Debt crowdfunding, also known as peer-to-peer (P2P) lending or crowdlending, is a form of crowdfunding in which individuals or businesses raise capital by borrowing money from a large number of investors through an online platform. In this model, investors lend money to borrowers with the expectation of receiving their principal investment back along with interest payments. Debt crowdfunding differs from equity crowdfunding, where investors receive ownership shares in the company in exchange for their investment. In debt crowdfunding, borrowers are obligated to repay the loan over a specified period, and investors earn interest on the funds they lend, without obtaining any ownership stake in the company. Debt crowdfunding platforms typically assess the creditworthiness of borrowers and assign a risk rating, which helps investors make informed decisions about the potential risks and rewards of lending to a particular borrower. This type of crowdfunding can be attractive to both borrowers and investors, as it can provide access to capital for businesses that might not qualify for traditional loans and offer potentially higher returns for investors compared to traditional fixed-income investments. Peer-to-peer (P2P) lending involves individual investors lending money directly to borrowers, typically through an online platform that matches lenders and borrowers based on specific criteria. P2P lending can be used for various purposes, including personal loans, business loans, and real estate loans. Invoice financing, also known as invoice discounting or factoring, enables businesses to raise capital by selling their outstanding invoices to investors at a discount. This arrangement allows businesses to access funds quickly without waiting for clients to pay their invoices. Revenue sharing loans allow investors to provide capital to businesses in exchange for a percentage of the business's future revenue. These loans are often used by early-stage businesses that may not have sufficient collateral or credit history for traditional loans. Secured loans require borrowers to provide collateral, such as real estate or equipment, to back the loan. In contrast, unsecured loans do not require collateral, and lenders assume more risk. Both secured and unsecured loans can be facilitated through debt crowdfunding platforms. Debt crowdfunding offers various benefits to borrowers, investors, and the broader financial ecosystem. Debt crowdfunding provides businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), with an alternative source of funding. This accessibility to capital can be especially valuable for businesses that may struggle to secure traditional loans due to limited credit history or collateral. Investing in debt crowdfunding allows investors to diversify their portfolios by funding loans across various sectors, geographies, and risk levels. This diversification can help investors mitigate risk and potentially generate more stable returns. Debt crowdfunding platforms often facilitate a quicker funding process than traditional banks, as they leverage technology to streamline loan application, approval, and disbursement processes. This speed can benefit borrowers seeking timely access to capital. Debt crowdfunding platforms generally have lower overhead costs than traditional banks, enabling them to offer competitive interest rates and fees to borrowers. Additionally, the competitive nature of the marketplace can drive down borrowing costs. Investing in debt crowdfunding can potentially yield higher returns for investors compared to traditional fixed-income investments, such as bonds or certificates of deposit, due to the higher risk associated with these loans. Despite its benefits, debt crowdfunding presents various risks and challenges for borrowers, investors, and platforms. Default risk refers to the possibility that a borrower may not repay their loan, resulting in losses for investors. While debt crowdfunding platforms often employ rigorous credit assessments, investors should be aware of the inherent risk associated with lending. Interest rate risk arises from fluctuations in market interest rates, which can impact the value of fixed-income investments. If interest rates rise, the value of existing loans with lower interest rates may decline, reducing the potential returns for investors. Platform risk encompasses various operational and financial risks associated with debt crowdfunding platforms. These risks include the potential for platform insolvency, cybersecurity breaches, or technology failures, which could negatively impact borrowers and investors. Regulatory and legal risks involve the potential for changes in laws, regulations, or government policies that could impact the debt crowdfunding industry. Such changes could affect the operations of platforms, borrowers' access to capital, or the returns and protections available to investors. Economic and market risks stem from broader economic factors, such as recessions, inflation, or market volatility, which could impact the performance of debt crowdfunding investments. These risks can result in increased default rates, reduced loan demand, or lower returns for investors. Several leading platforms have emerged in the debt crowdfunding industry, connecting borrowers and investors worldwide. LendingClub is a prominent P2P lending platform that offers personal loans, auto refinancing, and business loans to borrowers in the United States. The platform allows individual and institutional investors to invest in these loans and potentially earn competitive returns. Funding Circle is a global business loan platform that connects small businesses with investors, providing access to fast and affordable financing. The platform operates in the United States, United Kingdom, Germany, and the Netherlands. Prosper Marketplace is a P2P lending platform that focuses on providing personal loans to borrowers in the United States. Investors can invest in these loans for purposes such as debt consolidation, home improvement, or small business financing. Kiva is a nonprofit organization that facilitates microloans to borrowers worldwide, particularly in developing countries. Kiva connects borrowers with individual lenders who can fund loans for various purposes, including education, agriculture, and healthcare. Upstart is an AI-driven P2P lending platform that provides personal loans to borrowers in the United States. The platform uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to assess borrowers' creditworthiness, enabling more accurate risk assessment and pricing. The regulatory environment for debt crowdfunding varies across different countries and jurisdictions, impacting the industry's growth and operations. Regulations for debt crowdfunding differ significantly between countries. In the United States, platforms must comply with regulations from the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and state regulators. In the European Union, the European Commission has introduced harmonized regulations for crowdfunding platforms. Other countries, such as China and India, have also implemented regulations to govern debt crowdfunding activities. Regulations can have both positive and negative effects on debt crowdfunding platforms. On the one hand, regulations can help protect investors and borrowers, enhancing confidence in the industry. On the other hand, stringent regulations can hinder the growth of platforms by imposing additional costs and compliance burdens. Governments and financial regulators play a crucial role in promoting responsible lending practices within the debt crowdfunding industry. Regulatory oversight can help ensure that platforms employ proper risk assessment procedures, maintain transparency, adhere to anti-money laundering and consumer protection requirements. Adopting best practices can help borrowers and investors navigate the debt crowdfunding landscape more effectively and minimize risks. Both borrowers and investors should carefully assess creditworthiness when engaging in debt crowdfunding. Borrowers should ensure they have a strong credit profile and the ability to repay loans, while investors should conduct thorough due diligence on borrowers and platforms to evaluate the risk associated with each loan. Investors should diversify their debt crowdfunding investments across multiple loans, sectors, and risk levels to mitigate potential losses from any single loan default. Diversification can help to spread risk and provide more stable returns. Borrowers and investors must carefully read and understand the terms and conditions of each loan, including interest rates, repayment schedules, fees, and any applicable penalties. This understanding can help borrowers manage their debt effectively and allow investors to make informed investment decisions. Investors should actively monitor and manage their debt crowdfunding investments, regularly reviewing the performance of their loans and adjusting their portfolios as needed. This ongoing management can help investors to identify potential issues early and take appropriate action. Borrowers and investors may benefit from seeking professional advice from financial advisors, legal experts, or other professionals experienced in the debt crowdfunding industry. This advice can help to navigate the complexities of the industry and make informed decisions. Technological advancements, increased global adoption, and evolving regulatory frameworks are expected to shape the future of the debt crowdfunding industry. Emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain, have the potential to revolutionize the debt crowdfunding industry by enhancing credit assessment processes, improving platform security, and increasing operational efficiencies. As awareness of debt crowdfunding grows and regulations evolve, the industry may experience increased global adoption, providing borrowers and investors with greater access to capital and investment opportunities worldwide. The debt crowdfunding industry may increasingly integrate with other financial services and products, such as robo-advisors, banks, and insurance providers, to offer comprehensive financial planning as a solution to customers. As the debt crowdfunding industry matures, regulatory frameworks are expected to evolve to accommodate industry growth and innovation while maintaining investor and borrower protections. These changes could impact the industry's operations and future growth trajectory. Debt crowdfunding has emerged as an important alternative to traditional lending, offering benefits for borrowers, investors, and the broader financial ecosystem. By understanding the various types of debt crowdfunding, the associated benefits and risks, the key players in the industry, and best practices, stakeholders can better navigate this rapidly evolving sector. As technology continues to advance and regulations adapt, debt crowdfunding is poised for continued growth and innovation, making it an increasingly significant part of the global financial landscape. If you want to explore the ins and outs of debt crowdfunding, an expert in wealth management can help you navigate through it.What Is Debt Crowdfunding?
Types of Debt Crowdfunding
Peer-to-Peer Lending
Invoice Financing
Revenue Sharing Loans
Secured and Unsecured Loans
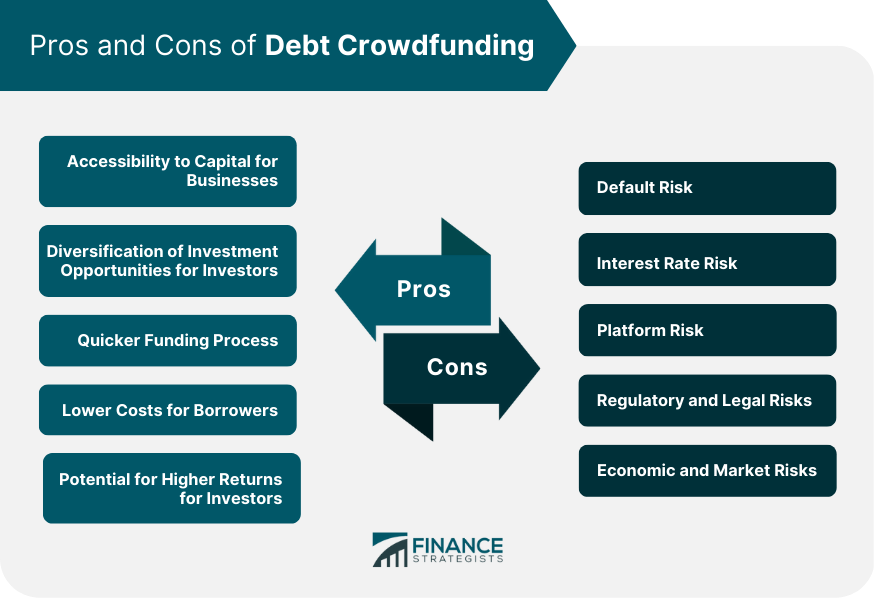
Benefits of Debt Crowdfunding
Accessibility to Capital for Businesses
Diversification of Investment Opportunities for Investors
Quicker Funding Process
Lower Costs for Borrowers
Potential for Higher Returns for Investors
Risks and Challenges of Debt Crowdfunding
Default Risk
Interest Rate Risk
Platform Risk
Regulatory and Legal Risks
Economic and Market Risks
Key Players in the Debt Crowdfunding Industry
LendingClub
Funding Circle
Prosper Marketplace
Kiva
Upstart
Regulatory Environment for Debt Crowdfunding
Overview of Regulations in Different Countries
Impact of Regulations on Debt Crowdfunding Platforms
The Role of Government and Financial Regulators in Promoting Responsible Lending Practices
Best Practices for Borrowers and Investors
Assessing Creditworthiness
Diversification of Investments
Understanding Loan Terms and Conditions
Active Monitoring and Management of Investments
Seeking Professional Advice
The Future of Debt Crowdfunding
Technological Advancements and Their Impact on the Industry
Potential for Increased Global Adoption
Integration with Other Financial Services and Products
Evolution of Regulatory Frameworks
Conclusion
Debt Crowdfunding FAQs
Debt crowdfunding, also known as marketplace lending or peer-to-peer (P2P) lending, is an alternative lending model that connects borrowers with investors through online platforms. Unlike traditional lending methods, where financial institutions act as intermediaries, debt crowdfunding allows investors to directly fund loans, often resulting in quicker funding processes, lower borrowing costs, and potential diversification for investors.
The main types of debt crowdfunding include peer-to-peer lending, invoice financing, revenue sharing loans, and secured and unsecured loans. Each type caters to different borrowers and investor needs, ranging from personal and business loans to funding based on future revenue or outstanding invoices.
Borrowers can benefit from increased accessibility to capital, competitive interest rates, and faster funding processes. Investors, on the other hand, can diversify their portfolios, potentially earn higher returns compared to traditional fixed-income investments, and participate in various types of loans across different sectors and risk levels.
Some of the key risks associated with debt crowdfunding include default risk, interest rate risk, platform risk, regulatory and legal risks, and economic and market risks. These risks can be mitigated through thorough due diligence, diversification of investments, understanding loan terms and conditions, active monitoring and management of investments, and seeking professional advice.
Regulatory frameworks governing debt crowdfunding vary across different countries and jurisdictions. These regulations can affect the operations of platforms, borrowers' access to capital, and the returns and protections available to investors. Regulatory frameworks also play a crucial role in promoting responsible lending practices and ensuring that platforms maintain transparency and adhere to consumer protection requirements.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











