The Option Pool refers to a portion of a company's shares set aside for future allocation to employees, advisors, or consultants, typically in the form of stock options or other equity incentives. An essential tool for startups and growing businesses, the option pool serves as a means to attract, retain, and motivate key talent by offering a piece of ownership in the company. The size of the option pool varies but is often between 10-20% of the company's outstanding equity, depending on the company's strategy and stage of growth. Creating an option pool may lead to dilution of existing shareholders' equity, as new shares are issued or reserved for distribution. However, it's viewed as a necessary trade-off for the potential growth brought by high-quality contributors incentivized by equity participation. Option pools play a pivotal role in startup companies. Since these nascent enterprises often lack the financial resources to compete with established companies' salary packages, they leverage equity to attract top-notch talent. By offering a stake in the company's future, startups can incentivize potential employees with the prospect of significant financial rewards if the company becomes successful. The option pool typically consists of employee stock options (ESOs), restricted stock units (RSUs), and sometimes stock appreciation rights (SARs). The allocation of these options is based on several factors, including an employee's role, contribution, tenure, and the startup's overall strategic plan. Prior to any external investment, founders set aside a certain percentage of company equity to form the option pool. The initial size of the option pool can vary greatly, but it's often in the range of 10% to 20% of the total equity. These options are then used to provide equity incentives to employees, advisors, and others who contribute to the company's growth. Post-investment, option pools can be diluted as additional shares are issued to investors. This can result in the reduction of the overall percentage of equity held by existing shareholders, including those who received options from the pool. The option pool plays a crucial role in the compensation packages of startup employees. Equity incentives can provide potential financial rewards that significantly exceed traditional salary and bonus structures, particularly if the company successfully exits through an event such as an acquisition or an IPO. Startups can use option pools as a powerful tool for attracting high-quality talent. Equity-based compensation allows these companies to compete with larger, more established organizations, which can often provide higher salaries. Beyond recruitment, option pools serve to motivate employees. The prospect of owning a piece of the company can encourage employees to perform at their best and contribute significantly to the organization's success. Option pools also promote employee retention. As most stock options vest over a period of time, typically four years, they create an incentive for employees to stay with the company. The size of the option pool is typically determined by the startup's founders in consultation with their investors. This decision is influenced by several factors, including the company's stage of development, its hiring needs, and the prevailing market conditions. Option pool sizes vary, but they typically range from 10% to 20% of the company's total equity. In many cases, investors will require the creation of an option pool as part of their investment terms. Various factors can influence the size of an option pool. These include the company's hiring plan, the level of competition for talent in the industry, the amount of capital raised, and the anticipated future funding rounds. Equity dilution occurs when a company issues new shares, reducing the percentage ownership of existing shareholders. This is a common occurrence in startups as they grow and raise more capital. When an option pool is created, it can lead to substantial dilution for the founders. This is because the pool is often created by issuing new shares, thereby decreasing the percentage of the company that the founders own. To mitigate dilution, founders and existing shareholders can negotiate provisions in the investment agreement. For instance, they may advocate for a smaller option pool or for the pool to be created post-investment, which shares the dilution more evenly between the founders and the new investors. The "option pool shuffle" is a negotiation tactic sometimes used by investors during funding rounds. It involves inflating the size of the option pool prior to investment, effectively reducing the founder's equity while keeping the investor's share undiluted. The shuffle can significantly impact founders and investors. For founders, it can result in a substantial decrease in their percentage ownership. On the other hand, it benefits investors by reducing their exposure to dilution. To navigate the option pool shuffle, founders can come prepared with a detailed hiring plan. This can help justify a smaller pool. They can also seek to have the pool established or increased post-investment, spreading the dilution between all shareholders. An Employee Stock Option Plan is a program that allows employees to purchase shares of their company at a predetermined price. This plan can be a component of the broader option pool. While ESOP and the option pool provide equity to employees, they differ in several ways. An ESOP is a specific plan that allows employees to buy shares, while an option pool can contain various forms of equity, including stock options, RSUs, and SARs. Within an option pool, an ESOP serves as a vehicle for employees to acquire and hold company shares. It provides a structured way for employees to participate in the company's financial success. Option pools are subject to various legal and regulatory requirements. These vary by jurisdiction but can include securities laws, tax laws, and corporate laws. Compliance with these laws is essential to avoid legal complications. To comply with legal and regulatory requirements, companies may need to disclose the creation and terms of the option pool to investors and potential investors. They may also need to register the pool with the relevant securities regulator and provide employees with specific information when granting options. Venture capitalists (VCs) often view an option pool as a necessary part of a startup's capital structure. It is seen as a tool to align the interests of employees with those of the company and its shareholders. VCs may require the creation of an option pool as a condition of their investment. Venture capital funding can have a significant impact on an option pool. When a startup raises VC funding, the size of the option pool may be increased to provide equity incentives for the new hires that will be needed to support growth. However, this can also lead to dilution for the existing shareholders. An option pool, an integral part of a startup's equity structure, earmarks a percentage of the company's shares to incentivize key contributors. It's a strategic instrument, including elements such as ESOs, RSUs, and sometimes SARs. Understanding the workings of the option pool is crucial for both founders and potential employees. It undergoes changes pre and post-investment and can result in dilution of equity for existing shareholders. Nonetheless, the benefits are manifold. An option pool not only serves as a magnet to attract top talent but also motivates employees, fostering a sense of ownership and long-term commitment to the organization's success. Its substantial role in shaping employee compensation packages underscores its importance in the startup ecosystem. Overall, the strategic use of option pools can significantly contribute to a startup's growth trajectory.Definition of Option Pool
Importance of Option Pools in Startup Companies
Understanding Option Pools
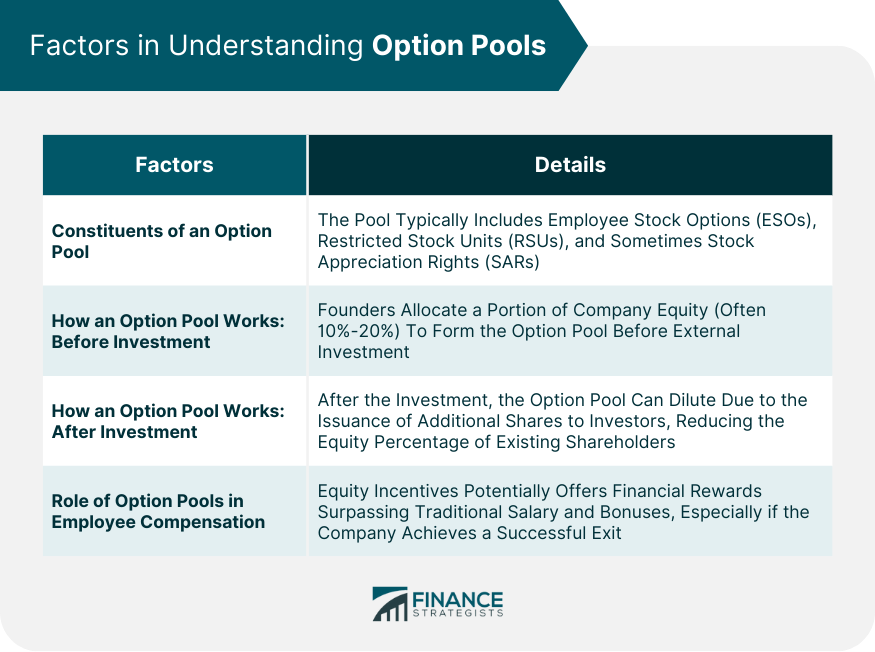
Constituents of an Option Pool
How an Option Pool Works
Before Investment
After Investment
Role of Option Pools in Employee Compensation
Benefits of an Option Pool
Attracting Talent
Motivating Employees
Encouraging Employee Retention
Option Pool Size
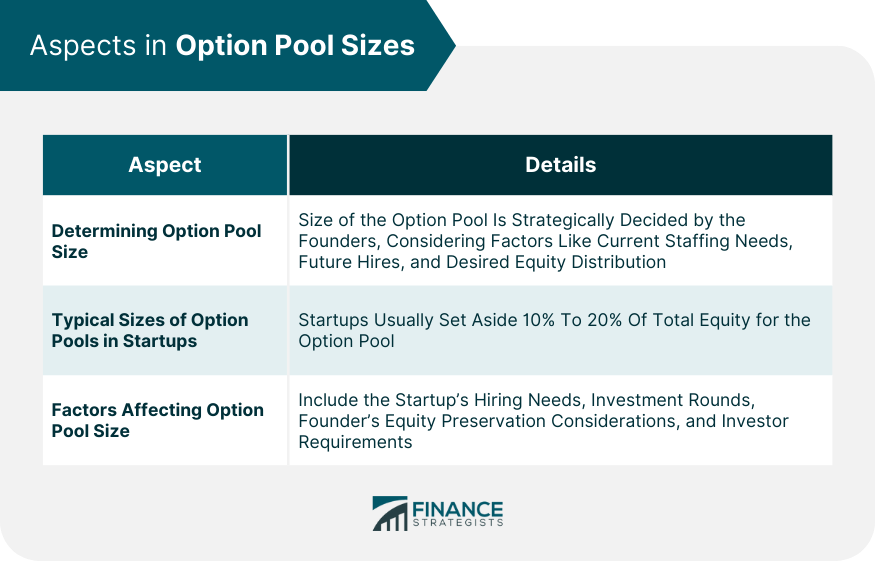
Determining Option Pool Sizes
Typical Sizes of Option Pools in Startups
Factors Affecting Option Pool Sizes
Dilution Through Option Pools
Concept of Equity Dilution
Effects of Option Pools on Founders' Equity
Mitigating Dilution Through Option Pools
Option Pool Shuffle
Understanding Option Pool Shuffles
How It Impacts Founders and Investors
Strategies to Negotiate Option Pool Shuffles
Employee Stock Option Plan (ESOP) and Option Pool
Understanding ESOP
Differences Between ESOP and Option Pools
Role of ESOP in an Option Pool
Legal and Regulatory Considerations of an Option Pool
Legal Framework Governing Option Pools
Compliance Requirements for Companies
Option Pool and Venture Capital
How Venture Capitalists View Option Pools
Impact of Venture Capital Funding on Option Pools
Conclusion
Option Pool FAQs
An option pool is a portion of a startup's equity, usually in the form of shares, that's set aside to incentivize key employees, advisors, and sometimes contractors. By offering a stake in the future growth of the company, startups can attract and retain talented individuals who can significantly contribute to the company's success.
Option pools can offer potential financial rewards that far exceed traditional salary structures, particularly if the company becomes highly successful. This opportunity to participate in the company's growth can help startups attract top talent. Moreover, since stock options usually vest over time, they encourage employees to stay with the company long-term.
The creation of an option pool often leads to equity dilution for the founders. This is because new shares are typically issued to form the option pool, which decreases the founders' percentage of ownership. It's crucial for founders to consider this potential dilution when planning the size of the option pool.
Option pools are subject to various legal and regulatory requirements, which can include securities laws, tax laws, and corporate laws. These laws may require companies to disclose the creation and terms of the option pool, register the pool with relevant securities regulators, and provide employees with specific information when granting options.
Venture capitalists often view option pools as an essential tool to align the interests of employees with those of the company and its shareholders. They may require the creation of an option pool as a condition of their investment. However, this can lead to additional dilution of existing shareholders' equity, including that of the founders.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











