Part-time work refers to employment with fewer hours per week compared to full-time positions, typically offering less than 35 hours of work. The prevalence of part-time work is significant, as it contributes to labor market flexibility, economic growth, and workforce adaptability. Individuals may opt for part-time work due to personal preferences, family commitments, or the pursuit of additional education or hobbies. Seasonal jobs are temporary positions that align with specific seasons or periods, such as holiday retail work or summer camp counseling. These jobs often attract students and individuals seeking short-term employment. Freelance work involves self-employment, where individuals offer their skills and expertise to multiple clients on a project or contract basis. This type of work allows for greater autonomy and flexibility. On-call work involves being available to work on an as-needed basis, usually with irregular hours. Workers in this category often fill in for full-time employees who are absent or cover sudden increases in workload. Temporary work is characterized by fixed-term contracts, often filling in for a full-time employee on leave or during peak work periods. These positions may lead to permanent opportunities, depending on the employer's needs. Job sharing refers to two or more individuals sharing the responsibilities of a single full-time position. This arrangement allows for greater work-life balance and flexibility for the employees involved. Budgeting and financial planning are crucial for part-time workers as they often face irregular income. Establishing a budget helps workers manage their money, prioritize expenses, and save for emergencies. Creating a financial plan also enables part-time workers to set and achieve short-term and long-term financial goals. Part-time workers must be aware of tax regulations and their implications. Income earned through part-time work is taxable, and workers may need to file their taxes differently than full-time employees. Tax deductions, credits, and filing requirements for part-time workers vary based on factors such as total income, marital status, and a number of jobs. Retirement planning is essential for part-time workers who may not have access to employer-sponsored retirement plans. It is crucial to explore alternative retirement savings options such as individual retirement accounts (IRAs) or other investment vehicles. Saving consistently and early can help secure a comfortable retirement for part-time workers. Part-time workers often lack access to employer-provided insurance benefits. They need to explore alternative insurance options, such as purchasing individual health, life, or disability insurance policies. Comparing different insurance plans can help part-time workers find affordable and comprehensive coverage that meets their needs. Part-time workers are protected by various labor laws, which ensure fair treatment and equal opportunities. These laws cover aspects such as minimum wage, overtime pay, and safe working conditions. Understanding these rights empowers part-time workers to advocate for themselves and take legal action if necessary. Overtime and minimum wage regulations vary by country, state, or region, and part-time workers must be familiar with these rules. Employers are generally required to pay part-time employees at least the minimum wage and may need to provide overtime pay under certain conditions. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for both workers and employers. Anti-discrimination laws protect part-time workers from unfair treatment based on factors such as race, gender, age, or disability. Employers must ensure equal opportunities for all workers, regardless of their employment status. Part-time workers should be aware of these laws and know how to address discrimination in the workplace if it occurs. Workplace health and safety regulations apply to part-time workers as well. Employers must provide a safe working environment and follow safety guidelines to prevent accidents or injuries. Part-time workers should be familiar with these regulations and know their rights to report unsafe conditions or practices. Part-time work increases labor force participation, allowing more individuals to engage in the workforce. This includes students, caregivers, and individuals nearing retirement who might not be able to commit to full-time work. Increased labor force participation can contribute to economic growth and development. Part-time work can help reduce unemployment rates by providing job opportunities for those who cannot work full-time. However, underemployment, where workers are unable to find full-time work, may still persist. Balancing part-time and full-time employment opportunities is essential for a healthy labor market. Part-time work contributes to job creation by allowing employers to hire multiple workers for a single position or to meet fluctuating demand. This flexibility can lead to more job openings and reduced unemployment. However, the quality and stability of these jobs must also be considered. Part-time work can contribute to increased productivity and economic growth, as workers can focus on specific tasks and maintain a better work-life balance. However, productivity gains may be offset if part-time workers lack access to training, resources, or job security. Ensuring that part-time workers have opportunities for growth and development can maximize their productivity and impact the economy. The gig economy, characterized by short-term, flexible work arrangements, has expanded the part-time work landscape. While it provides workers flexibility and autonomy, it raises concerns about job security, worker rights, and income stability. Policymakers and stakeholders must address these issues to ensure a sustainable gig economy. Part-time work allows individuals to better balance their professional and personal lives, giving them more time for family, hobbies, or other pursuits. Part-time workers often enjoy more flexible schedules, allowing them to accommodate other commitments, such as childcare, education, or additional jobs. Working part-time can enable individuals to pursue multiple income streams, increasing financial security and diversifying their skillset. Part-time work can provide individuals with the time and flexibility needed to pursue personal interests, hobbies, or further education. Part-time employment can expose workers to a variety of industries, roles, and experiences, helping them develop a diverse skill set and broadening their career prospects. Part-time work often results in inconsistent income due to fluctuating hours and the temporary nature of some positions, making financial planning more challenging. Job security is generally lower for part-time workers, as they may be more vulnerable to layoffs or contract terminations compared to full-time employees. Part-time workers may receive fewer employee benefits, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off, compared to their full-time counterparts. Working part-time may limit opportunities for advancement and professional growth, potentially leading to career stagnation. Juggling multiple part-time jobs or commitments can be challenging, as individuals must effectively manage their time and priorities to avoid burnout and maintain productivity. Part-time work offers numerous benefits and challenges for workers, employers, and the economy. Financial planning, legal considerations, and the impact on the economy are essential aspects to consider when exploring part-time work. Future trends indicate an increasing demand for flexibility and non-traditional work arrangements. Part-time work can be a valuable and fulfilling option for individuals seeking greater work-life balance or the opportunity to pursue multiple interests. However, weighing the potential challenges, such as inconsistent income and limited benefits, is essential against the advantages of flexibility and personal fulfillment. To successfully navigate the financial challenges and opportunities associated with part-time work, it is advisable to consult a financial advisor.What Is Part-Time Work?
Types of Part-Time Work
Seasonal Jobs
Freelance Work
On-Call Work
Temporary Work
Job Sharing

Financial Considerations in Part-Time Work
Budgeting and Financial Planning
Tax Implications for Part-Time Workers
Retirement and Pension Considerations
Insurance Options for Part-Time Workers
Legal and Regulatory Considerations in Part-Time Work
Labor Laws and Rights of Part-Time Workers
Overtime and Minimum Wage Regulations
Anti-Discrimination Laws
Health and Safety Regulations
Impact of Part-Time Work on the Economy
Labor Force Participation
Unemployment Rates
Job Creation
Productivity and Economic Growth
Gig Economy and Its Implications
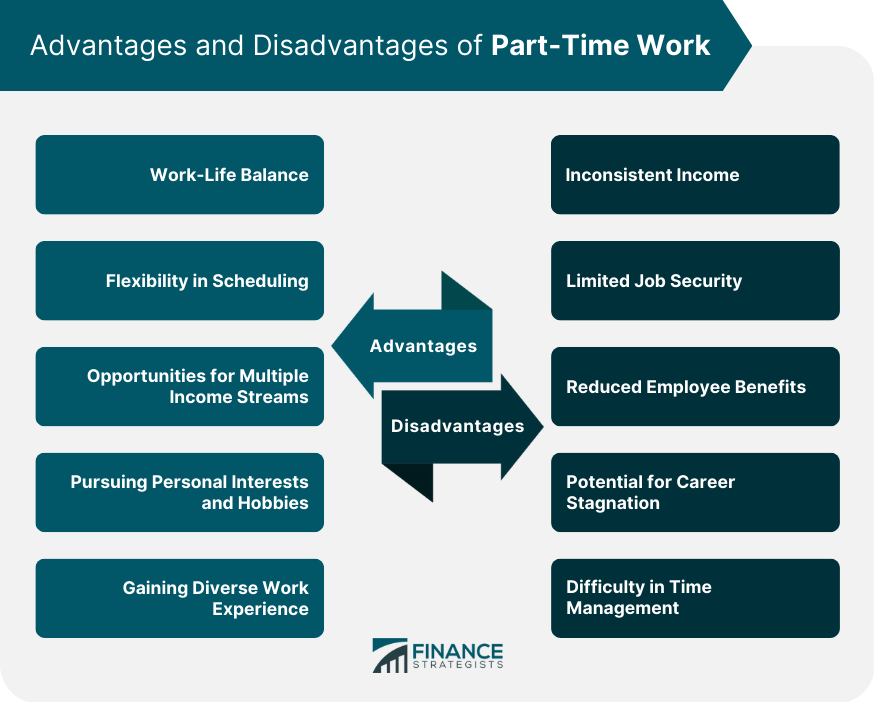
Advantages of Part-Time Work
Work-Life Balance
Flexibility in Scheduling
Opportunities for Multiple Income Streams
Pursuing Personal Interests and Hobbies
Gaining Diverse Work Experience
Disadvantages of Part-Time Work
Inconsistent Income
Limited Job Security
Reduced Employee Benefits
Potential for Career Stagnation
Difficulty in Time Management
Final Thoughts
Part-Time Work FAQs
Some important financial considerations for part-time workers include budgeting and financial planning, understanding tax implications, planning for retirement and pensions, and exploring insurance options. These factors can help part-time workers manage their finances effectively and prepare for a secure financial future.
Part-time workers are subject to various legal and regulatory considerations, such as labor laws and rights, overtime and minimum wage regulations, anti-discrimination laws, and health and safety regulations. Understanding these rules and regulations is essential for both workers and employers to ensure compliance and fair treatment.
Part-time work can influence the economy in several ways, including increased labor force participation, reduced unemployment rates, job creation, and potential gains in productivity and economic growth. However, the gig economy and its implications, such as job security and income stability, must also be considered.
Part-time work offers advantages such as work-life balance, flexibility in scheduling, opportunities for multiple income streams, pursuing personal interests, and gaining diverse work experience. However, it has disadvantages such as inconsistent income, limited job security, reduced employee benefits, potential for career stagnation, and difficulty in time management while juggling multiple part-time jobs or commitments.
Part-time workers can safeguard their financial well-being by establishing a budget, planning for retirement, understanding tax implications, and seeking insurance options. Consulting a financial advisor can provide valuable guidance on managing finances effectively and making informed decisions related to part-time work.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











