Student loan consolidation involves combining multiple student loans into a single loan, often with a new lender, making it easier for borrowers to manage their debt. The primary purpose of consolidating student loans is to simplify loan management, potentially secure better loan terms, and provide an opportunity to lower monthly payments. Consolidating student loans can offer several benefits, such as simplifying loan management and potentially lowering monthly payments, but it can also have drawbacks, like losing specific loan benefits or extending the repayment period. Federal loan consolidation allows borrowers to combine their federal student loans into a single loan through a Direct Consolidation Loan. A Direct Consolidation Loan is a federal loan offered by the U.S. Department of Education, allowing borrowers to merge multiple federal student loans into one. Federal loans that are eligible for consolidation include Direct Subsidized and Unsubsidized Loans, Perkins Loans, and Federal Family Education Loan (FFEL) Program Loans, among others. The interest rate for a Direct Consolidation Loan is a fixed rate, calculated as the weighted average of the interest rates on the loans being consolidated, rounded up to the nearest one-eighth of a percent. Private loan consolidation, also known as refinancing, involves obtaining a new loan from a private lender to pay off existing student loans. Private consolidation loans are provided by private lenders, such as banks or credit unions, and can be used to consolidate both federal and private student loans. Eligibility for private consolidation loans varies depending on the lender's requirements, but generally, both federal and private student loans can be consolidated. Interest rates for private consolidation loans depend on factors like credit score, loan term, and lender, and may be either fixed or variable. Before consolidating, borrowers should gather information on all their existing loans, such as loan servicers, outstanding balances, interest rates, and loan terms. It's important for borrowers to assess their current loan terms and benefits to determine if consolidation is the best option and if any benefits may be lost through consolidation. Applying for a Direct Consolidation Loan is done through the Federal Student Aid website, where borrowers can complete the online application and electronically sign the promissory note. When applying for federal loan consolidation, borrowers must provide personal identification information, and details about existing loans, and select a repayment plan. When considering private loan consolidation, borrowers should research and compare various lenders, interest rates, loan terms, and additional benefits to find the best fit for their financial situation. Private lenders typically require a good credit score for loan consolidation, as the credit score will influence the interest rate and terms offered. If a borrower has a lower credit score, they may consider using a co-signer with a strong credit history to help secure better loan terms and increase the likelihood of approval. Consolidating student loans can streamline the repayment process by allowing borrowers to make a single monthly payment instead of multiple payments to different lenders. Consolidating loans may result in lower monthly payments by extending the repayment period or securing a lower interest rate. Federal loan consolidation offers fixed interest rates, providing predictability in monthly payments and protecting borrowers from future rate increases. Consolidation may allow borrowers to extend their repayment term, which can lower monthly payments but may result in paying more interest over time. Federal loan consolidation may provide borrowers with access to additional repayment plans, such as income-driven plans, and forgiveness programs like Public Service Loan Forgiveness. Consolidating student loans may result in the loss of certain benefits, such as interest rate discounts, loan cancellation options, or borrower protections from the original loans. While consolidation may lower monthly payments, it may also extend the repayment period, potentially increasing the total amount paid in interest over time. Consolidation can extend the repayment term, which may seem beneficial for lowering monthly payments but can result in paying more interest over the life of the loan. There are certain limitations to federal loan consolidation, such as the inability to consolidate private loans, and some federal loans may not qualify for certain repayment plans after consolidation. Refinancing involves obtaining a new loan with better terms, such as a lower interest rate, to pay off one or more existing student loans, which can be an alternative to consolidation. Income-driven repayment plans adjust monthly loan payments based on a borrower's income and family size, providing a more affordable option for borrowers struggling with high payments. Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) is a federal program that forgives the remaining balance on Direct Loans for borrowers who work in qualifying public service jobs and make 120 qualifying monthly payments. PAYE and REPAYE are income-driven repayment plans that cap monthly payments at 10% of discretionary income and provide loan forgiveness after 20 or 25 years of qualifying payments. When deciding whether to consolidate student loans, borrowers should consider their financial situation, the benefits and drawbacks of consolidation, and any potential loss of loan benefits. Borrowers should assess their financial situation and long-term goals to determine if consolidation is the best option for managing their student loan debt. It's important for borrowers to research and compare different consolidation options to make an informed decision that aligns with their financial goals and needs. Seeking guidance from a financial advisor or a student loan expert can help borrowers navigate the complexities of student loan consolidation, evaluate their options, and make informed decisions tailored to their specific financial situations.What Is Student Loan Consolidation?
Types of Student Loan Consolidation
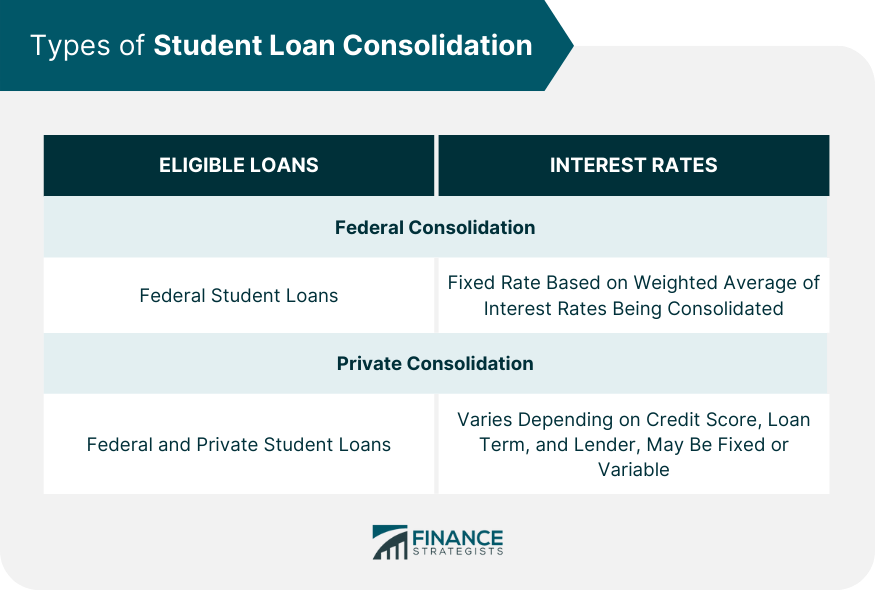
Federal Loan Consolidation
Direct Consolidation Loan
Eligible Loans
Interest Rates
Private Loan Consolidation
Private Consolidation Loans
Eligible Loans
Interest Rates and Terms
How to Consolidate Student Loans
Prepare for Consolidation
Gathering Loan Information
Evaluating Current Loan Terms and Benefits
Apply for Federal Loan Consolidation
Online Application Process
Required Documents
Apply for Private Loan Consolidation
Comparing Lenders and Loan Terms
Credit Score Requirements
Co-signer Options
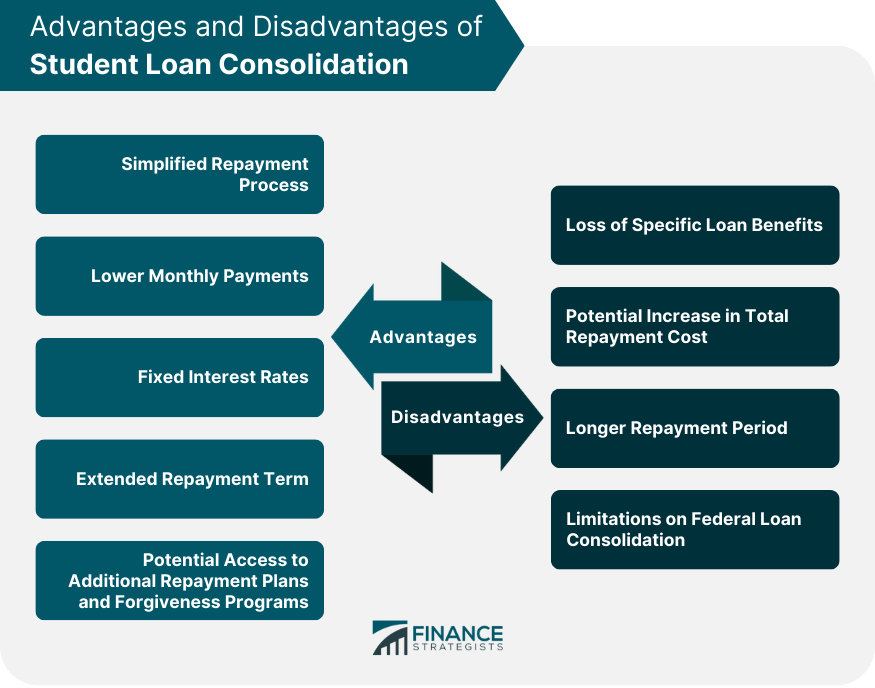
Advantages of Student Loan Consolidation
Simplified Repayment Process
Lower Monthly Payments
Fixed Interest Rates
Extended Repayment Term
Potential Access to Additional Repayment Plans and Forgiveness Programs
Disadvantages of Student Loan Consolidation
Loss of Specific Loan Benefits
Potential Increase in Total Repayment Cost
Longer Repayment Period
Limitations on Federal Loan Consolidation
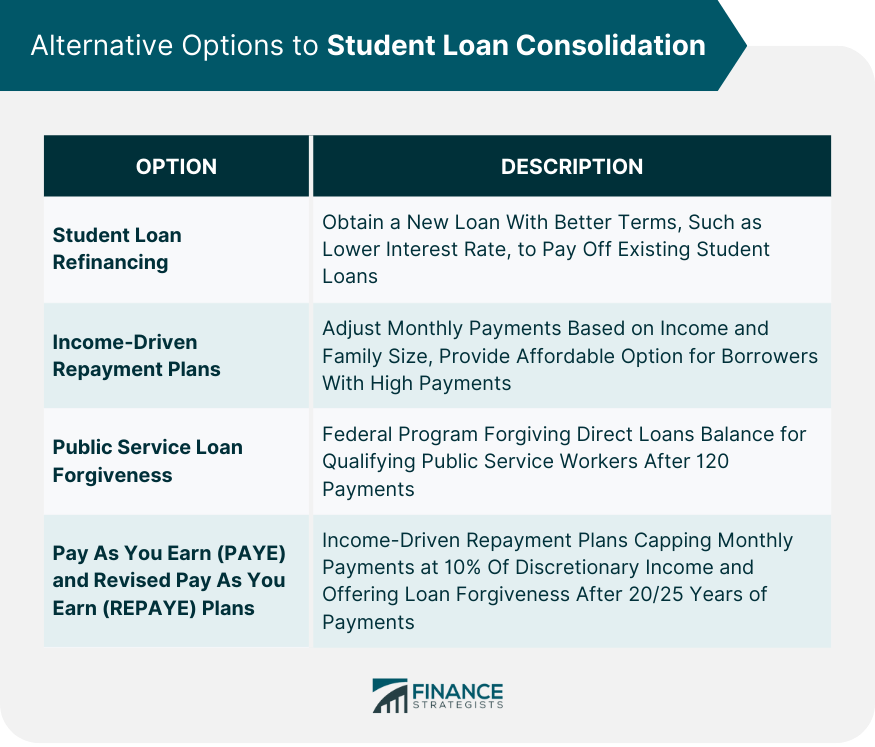
Alternative Options to Student Loan Consolidation
Student Loan Refinancing
Income-Driven Repayment Plans
Public Service Loan Forgiveness
Pay As You Earn (PAYE) and Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE) Plans
Final Thoughts
Student Loan Consolidation FAQs
Student loan consolidation involves combining multiple student loans into a single loan, often with a new lender, to simplify your loan management, potentially secure better terms, and lower your monthly payments.
Federal student loan consolidation combines eligible federal loans into a single Direct Consolidation Loan, with a fixed interest rate and access to various repayment plans. Private student loan consolidation, also known as refinancing, involves obtaining a new loan from a private lender to pay off your existing loans, which can include both federal and private loans.
Yes, student loan consolidation can potentially lower your monthly payments by securing a lower interest rate or extending the repayment term. However, it's essential for you to consider the potential drawbacks, such as losing specific loan benefits or increasing the total repayment cost.
Yes, alternatives to student loan consolidation include student loan refinancing, income-driven repayment plans, Public Service Loan Forgiveness, and Pay As You Earn (PAYE) and Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE) plans.
To determine if student loan consolidation is the right choice, assess your financial situation and goals, research and compare different consolidation options, and consider seeking guidance from a financial advisor or student loan expert.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











