Security Token Offerings are a fundraising method in which companies issue digital tokens, known as security tokens, that represent ownership or rights in the underlying assets. These tokens are subject to securities regulations and provide investors with various financial rights, such as dividends, interest, or voting rights, depending on the type of security token. STOs differ from Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) in that they are backed by real-world assets and are subject to regulatory oversight, offering greater protection to investors. On the other hand, Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) involve the issuance of traditional shares through stock exchanges. STOs combine the benefits of ICOs and IPOs, providing a more efficient and cost-effective method for companies to raise capital while offering investors increased transparency and security. STOs have emerged as a valuable alternative to traditional fundraising methods, as they offer increased liquidity, lower costs, and global accessibility, among other benefits. By leveraging blockchain technology, STOs have the potential to reshape the financial ecosystem and provide new opportunities for businesses and investors alike. Equity tokens represent ownership in a company, similar to traditional shares. Investors holding equity tokens are entitled to a proportionate share of the company's profits and may have voting rights, depending on the terms of the offering. Debt tokens represent a debt obligation, such as corporate bonds or loans, issued by the company. Investors holding debt tokens are entitled to receive periodic interest payments and the principal amount upon maturity. Real estate tokens represent fractional ownership in a physical property, such as commercial or residential real estate. This allows investors to gain exposure to real estate investments with lower capital requirements and increased liquidity compared to traditional real estate investments. Asset-backed tokens are digital representations of ownership in a specific asset, such as precious metals, artwork, or intellectual property. These tokens enable fractional ownership and offer increased liquidity for traditionally illiquid assets. In the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) oversees and regulates STOs. Companies issuing security tokens must comply with various securities laws and registration requirements, including the Securities Act of 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. The Howey Test, established by the Supreme Court, determines whether a digital asset qualifies as a security. If a token meets the criteria of the Howey Test, it is subject to securities regulations and must comply with SEC requirements. In the European Union, the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) is responsible for regulating STOs. ESMA provides guidance on the application of existing securities regulations to STOs and collaborates with national regulators to ensure a harmonized approach across the region. STOs in the European Union are subject to the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive II (MiFID II) and the Prospectus Regulation. These regulations govern the issuance and trading of securities, ensuring investor protection and market integrity. The Asia-Pacific region has a diverse regulatory landscape, with varying approaches to STOs across key jurisdictions, including China, Japan, South Korea, and Singapore. While some countries have strict regulations in place, others are more lenient or have yet to fully regulate STOs. As the market continues to grow, it is crucial for issuers and investors to stay informed about the specific regulations in each jurisdiction. Cross-border STOs may be subject to regulations in multiple jurisdictions. Companies must ensure compliance with all relevant regulations and obtain necessary approvals from local authorities before issuing security tokens to foreign investors. STOs provide increased liquidity to investors, as security tokens can be more easily traded on secondary markets compared to traditional securities, such as private equity shares or real estate investments. STOs enable companies to raise capital at a lower cost compared to traditional methods, as they streamline the issuance process and eliminate the need for intermediaries, such as underwriters and stock exchanges. Blockchain technology ensures that all transactions are recorded in a transparent and tamper-proof manner, providing increased transparency for investors. Furthermore, security tokens can be programmed to automate compliance with securities regulations, reducing the risk of non-compliance. STOs enable companies to access a global pool of investors, as security tokens can be traded across borders without the need for traditional intermediaries. This expands the potential investor base and provides new investment opportunities for individuals worldwide. STOs allow for the fractionalization of assets, enabling investors to gain exposure to high-value investments with lower capital requirements. This democratizes access to previously inaccessible investment opportunities. Security tokens can be programmed with smart contracts, which automate processes such as dividend distribution, voting rights, and compliance checks. This reduces administrative burdens and enhances efficiency in the management of securities. The regulatory landscape for STOs is still evolving, with varying levels of clarity and harmonization across jurisdictions. This presents challenges for companies seeking to navigate the complex regulatory environment and may result in delays or increased costs. As STOs are a relatively new concept, market adoption and investor education are essential for their success. Companies must communicate the benefits and risks associated with STOs effectively to attract investors and drive market growth. As STOs rely on blockchain technology, they are subject to potential technology-related risks, such as cyberattacks, software vulnerabilities, and network congestion. Ensuring the security and scalability of the underlying infrastructure is critical for the success of STOs. Valuing and pricing security tokens can be challenging, as there may be limited historical data or comparable assets available. Accurate valuation and pricing are essential for attracting investors and ensuring a fair market. Although STOs offer increased liquidity compared to traditional securities, the secondary market for security tokens is still relatively limited. The development of robust secondary markets is necessary to unlock the full potential of STOs. Issuers are companies that seek to raise capital through the issuance of security tokens. They must comply with all relevant securities regulations and ensure that their offerings are transparent, secure, and compliant. Investors in STOs can include institutional investors, accredited investors, and retail investors, depending on the regulatory framework in each jurisdiction. Investors must perform due diligence and carefully assess the risks associated with security token investments. Security token platforms facilitate the issuance, management, and trading of security tokens. These platforms must ensure compliance with securities regulations and provide a secure, user-friendly experience for issuers and investors. Custodians are responsible for the safekeeping of security tokens on behalf of investors. They must employ robust security measures to protect digital assets from theft, loss, or unauthorized access. Legal and advisory services play a critical role in the STO ecosystem, as they help issuers navigate the complex regulatory landscape and ensure compliance with all relevant laws and regulations. These services may include legal counsel, accounting, tax, and compliance advisory. STOs offer a promising alternative to traditional fundraising methods, combining the benefits of ICOs and IPOs while providing increased investor protection and regulatory oversight. With the potential to reshape the financial ecosystem, STOs present new opportunities for businesses and investors alike. However, challenges and risks, such as regulatory uncertainties and limited secondary markets, must be addressed for STOs to reach their full potential. As the STO market continues to evolve, businesses and investors must stay informed about regulatory developments, market trends, and technological advancements. By understanding the opportunities and challenges associated with STOs, businesses can make informed decisions about whether to pursue this fundraising method, while investors can better assess the risks and rewards of security token investments.What Are Security Token Offerings (STOs)?
Definition of STOs
Comparison With Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and Initial Public Offerings (IPOs)
Importance of STOs in the Financial Ecosystem
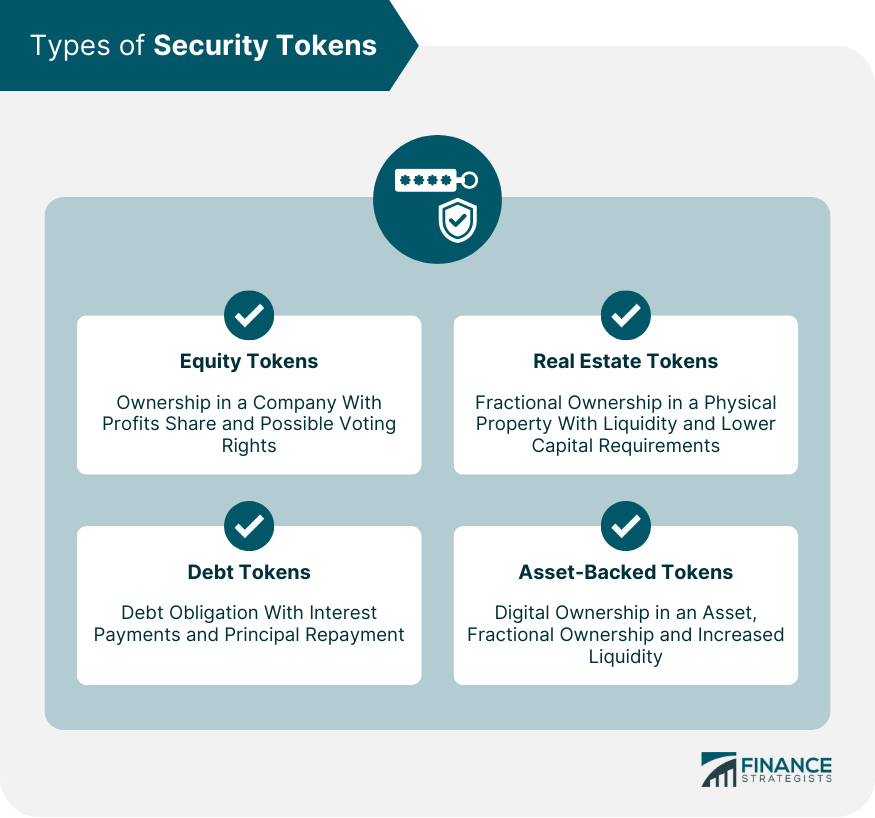
Types of Security Tokens
Equity Tokens
Debt Tokens
Real Estate Tokens
Asset-Backed Tokens
Regulatory Framework for Security Token Offerings
United States
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
Howey Test and Securities Regulations
European Union
European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA)
MiFID II and Prospectus Regulation
Asia-Pacific
Regulatory Landscape in Key Jurisdictions (China, Japan, South Korea, and Singapore)
Cross-Border Considerations
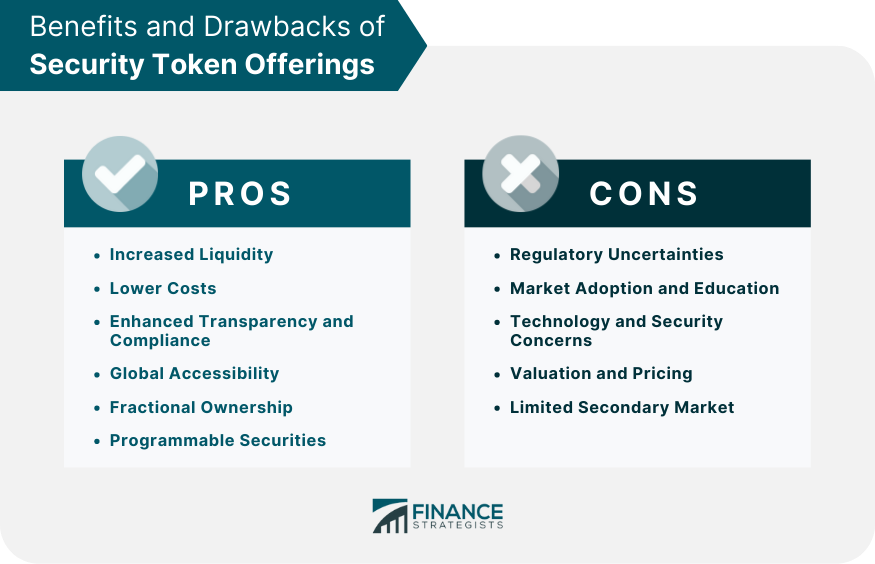
Advantages of Security Token Offerings
Increased Liquidity
Lower Costs
Enhanced Transparency and Compliance
Global Accessibility
Fractional Ownership
Programmable Securities
Challenges and Risks of Security Token Offerings
Regulatory Uncertainties
Market Adoption and Education
Technology and Security Concerns
Valuation and Pricing
Limited Secondary Market
The STO Ecosystem
Issuers
Investors
Security Token Platforms
Custodians
Legal and Advisory Services
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Potential Implications for Businesses and Investors
Security Token Offerings (STOs) FAQs
An STO, or Security Token Offering, is a fundraising method in which companies issue digital tokens that represent ownership in a real-world asset, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate. These tokens are regulated by securities laws and are considered securities, hence the name "security" token offering.
An ICO, or Initial Coin Offering, is a fundraising method in which companies issue tokens that do not represent ownership in a real-world asset. These tokens are often used to raise funds for new cryptocurrency projects. In contrast, an STO issues tokens that represent ownership in real-world assets and are subject to securities laws, making them a more regulated and secure investment option.
Investors who meet certain requirements, such as being accredited or qualified, are eligible to invest in STOs. Accredited investors are typically high net worth individuals or institutions that meet certain financial requirements, while qualified investors have a certain level of financial knowledge or experience. These requirements vary by country and jurisdiction, so it's important to consult with a legal professional before investing.
Investing in an STO offers several benefits, including fractional ownership of assets, 24/7 market access, and increased transparency through the use of blockchain technology. STOs also provide greater regulatory compliance and investor protection than ICOs, making them a more secure investment option.
As with any investment, there are risks associated with investing in an STO. The value of the tokens may fluctuate based on market conditions, and there is a risk of loss if the value of the underlying asset decreases. Additionally, the regulatory landscape for STOs is still evolving, and there may be uncertainty around compliance requirements and potential changes to securities laws. It's important to carefully evaluate the risks and benefits of investing in an STO before making a decision.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











