Budgeting needs and wants play a critical role in personal finance management and achieving financial stability. Needs are the essential expenses required for a person's basic survival and well-being, such as food, shelter, clothing, healthcare, and basic transportation. Properly addressing these needs ensures that individuals can maintain a stable and secure lifestyle. On the other hand, wants are non-essential items and services that can enhance one's quality of life but are not necessary for survival or basic well-being. Examples include entertainment, dining out, vacations, and luxury items. While it is natural to desire and indulge in these wants, it is crucial to strike a balance between them and essential needs to maintain financial stability. Understanding the distinction between needs and wants enables individuals to prioritize their expenses, allocate funds more efficiently, and work towards long-term financial goals. Needs refer to the essential items and services required for a person's basic survival and well-being. These typically include: Food and Water: Sufficient nourishment to maintain a healthy body and mind. Shelter and Utilities: Safe and secure housing, including rent or mortgage payments, electricity, water, and gas. Clothing: Appropriate attire to protect oneself from the elements and maintain personal hygiene. Healthcare: Access to medical services, insurance, and medications as needed. Basic Transportation: A reliable means of getting to work, school, and other necessary destinations. Assessing and prioritizing personal needs is essential for creating a tailored financial plan. Individual needs may vary based on factors such as personal circumstances, geographical location, and lifestyle choices. By considering these factors, you can ensure that your budget addresses your unique needs. To assess your needs accurately, list essential expenses, such as housing, food, transportation, healthcare, and clothing. Next, prioritize these expenses based on their importance to your well-being and the consequences of not meeting them. This process will help you allocate funds more efficiently, ensuring that your most pressing needs are met before considering discretionary spending. Ultimately, understanding and prioritizing your needs will provide a solid foundation for financial stability and enable you to work towards long-term financial goals. Managing your needs is crucial for financial stability. Here are some strategies to help: Tracking Expenses: Record all your spending to identify areas for potential savings. Creating a Needs-Based Budget: Allocate funds for essential expenses first, ensuring that your needs are met before considering wants. Finding Ways to Reduce Costs: Look for opportunities to save on necessities, such as buying in bulk, using coupons, or opting for generic brands. Wants are non-essential items and services that can enhance one's quality of life but are not required for survival or basic well-being. Examples include: Entertainment and Hobbies: Movies, concerts, sports events, and leisure activities. Eating Out and Leisure Activities: Dining at restaurants, ordering takeout, or participating in recreational activities. Vacations and Travel: Getaways, trips, and excursions for pleasure. Luxury Items and Electronics: High-end clothing, gadgets, and other non-essential possessions. Understanding the impact of wants on financial stability is vital for responsible money management. Although indulging in wants can provide pleasure and improve one's quality of life, excessive spending on non-essential items may lead to financial strain and difficulty in meeting essential needs. Striking a balance between satisfying wants and maintaining financial stability involves setting limits on discretionary spending, prioritizing long-term financial goals, and evaluating the true value of non-essential items before purchasing. Doing so lets you enjoy the occasional luxury without sacrificing your financial security. Incorporating mindful spending habits and regularly reviewing your financial situation will help you make informed decisions about your wants, allowing you to maintain a healthy balance between enjoyment and financial responsibility. Ultimately, understanding the impact of wants on your financial stability will contribute to a more sustainable and fulfilling financial future. Balancing wants with financial goals is essential for maintaining financial stability while still enjoying life's pleasures. To avoid overspending on wants, keeping your long-term financial objectives in mind is crucial. These may include saving for retirement, paying off debt, investing in a home, or building an emergency fund. By aligning your spending habits with your financial goals, you can make more informed decisions about your wants and ensure that your discretionary spending does not compromise your financial well-being. This may involve setting limits on non-essential expenses, finding alternative ways to satisfy wants, or prioritizing which wants are most meaningful to you. Developing a clear understanding of your financial goals and incorporating them into your budget will allow you to strike a balance between fulfilling your desires and securing your financial future. Adopting this balanced approach will help you achieve financial success while still enjoying the occasional indulgence. A comprehensive budget can help you manage both needs and wants effectively. To create one: List All Income Sources and Expenses: Detail your monthly income and categorize your expenses as needs or wants. Categorize Expenses Into Needs and Wants: Differentiate between essential and non-essential spending. Set Spending Limits for Wants: Allocate a portion of your income for discretionary spending without compromising your needs or financial goals. Regularly saving and investing a portion of your income can help you achieve your financial goals and create a safety net for emergencies. The 50/30/20 rule is a simple guideline for managing your finances: Allocate 50% of your income to essential needs. Dedicate 30% of your income to wants and discretionary spending. Set aside 20% of your income for savings, investments, and debt repayment. This rule can be adjusted according to your personal circumstances and priorities, but it serves as a helpful starting point for balancing needs and wants. As your financial situation and goals change, reviewing and adjusting your budget is essential. Regularly reevaluate your spending habits and make necessary changes to stay on track with your financial goals. Impulse spending and consumerism can lead to overspending on wants. To manage these temptations, establish a waiting period before making non-essential purchases and consider the long-term value of the item in question. Social pressures and lifestyle inflation can encourage excessive spending on wants. To counteract this, focus on your financial goals and values, and remember that material possessions do not define your self-worth. There are often alternative ways to satisfy wants without overspending. For example, look for affordable or free entertainment options, cook at home instead of dining out, or borrow items from friends or family instead of purchasing them. Understanding and balancing needs and wants is crucial to achieving financial stability and long-term success. By identifying and managing essential expenses, setting realistic spending limits for non-essential items, and continuously reviewing and adjusting your budget, you can maintain a secure financial footing while still enjoying life's pleasures. Key points to remember include the importance of distinguishing between needs and wants, creating a comprehensive budget, prioritizing long-term financial goals, and adopting mindful spending habits to avoid overspending on wants. If you find it challenging to strike the right balance between your needs and wants or require guidance in managing your personal finances, consider seeking the help of a professional financial advisor. Their expertise can provide valuable insights and tailored strategies to help you achieve financial stability and reach your financial goals.Budgeting Needs vs Wants: Overview

What Are Needs?
Assessing and Prioritizing Personal Needs
Strategies for Managing Needs

What Are Wants?
Understanding the Impact of Wants on Financial Stability
Balancing Wants With Financial Goals
Practical Tips for Balancing Needs vs Wants
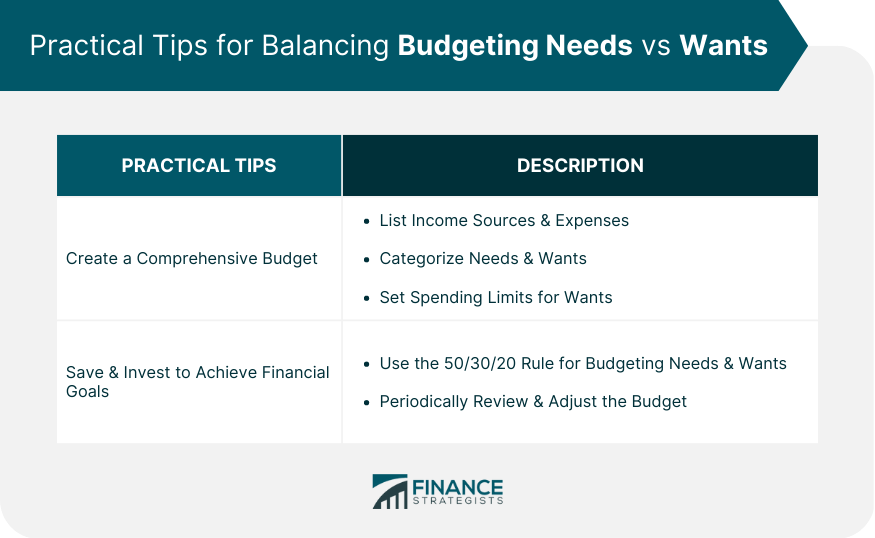
Creating a Comprehensive Budget
Saving and Investing to Achieve Financial Goals
Using the 50/30/20 Rule for Needs and Wants
Periodically Reviewing and Adjusting the Budget
Overcoming Challenges in Budgeting Needs vs Wants
Managing Impulse Spending and Consumerism
Dealing with Social Pressures and Lifestyle Inflation
Finding Creative Ways to Satisfy Wants without Overspending
The Bottom Line
Budgeting Needs vs Wants FAQs
Needs are essential items and services required for a person's basic survival and well-being, such as food, shelter, clothing, healthcare, and basic transportation. Wants are non-essential items and services that can enhance one's quality of life but are not required for survival, such as entertainment, vacations, and luxury items.
Distinguishing between needs and wants is crucial for financial stability, as it helps ensure that essential expenses are prioritized and met before spending on non-essential items. This distinction also allows for better management of personal finances and progress toward long-term financial goals.
To balance budgeting your needs and wants, create a comprehensive budget that first allocates funds for essential expenses, sets spending limits for wants, and prioritizes saving and investing. The 50/30/20 rule can be a helpful guideline for managing finances, with 50% allocated to needs, 30% to wants, and 20% to savings and debt repayment.
Effective strategies for managing needs include tracking expenses to identify potential savings, creating a needs-based budget, and finding ways to reduce costs, such as buying in bulk, using coupons, or opting for generic brands.
To avoid overspending on wants, consider your long-term financial goals, establish a waiting period before making non-essential purchases, and explore creative ways to satisfy wants without overspending, such as looking for affordable or free entertainment options or borrowing items from friends or family.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











