financial health based on accessible income.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











