Drag-along rights, also known as "bring-along" or "compulsory acquisition" rights, are contractual provisions that allow majority shareholders to force minority shareholders to participate in the sale of a company. These rights are found in shareholders' agreements or articles of association and are intended to prevent minority shareholders from obstructing a complete sale by refusing to sell their own shares. This makes drag-along rights beneficial for majority shareholders looking to sell, especially when encountering resistance from minority shareholders. Additionally, these rights protect minority shareholders' interests by ensuring that the buyer offers the same terms to all shareholders, fostering a fair sales process. The legal basis for drag-along rights stems from contractual law, as these rights are usually embodied in a contract, such as a shareholders' agreement or a company's articles of association. Legally, drag-along rights must be exercised fairly and reasonably, without oppression or unfair prejudice to minority shareholders. It's important to note that any exercise of drag-along rights is subject to applicable securities laws and regulations. Across jurisdictions, there are variations in the regulation and recognition of drag-along rights. For instance, in the U.S, the Delaware General Corporation Law does not specifically mention drag-along rights. Instead, these rights are usually enforced through shareholders' agreements. In the European Union, drag-along rights are recognized and enforceable under the Second Company Law Directive, with individual member countries having their own additional regulations. For instance, in Germany, drag-along rights can be enforced if they are included in the company's articles of association. In Asian jurisdictions like Singapore and Hong Kong, while there is no specific legislation regarding drag-along rights, they are typically governed by shareholders' agreements and the general principles of contract law. The first step in implementing drag-along rights begins with the majority shareholder(s). They receive a purchase offer from a potential buyer expressing interest in acquiring their shares in the company. This offer must be detailed, outlining the proposed terms of sale, including the intended purchase price. Once a purchase offer has been received, the majority shareholder(s) invoke the drag-along provision. They inform the minority shareholders of their intent to sell their shares and provide details of the purchase offer. This notification serves as an official acknowledgement that the majority shareholder(s) are initiating the drag-along rights. The third step involves the majority shareholders providing adequate information to the minority shareholders about the proposed sale. This should include comprehensive details about the prospective buyer, the intended purchase price, and the terms and conditions of the sale agreement. Providing this information enables the minority shareholders to make an informed decision about the proposed sale. They are given the opportunity to scrutinize the terms and understand how the sale might impact their interests in the company. The final step in implementing drag-along rights is the execution of the sale on the agreed terms. Despite any initial reluctance, the minority shareholders will have their shares sold under the drag-along provision. They are obliged to comply with this sale due to the agreement's terms. Both majority and minority shareholders have distinct rights and responsibilities in the context of drag-along rights. Majority shareholders hold the right to invoke drag-along rights and sell their shares. Nonetheless, they are responsible for ensuring that the sale process is fair and equitable. They must guarantee that all minority shareholders receive identical terms and conditions as part of the sale. On the other hand, minority shareholders have the right to receive complete and accurate information about the proposed sale. They are entitled to the same purchase offer as the majority shareholders. When a valid drag-along provision is invoked, minority shareholders bear the responsibility to cooperate in the sale process. They are obliged to sell their shares in accordance with the agreed terms and conditions. The terms and conditions associated with the implementation of drag-along rights must ensure that the same price, terms, and conditions that apply to the majority shareholders also apply to the minority shareholders. In essence, the sale price per share received by the majority shareholders should be the same as the price received by the minority shareholders. The objective is to uphold fairness and prevent discrimination during the sale process. Although drag-along rights may appear to predominantly benefit majority shareholders, minority shareholders still have some safeguards in place. Minority shareholders have the right to receive the same price, terms, and conditions as the majority shareholders in the event of a sale. Furthermore, they are entitled to receive all necessary information regarding the proposed transaction, including the identity of the buyer and the terms of the sale agreement. Failure to implement drag-along rights properly may lead to legal and financial consequences. Majority shareholders who fail to provide adequate information or offer fair terms may face legal action from minority shareholders. On the other hand, minority shareholders who refuse to cooperate with validly exercised drag-along rights could be liable for breach of contract. Financially, the implications could be severe for the company, with potential deals falling through and a decrease in the company's market value. Tag-along rights, also known as co-sale rights, offer protection to minority shareholders. When the majority shareholders sell their stake, tag-along rights ensure that the minority shareholders have the option to join the transaction and sell their shares at the same terms and conditions. While drag-along rights allow the majority shareholders to compel the minority shareholders to sell their shares, tag-along rights provide the minority shareholders the option to participate in a sale initiated by the majority shareholders. The primary difference is the element of compulsion present in drag-along rights and absent in tag-along rights. Tag-along rights are particularly useful for minority shareholders when the majority shareholders are selling their shares to a buyer who is willing to pay a premium price. By tagging along, the minority shareholders can also benefit from the premium price. These rights also serve to protect minority shareholders from remaining in a company under potentially unfavorable new management. Drag-along rights are provisions in shareholder agreements that enable majority shareholders to require minority shareholders to participate in the sale of a company. They are useful for ensuring a smooth and complete sale, especially when a buyer wants to acquire 100% of the company's shares. To implement drag-along rights, the clause is invoked after receiving a purchase offer, informing all shareholders, including the minority ones, about the sale and its terms and executing the sale accordingly. These rights cover important aspects such as the sale price, fairness of terms, equal treatment of minority shareholders, and the responsibilities of both majority and minority shareholders during the sale process. Considering the complexity and potential impact of these rights on shareholder interests, it's advisable to seek professional guidance. Consulting a financial advisor or attorney specializing in corporate law can provide valuable insights tailored to your specific situation. What Are Drag-Along Rights?
Legal and Regulatory Framework for Drag-Along Rights
Legal Foundation for Drag-Along Rights
Global Regulatory Variations and Implications
Process of Implementing Drag-Along Rights
Step 1: Receiving the Purchase Offer
Step 2: Invoking the Drag-Along Provision
Step 3: Providing Adequate Information to Minority Shareholders
Step 4: Making an Informed Decision
Step 5: Executing the Sale

Rights and Responsibilities of Majority and Minority Shareholders
Rights and Responsibilities of Majority Shareholders
Rights and Responsibilities of Minority Shareholders

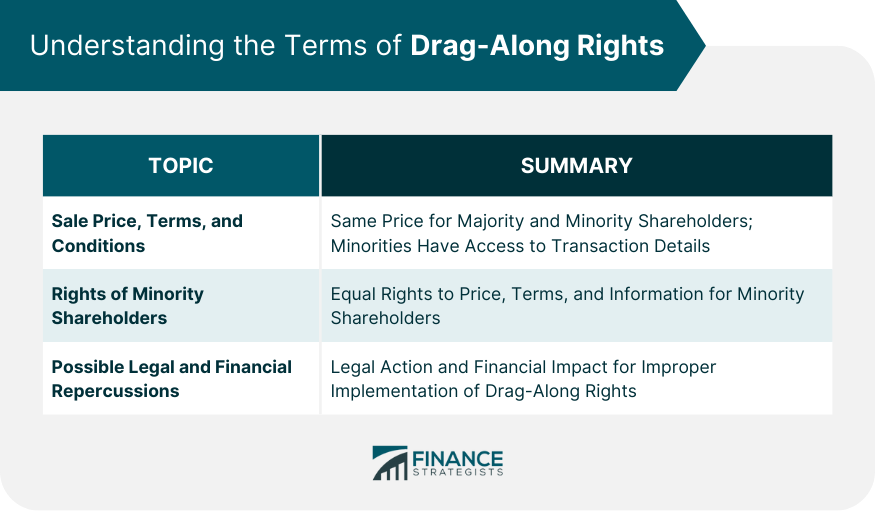
Understanding the Terms of Drag-Along Rights
Sale Price, Terms, and Conditions
Rights of Minority Shareholders
Possible Legal and Financial Repercussions
Tag-Along Rights vs Drag-Along Rights
Definition of Tag-Along Rights
Differences Between Tag-Along and Drag-Along Rights
Practical Applications of Tag-Along Rights

Final Thoughts
Drag-Along Rights FAQs
Drag-along rights are provisions in a contract that allows majority shareholders to force minority shareholders to join in the sale of a company.
When a majority shareholder decides to sell their shares, they can invoke drag-along rights, compelling the minority shareholders to also sell their shares at the same terms and conditions.
The primary purpose of drag-along rights is to facilitate the complete sale of a company without being hindered by minority shareholders.
Under drag-along rights, minority shareholders are entitled to the same price, terms, and conditions as the majority shareholders during a sale.
While drag-along rights allow majority shareholders to compel minority shareholders to sell their shares, tag-along rights provide minority shareholders the option to join in a sale initiated by the majority shareholders.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











