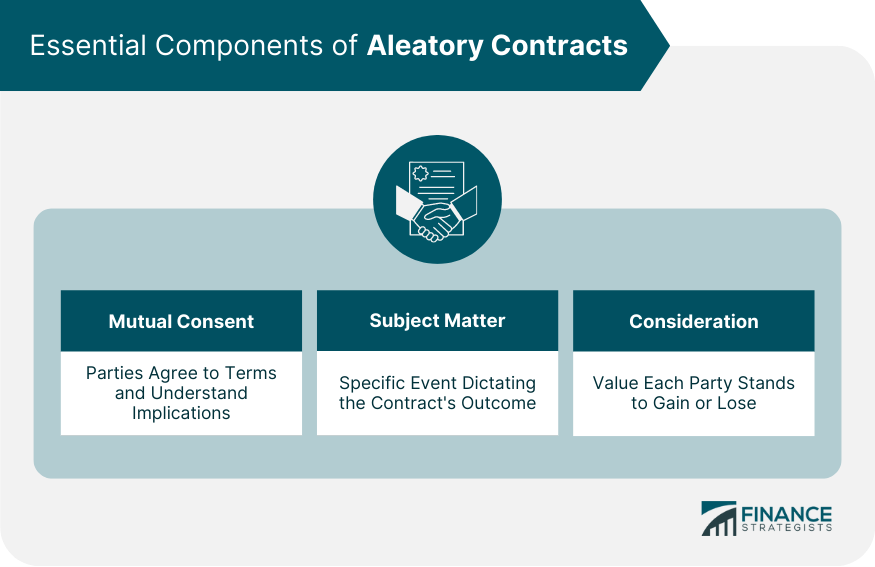
An aleatory contract is an agreement in which the parties' outcomes are uncertain and dependent upon a specific event or circumstance. It's a contractual agreement where the performance of one or both parties is contingent on a particular uncertain event. In terms of its importance, aleatory contracts are vital to numerous sectors within our economy, predominantly in industries that deal with inherent risks or uncertain events, such as insurance or gambling. They allow for risk transfer and sharing, providing a safeguard and a financial strategy for unforeseen circumstances. For an aleatory contract to be considered valid and enforceable, it must consist of certain key components: mutual consent, subject matter, and consideration. Mutual Consent: All parties involved in the contract must agree with the terms. This means they must understand the contract's nature and the uncertain event's implications that determine the contract's outcome. Subject Matter: This refers to the specific event or condition that will dictate the outcome of the contract. It must be clearly defined. For instance, in an insurance policy, the subject matter might be the life of the insured person or their property. Consideration: This component refers to what each party stands to gain or lose from the contract. The consideration must hold some value, but it doesn't necessarily have to be monetary. It could be a service, a promise, a right, or any other item or act of value. Delving into the specifics of how aleatory contracts function, it's crucial to understand that they operate based on a principle of uncertainty. This denotes that the values to be derived by each party from the contract remain undetermined at the onset of the agreement. Only the occurrence or non-occurrence of a specific event, such as an accident or a natural disaster, establishes the final obligation or benefit for each party involved. Mutual agreement and risk sharing form the bedrock of aleatory contracts. Every party entering the agreement understands and accepts that the outcome of the contract hinges on unpredictable future circumstances. Risks and potential benefits are shared among the parties, making each agreement a balanced gamble based on possible future scenarios. Aleatory contracts play a crucial role in risk management by transferring potential risks from one party to another. They safeguard individuals and businesses from financial losses from unforeseen events, thus providing a layer of security. From a broader perspective, aleatory contracts are powerful tools for financial planning. By offering financial protection and predictability amid uncertainty, they allow individuals and businesses to strategize their finances with the knowledge that a safety net exists. Moreover, aleatory contracts offer a high degree of flexibility. They can be tailored to fit the specific needs or situations of the parties involved, making them adaptable tools in various scenarios. Despite the numerous benefits, aleatory contracts present several challenges. One such challenge is their inherent unpredictability. Given their dependence on uncertain events, parties may experience significant losses if the outcomes do not favor them. The possibility of disproportionate results is another challenge that parties must consider. Depending on how events unfold, one party can reap substantial benefits while the other party gains little to nothing. Lastly, aleatory contracts can often be challenging to understand due to their complexity. Terms and conditions may be intricate, requiring thorough scrutiny and, often, professional advice to comprehend fully. Aleatory contracts are more common than many might assume. Within the insurance industry, they serve as the backbone for various types of policies. Insurance contracts are prime examples of aleatory contracts; an insurer promises to compensate the policyholder a certain amount during a specified, uncertain event, such as theft, illness, or accident. If such an event does not occur, the insurer retains the premiums, leading to potentially uneven outcomes. The gambling and betting sector is another industry where aleatory contracts dominate. When a person places a bet on an uncertain outcome, such as a horse race's result or a roulette wheel's spin, they effectively enter into an aleatory contract. Here, the uncertainty of the outcome directly influences the potential gains or losses. In finance, certain types of derivatives also serve as examples of aleatory contracts. An options contract, for instance, allows the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price before or on a specific date. The payoff hinges on the asset's price at the contract's expiration, which, by nature, remains uncertain. Aleatory contracts, where the parties' performance is contingent upon an uncertain event, contrast starkly with commutative contracts. In a commutative contract, both parties exchange values that are perceived as equivalent at the time of the contract, and the performance of each party is fixed and known at the outset. This key difference between aleatory and commutative contracts can significantly impact real-world interactions and transactions. The aleatory contract may yield a substantially more advantageous outcome for one party, dependent entirely upon the unfolding of an uncertain event. In contrast, a commutative contract is designed to ensure both parties stand to benefit equally, given that the value exchanged is known and deemed equivalent from the onset. As a result, the choice between an aleatory contract and a commutative contract can depend on various factors, including one's tolerance for risk, desired outcomes, and the level of predictability they require. Aleatory contracts play a significant role in managing risk and providing financial security in various industries, such as insurance, gambling, and finance. These contracts operate based on uncertainty and the occurrence of specific events, allowing for risk transfer and shared benefits. While aleatory contracts offer benefits such as risk management, flexibility, and financial planning, they also present challenges, including unpredictability and the potential for disproportionate outcomes. Understanding the essential components of aleatory contracts, their mechanics, and their applications in real-life scenarios is crucial for both parties involved. Additionally, distinguishing aleatory contracts from commutative contracts highlights the differences in performance dependence and outcomes. Ultimately, the choice between aleatory and commutative contracts depends on risk tolerance, desired outcomes, and the level of predictability required in a particular situation.What Is an Aleatory Contract?
Essential Components of Aleatory Contracts
Mechanics of Aleatory Contracts
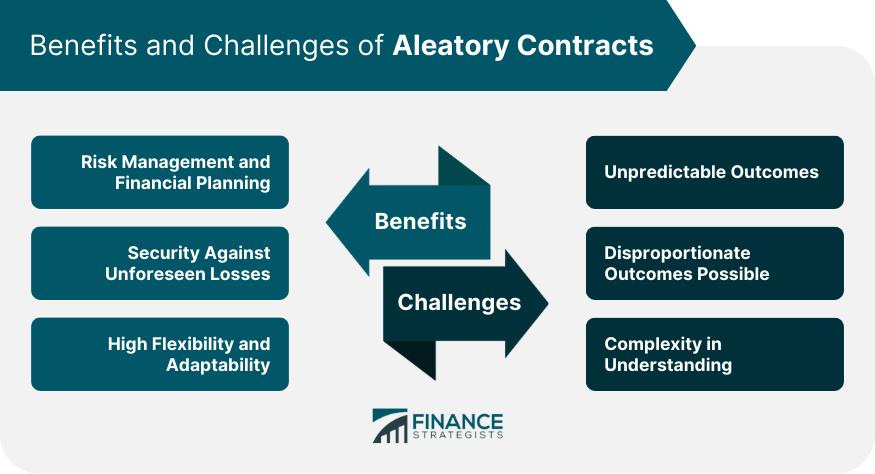
Benefits and Challenges of Aleatory Contracts
Benefits
Challenges
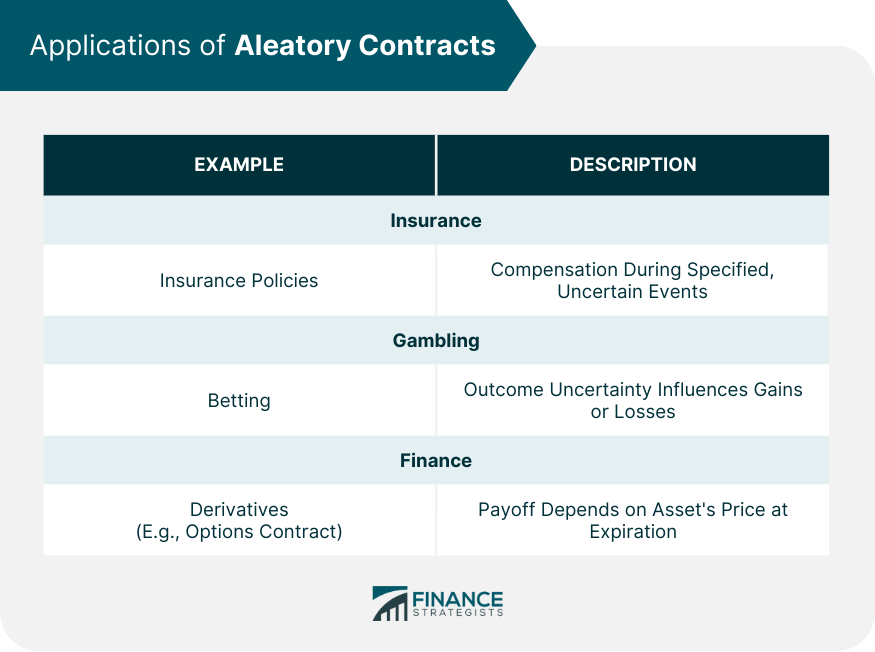
Applications of Aleatory Contracts
Aleatory Contracts vs Commutative Contracts
Main Differences
Practical Implications

Conclusion
Aleatory Contract FAQs
An aleatory contract is a type of agreement where the outcomes are uncertain and contingent upon a specific event or circumstance. It introduces an element of unpredictability into the contract.
The key components of an aleatory contract are mutual consent, subject matter, and consideration. All parties involved must agree to the terms, the contract must have a clearly defined event or condition that determines its outcome, and each party must provide something of value as consideration.
The pros of aleatory contracts include their role in risk management and financial planning. They provide a safeguard against unforeseen losses and allow individuals and businesses to strategize their finances in the face of uncertainty. However, aleatory contracts also come with cons, such as unpredictable outcomes and the potential for complexity in understanding the terms and conditions.
Aleatory contracts are commonly applied in sectors such as insurance, gambling, and finance. In insurance, they form the basis for various types of policies. In gambling, they govern bets placed on uncertain outcomes. In finance, certain types of derivatives, such as options contracts, exhibit characteristics of aleatory contracts.
Aleatory contracts differ from commutative contracts in terms of performance dependence and outcomes. Aleatory contracts depend on uncertain events, and the outcomes are not known or fixed at the outset. In contrast, commutative contracts involve exchanges of value that are perceived as equivalent at the time of the contract, and the performance of each party is predetermined and fixed.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.











