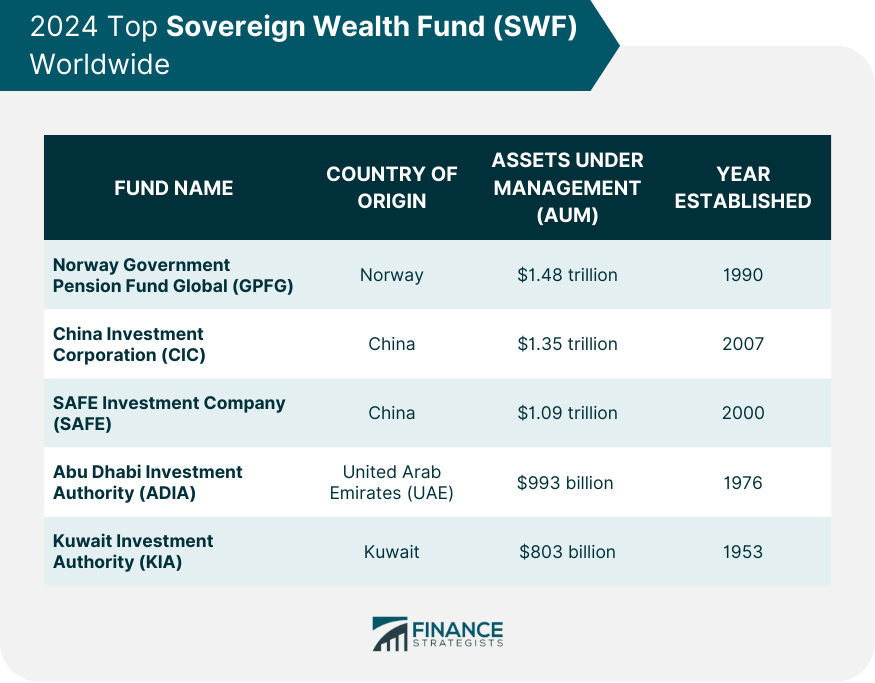
A Sovereign Wealth Fund (SWF) is a large pool of capital managed by a country's government to achieve specific economic and social goals. These funds are invested in various assets such as stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities, and other financial instruments. SWFs are typically funded from the savings of state-owned enterprises, foreign currency reserves from central banks, or commodity exports. The size and composition of each SWF can vary significantly between countries based on their respective economic circumstances. Each country has various reasons for setting up an SWF. However, the most common purpose of establishing one is to diversify and protect a country's economy. For instance, this fund can be used as emergency reserves for potential future global financial shocks. Sovereign wealth funds invest a country's wealth to achieve the government's economic and social objectives. These funds provide countries with an additional method to diversify their economies and reduce risk exposure. They also give governments a chance to invest in global markets outside their own countries, which can get them better returns on their investments. This increases the earning potential on foreign exchanges and provides additional economic stability. Furthermore, SWFs are a valuable tool to help countries build up buffers and savings for future generations to be better prepared for future economic shocks. Proper use of SWFs leads to long-term economic growth and stability. In addition to providing an alternative form of investment for governments and enterprises worldwide, SWFs have also been used to increase financial transparency and accountability in many countries. By making their investment decisions public, these funds help promote corporate governance standards across the globe. This encourages market stability and reduces risks associated with certain types of investments. SWFs can be categorized into different types according to their purpose, and the most common types include: These funds are designed to provide financial stability during times of economic crisis and help prevent potential recessions. They are typically funded from the profits of commodity exports, foreign currency reserves, or taxation surpluses. The need to use these funds also arises when there is a significant change in the international market, an oil or natural resource price hike, or social and political instability that could affect a country's economy. When this happens, governments use the funds to help stabilize their currencies and mitigate the potential impacts of said event. Savings or Future Generation Funds are designed to provide long-term financial security for future generations. These funds are typically funded through taxation surpluses, profits from state-owned enterprises, or foreign currency reserves. These funds aim to ensure that the current generation does not deplete their savings and to create a buffer for future generations in case of economic shocks or other unexpected events. In addition, countries establish this fund to meet the expenditures associated with the aging population. It reduces the burden on the government's budget in the coming years. The primary objective of the account is to generate funds that can be invested in high-yielding long-term investments. These funds are established for various investment purposes where earnings are set for a defined purpose, mainly supporting long-term initiatives. These funds are mainly used as a reserve for investment opportunities to achieve long-term financial objectives. Additionally, these funds ensure sufficient capital is available for making investments when opportunities arise. A country's pension system can be funded through a pension reserve fund. With this fund structure, the government's budget is not solely responsible for pension payments. This provides a sufficient amount of money available to pay out pensions when they become due. It also helps governments plan and forecast how much money will be needed in the future. The government also uses this fund to invest in long-term pension schemes for its citizens. Strategic Development Sovereign Wealth Funds (SDSWF) are created to provide financial support for initiatives that improve economic development. For instance, this type of fund can be invested in physical infrastructure and human capital projects. Ultimately, an SDSWF's goal is to increase the prosperity of a country while also generating returns for investors. With these funds, governments can sustain economic development, create jobs, reduce poverty levels and enhance the overall well-being of their citizens. SWFs have become increasingly popular as governments look for ways to maximize investment returns and promote economic growth. The following are the top SWFs worldwide in terms of total assets: 1. Norway Government Pension Fund Global (GPFG) The Norway Government Pension Fund Global (GPFG) is the world's largest sovereign wealth fund, established by the Norwegian government to save surplus oil revenues for future generations. It invests mainly in global equities (around 70%) but also holds smaller allocations in fixed income, real estate, and unlisted infrastructure. The GPFG is known for its long-term investment horizon, focus on sustainability, and ethical guidelines. 2. China Investment Corporation (CIC) The China Investment Corporation (CIC) is a Chinese state-owned investment fund tasked with investing China's foreign exchange reserves. It invests in a diversified portfolio of global assets, including equities, fixed income, real estate, and private equity. The CIC has been active in promoting Chinese outbound investment and supporting the development of key sectors like technology and infrastructure. 3. SAFE Investment Company (SAFE) The SAFE Investment Company (SAFE) is another Chinese state-owned investment fund, primarily responsible for managing China's social security reserves. It invests mainly in domestic fixed income and equities, supporting the stability and growth of the Chinese financial system. SAFE also plays a role in funding social security benefits and promoting long-term social welfare. 4. Abu Dhabi Investment Authority (ADIA) The Abu Dhabi Investment Authority (ADIA) is the sovereign wealth fund of the Emirate of Abu Dhabi, one of the seven emirates that make up the UAE. It invests in a broad range of global assets, including equities, fixed income, real estate, and private equity. ADIA is known for its long-term investment horizon and cautious approach to risk management. 5. Kuwait Investment Authority (KIA) The Kuwait Investment Authority (KIA) is the sovereign wealth fund of Kuwait, established to manage the country's surplus oil revenues. It invests in a diversified portfolio of global assets, with a focus on equities and fixed income. The KIA is known for its conservative investment strategy and focus on preserving capital. These funds play an important role in the global economy, and their activities can have a significant impact on financial markets and asset prices. SWFs can also be divided into two categories: commodity-based funds and non-commodity-based funds. These categories differ based on the source of their funding. Commodity-based funds are funded using government-owned or taxed exports of commodities. For example, the proceeds from the export of natural resources such as oil, natural gas, or gold can be used to fund a commodity-based sovereign wealth fund. On the other hand, non-commodity funds are often financed by a transfer from the central bank's official foreign exchange reserves and rely on external assets to finance their activities. A Sovereign Wealth Fund (SWF) is a large pool of capital managed by a country's government to achieve specific economic and social goals. These funds invest a nation's riches to fulfill its economic and social goals. For instance, these funds help countries diversify their economies to minimize risk. They also allow governments to invest in foreign markets for higher profits. This boosts foreign currency exchange earnings and economic stability. SWFs can be categorized by purpose or by their source of funding. When divided according to purpose, SWFs can be classified into stabilization funds, savings funds, reserve investment funds, pension reserve funds, or strategic development funds. When SWFs are grouped according to their source funding, they have two main types: commodity-based funds, which rely primarily on natural resources, and non-commodity funds, which depend mainly on external assets, such as foreign exchange reserves. Overall, SWFs have become essential to many countries' fiscal strategies worldwide. This is because these funds help governments protect their wealth while also allowing them to benefit from growth opportunities in global markets.What Is a Sovereign Wealth Fund (SWF)?
Purpose of a Sovereign Wealth Fund
Types of Sovereign Wealth Funds
Stabilization Fund
Savings or Future Generation Fund
Reserve Investment Fund
Pension Reserve Fund
Strategic Development Sovereign Wealth Funds (SDSWF)

2023 Top SWFs Worldwide
Commodity vs Non-Commodity SWFs
Final Thoughts
Sovereign Wealth Fund (SWF) FAQs
The US has no sovereign wealth fund directly controlled by the federal government. However, several states have their own sovereign wealth funds. These include the Alaska Permanent Fund and the Texas Permanent School Fund.
A sovereign wealth fund's primary role is to invest a nation's resources to generate returns. SWFs can also be used to finance government initiatives or provide an economic cushion in times of crisis.
Sovereign wealth funds aim to generate returns through their investments. This is usually achieved by investing in a mix of assets with different levels of risk, such as stocks and bonds or real estate. The fund's performance will depend on its investments' success and the ability to generate profits through these investments.
Sovereign wealth funds benefit a nation's citizens by providing financial stability and an economic cushion in times of crisis. These funds can also finance various government initiatives or projects, such as infrastructure development.
A team of investment managers manages sovereign wealth funds. These individuals have the task of ensuring that the fund meets its objectives and maximizes returns. The team is typically led by a board of directors or trustees who oversee the fund's activities.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











