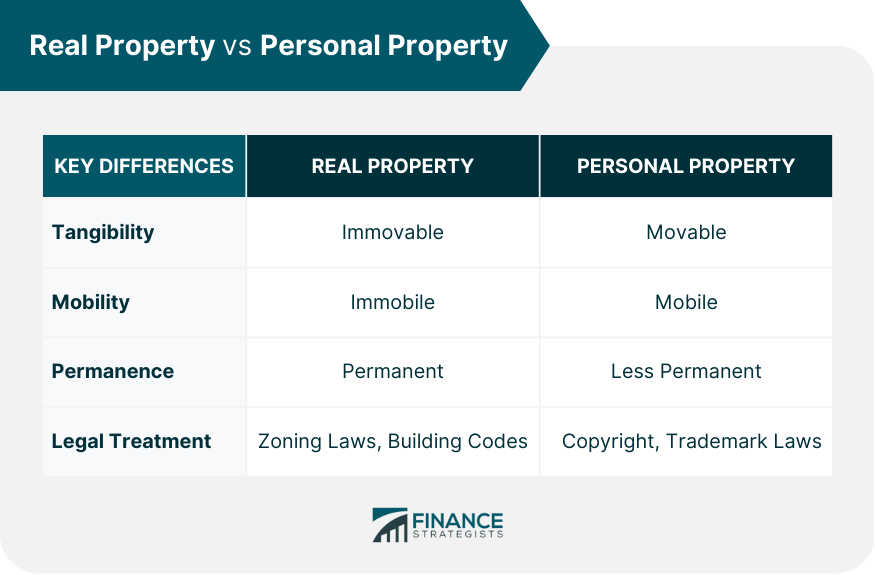
Real property and personal property are two distinct property categories with different legal and financial characteristics. Real property refers to physical land and structures and the natural resources found on that land, such as oil or minerals. On the other hand, personal property refers to movable items, such as cars, furniture, and stocks. Understanding the difference between these two property types is important for legal, financial, and practical reasons, as they are subject to different legal protections, transfer processes, and ownership rights. Knowing the distinction between real and personal property can help property owners make informed investment decisions and avoid legal or financial complications. Real property, or real estate, refers to land and any permanent structures built on that land, such as buildings or houses. Real property can also include natural resources found on the land, such as oil, minerals, or water. Here are some key characteristics of real property: Ownership Rights. Real property owners have the right to use and occupy the land and sell or transfer ownership of the property. Transfer Process. Real property can be transferred through a legal document known as a deed, which must be recorded with the county or state where the property is located. Legal Protections. Real property is subject to legal protections, such as zoning laws and building codes, which are designed to protect the health and safety of occupants and the community. Examples of real property include: A house and the land it sits on A commercial building and the land it occupies A farm and the land it operates on An oil well and the land it is drilled on Personal property, also known as movable property, refers to anything that is not real property and can be relocated from one location to another. This can include tangible items, such as cars, furniture, and jewelry, as well as intangible items, such as stocks and patents. Here are some key characteristics of personal property: Ownership Rights. Personal property owners have the right to use, sell, or transfer property ownership. Transfer Process. Personal property can be transferred through a bill of sale or another legal document as proof of ownership. Legal Protections. Personal property is subject to legal protections, such as copyright or trademark laws, designed to protect owners' intellectual property rights. Examples of personal property include: A car Furniture Jewelry Stocks and other investments Patents and Trademarks While both real property and personal property involve ownership rights and transfer processes, there are some key differences between the two. Here are some of the main differences to keep in mind: One of the main differences between real property and personal property is tangibility. Real property refers to physical land and structures that are immovable and permanently attached to the ground. On the other hand, personal property refers to movable items that can be transported from one location to another. Another key difference between real property and personal property is mobility. Real property is typically immobile and permanently attached to the ground, while personal property is movable and can be transported from one location to another. Real property is generally more permanent than personal property. Structures built on real property are designed to be permanent and often require significant investment to build or maintain. On the other hand, personal property can be replaced or disposed of more easily. Real property and personal property are also treated differently under the law. Real property is subject to zoning laws, building codes, and other legal protections that are designed to protect the health and safety of occupants and the community. On the other hand, personal property is subject to different legal protections, such as copyright or trademark laws. Understanding the difference between real property and personal property is important for several reasons. Some of the most important reasons to learn the difference between these two kinds of property are as follows: Understanding the difference between real property and personal property is crucial for legal reasons. The legal protections and transfer processes for each property type are different, and failing to understand these distinctions can result in legal complications or disputes. For example, if you purchase a piece of real property without understanding your area's zoning laws or building codes, you could face legal consequences if you violate these laws. Similarly, you need to properly transfer ownership of the real property through a legal document like a deed to avoid legal disputes or complications down the line. Understanding the difference between real property and personal property is also important for financial reasons. Owning real property can be a significant investment, and it is important to understand the financial implications of this investment. For example, real property may appreciate in value over time, providing a potential return on investment. However, the real property also comes with financial obligations, such as property taxes and maintenance costs. Understanding these financial implications can help property owners make informed investment decisions. Finally, understanding the difference between real property and personal property is important for practical reasons. Knowing which type of property you own can help you decide how to use or dispose of that property. For example, if you own real property, you may want to invest in improvements or renovations to increase its value. If you own personal property, you may want to sell or donate items you no longer need or want. Real property and personal property are two distinct types of property with different legal and financial characteristics. While real property refers to physical land and structures, personal property refers to movable items that can be transported from one location to another. Understanding the difference between these two types of property is important for legal, financial, and practical reasons, as it can help property owners make informed decisions about their investments and avoid legal or financial complications down the line. If you need help investing in real property or managing your personal property, it is a good idea to seek the advice of a financial advisor. A financial advisor can help you make informed investment decisions and manage your assets effectively.Overview of Real Property vs Personal Property
Real Property
Personal Property
Key Differences Between Real Property and Personal Property
Tangibility
Mobility
Permanence
Legal Treatment
Importance of Understanding the Difference
Legal Implications
Financial Implications
Practical Implications
Conclusion
Real Property vs Personal Property FAQs
Real property refers to physical land and structures, while personal property refers to movable items. Real property is more permanent and subject to legal protections like zoning laws, while personal property is more easily transferable and subject to other legal protections like copyright laws.
Examples of real property include land, buildings, farms, and natural resources like oil or minerals. These types of property are typically immobile and permanently attached to the ground.
Real property is typically transferred through a legal document known as a deed, which must be recorded with the county or state in which the property is located.
Personal property includes cars, furniture, jewelry, stocks, other investments, patents, and trademarks. These types of property are typically movable and can be transported from one location to another.
Understanding the difference between real property and personal property is important for legal, financial, and practical reasons. It can help property owners make informed investment decisions, avoid legal or financial complications, and manage their assets effectively. A financial advisor can provide additional guidance on navigating the complex world of property ownership.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











