Envelope budgeting is a simple yet effective method for managing personal finances. It involves assigning specific amounts of money to separate "envelopes" for various spending categories. This system helps individuals track their spending, prioritize expenses, and save money. The concept of envelope budgeting has been around for decades. In the past, people physically divided their cash into envelopes labeled with different expense categories. Today, this method has evolved to incorporate digital tools, making it easier to manage finances while maintaining the core principles of envelope budgeting. Envelope budgeting promotes financial discipline by encouraging individuals to allocate funds for specific purposes. It helps people avoid overspending, as they can only spend what's available in each envelope. By sticking to the limits set for each category, individuals can develop better money management habits. One of the main advantages of envelope budgeting is its visual representation of finances. Seeing the envelopes and their remaining balances helps individuals understand their spending habits and make better decisions. This tangible representation can be especially helpful for those who struggle with traditional budgeting methods. Envelope budgeting is particularly effective in curbing overspending. When funds in an envelope are depleted, individuals must either stop spending in that category or reallocate funds from another envelope. This forces people to think critically about their spending choices and prioritize their expenses. A primary challenge of envelope budgeting is the difficulty in tracking electronic transactions. As many people use debit or credit cards for most purchases, it can be harder to visualize spending within the envelope system. Some individuals may find it difficult to translate the physical envelope concept to electronic transactions. Using physical cash envelopes can be inconvenient and pose security risks. Carrying cash can be bulky and risky, particularly when dealing with large amounts of money. Additionally, if the envelopes are lost or stolen, there is no way to recover the funds. Envelope budgeting can sometimes be too rigid for individuals with fluctuating expenses. Unexpected expenses may arise, requiring the reallocation of funds between envelopes. This can make the system feel restrictive and challenging to maintain for some people. To create an envelope budget, the first step is to determine your total monthly income. This includes your salary, any freelance income, and other sources of income such as investments or rental properties. Having an accurate picture of your income allows you to create a realistic budget that reflects your financial situation. Next, list your monthly expenses, dividing them into two categories: fixed and variable expenses. Fixed expenses are bills that remain consistent each month, such as rent, mortgage payments, or car payments. Variable expenses fluctuate monthly, such as groceries, entertainment, and clothing. Once you've identified your expenses, allocate a specific amount of money to each envelope based on your spending needs and priorities. Make sure to distribute your income among all expense categories, including savings and debt repayment. The goal is to allocate every dollar of your income to an envelope, ensuring your spending aligns with your financial goals. Zero-based budgeting is a method where every dollar of income is allocated to a specific expense category, resulting in a net income of zero. This method is similar to envelope budgeting but focuses on meticulously planning each expense rather than relying on pre-determined spending limits. The 50/30/20 rule is a straightforward budgeting approach that divides income into three categories: 50% for necessities, 30% for discretionary spending, and 20% for savings and debt repayment. This method offers a simple framework for managing finances without the need for detailed expense tracking. Pay-yourself-first budgeting prioritizes savings and investments by setting aside a predetermined portion of your income before allocating funds for other expenses. This method encourages financial growth and stability, as it ensures that savings goals are met before spending on non-essential items. Incorporating technology into the envelope budgeting system can simplify the process and address some of its challenges. Budgeting apps and tools can help users track expenses, manage digital transactions, and monitor their financial progress in real-time, all while adhering to the principles of envelope budgeting. Digital envelope systems offer a modernized version of the traditional envelope budgeting method. These systems use virtual envelopes to allocate funds for various expense categories, making it easier to track electronic transactions and adjust budgets as needed. Digital envelope systems provide the benefits of envelope budgeting while addressing some of its limitations. To succeed with envelope budgeting, it's essential to create a realistic budget based on your actual income and expenses. Overestimating or underestimating your spending needs can lead to financial stress and make it difficult to stick to your budget. Regularly monitoring your envelope balances is crucial for staying on track with your financial goals. Checking your envelopes frequently can help you identify areas where you may be overspending and make adjustments as needed to avoid financial setbacks. As your financial situation changes, your envelope budget should evolve accordingly. Whether you experience a change in income, new financial goals, or unexpected expenses, it's essential to update your budget to reflect these changes and maintain financial control. Envelope budgeting is a simple yet effective method of managing personal finances by assigning specific amounts of money to separate "envelopes" for various spending categories. The benefits of envelope budgeting include promoting financial discipline, visual representation of finances, and reducing overspending. However, some challenges and limitations exist, such as difficulty with electronic transactions, inconvenience and security concerns, and rigidity in spending. To create an envelope budget, determine monthly income, list monthly expenses, and allocate funds to envelopes. Alternatives to envelope budgeting include zero-based budgeting, the 50/30/20 rule, and pay-yourself-first budgeting. Integrating technology with envelope budgeting, such as budgeting apps and digital envelope systems, can simplify the process and address some of its challenges. To succeed with envelope budgeting, it's essential to create a realistic budget based on actual income and expenses, regularly monitor envelope balances, and adjust the budget for life changes. Envelope budgeting is a great way to prioritize expenses, track spending, and save money, helping individuals achieve financial stability and controlWhat Is Envelope Budgeting?
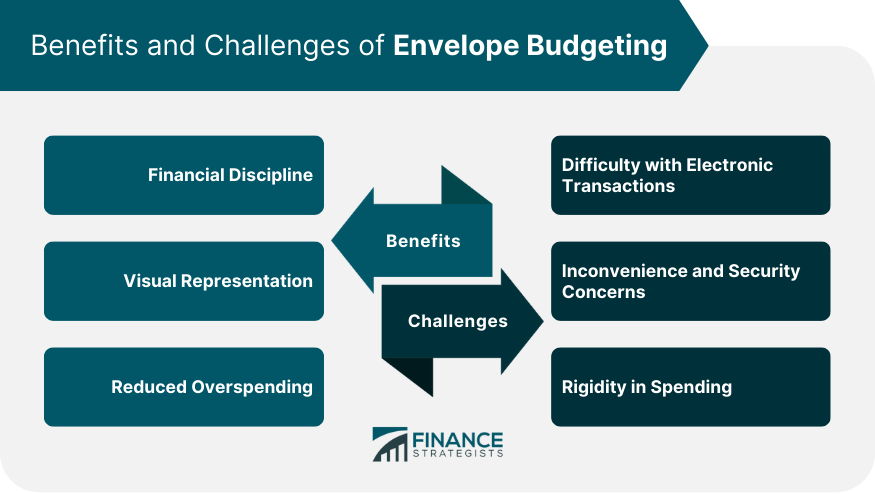
Benefits of Envelope Budgeting
Financial Discipline
Visual Representation
Reduced Overspending
Challenges and Limitations of Envelope Budgeting
Difficulty With Electronic Transactions
Inconvenience and Security Concerns
Rigidity in Spending
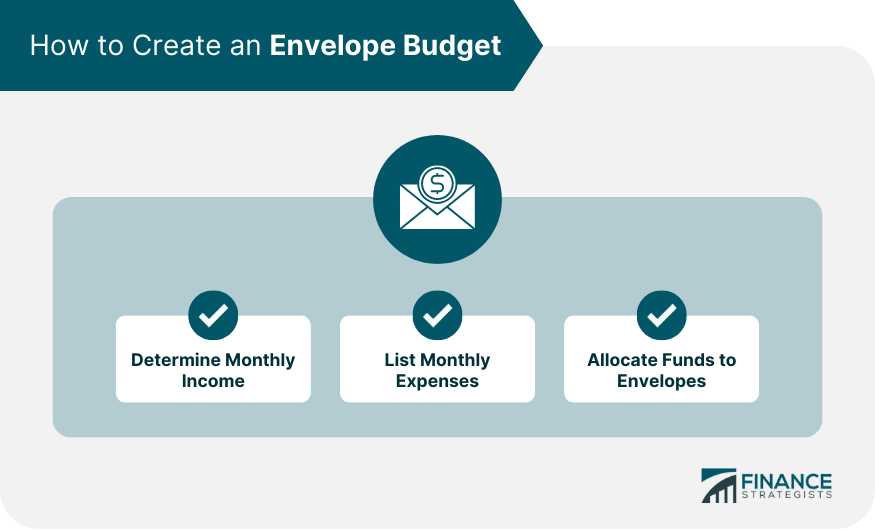
Creating an Envelope Budget
Determine Monthly Income
List Monthly Expenses
Allocate Funds to Envelopes
Alternatives to Envelope Budgeting
Zero-Based Budgeting
50/30/20 Rule
Pay-Yourself-First Budgeting
Integrating Technology With Envelope Budgeting
Budgeting Apps and Tools
Digital Envelope Systems
Tips for Success With Envelope Budgeting
Realistic Budgeting
Regular Monitoring
Adjusting for Life Changes
Bottom Line
Envelope Budgeting FAQs
Envelope budgeting is a budgeting technique where you set aside cash in labeled envelopes for various categories of expenses, such as groceries, utilities, etc.
Envelope budgeting can help you control your spending, avoid overspending, and keep track of your expenses. It can also help you save money and avoid debt.
One challenge of envelope budgeting is that it requires discipline and consistency to maintain. Another challenge is that it may not work well for people who prefer using credit cards or digital payment methods.
To create a realistic budget for envelope budgeting, start by tracking your actual income and expenses. This will help you determine how much money you need to allocate to each spending category. Be honest about your spending habits and avoid overestimating or underestimating your spending needs to avoid financial stress.
Envelope budgeting can work for anyone who is willing to commit to it and make it a habit. It may be particularly useful for people who struggle with overspending or impulse buying.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











